Abstract
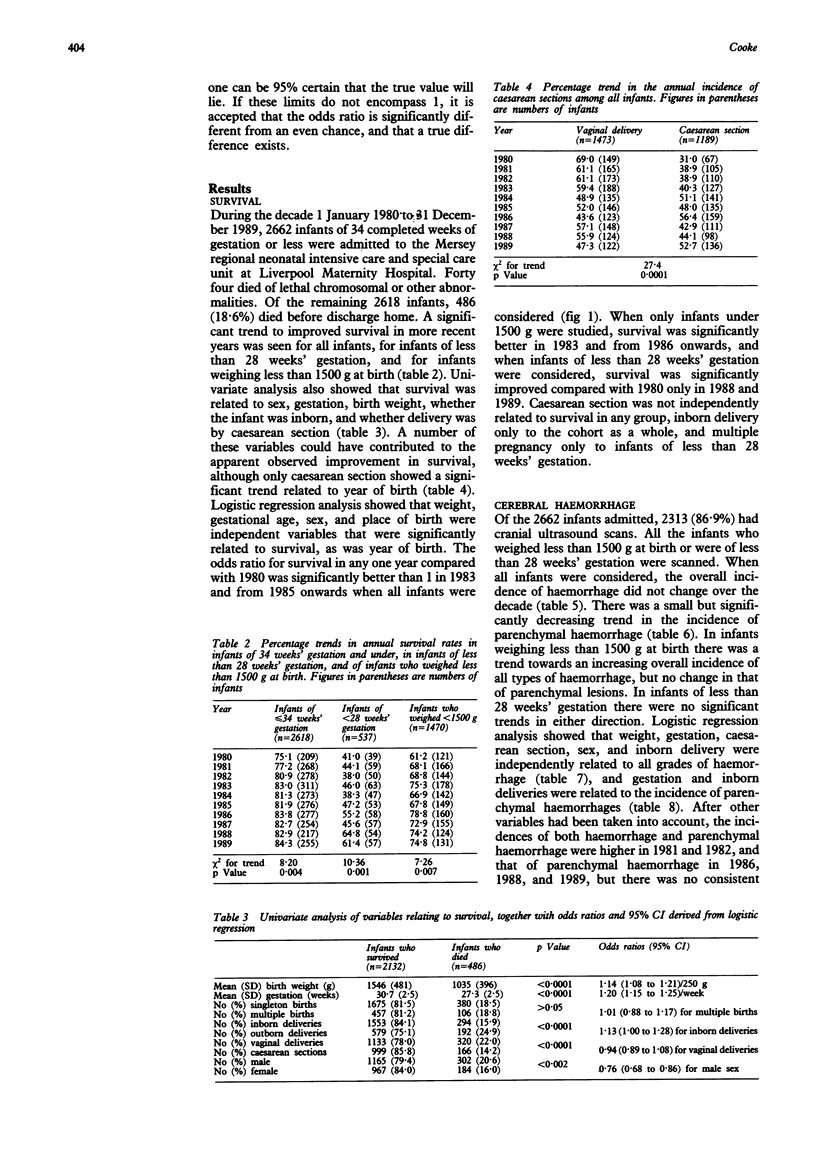
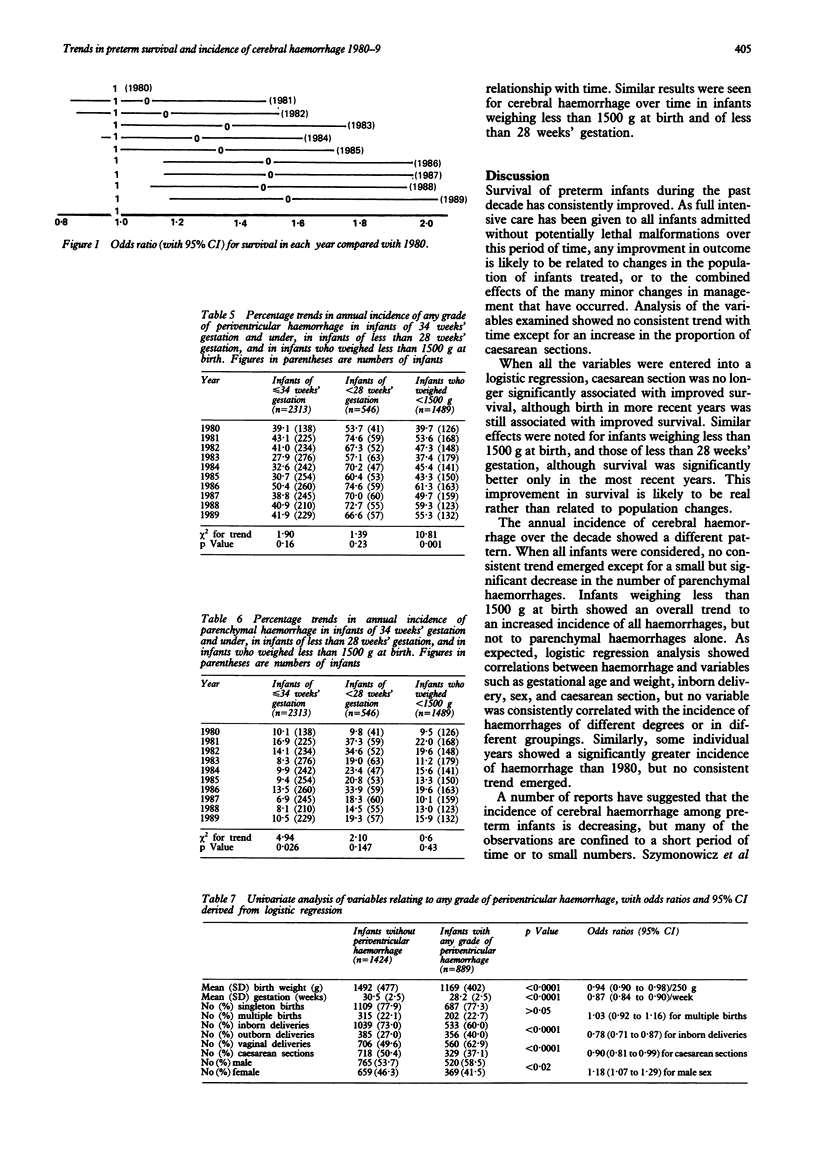
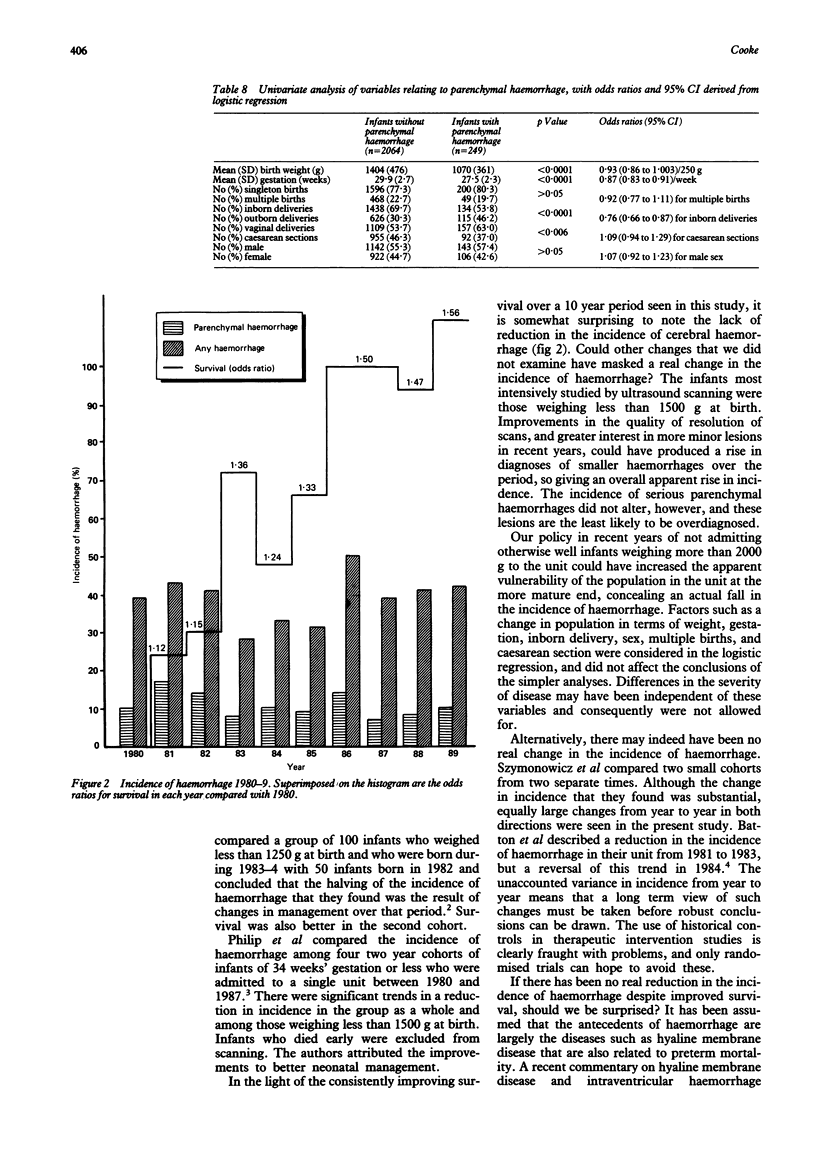
The annual survival rates and incidence of cerebral haemorrhage in 2618 preterm infants of 34 weeks' gestation or less were examined in one referral centre over a 10 year period from January 1980 to December 1989. Survival was independently related to weight, gestation, sex, and inborn delivery. When these variables had been taken into account, survival was 56% greater at the end of the decade compared with 1980. The incidence of cerebral haemorrhage (diagnosed by cranial ultrasound scanning) was related to birth weight, gestation, sex, inborn delivery, and caesarean section, but there was no significant trend in the incidence with time. Rates of caesarean section in this group increased from 31% in 1980 to over 50% more recently. Haemorrhage affecting the brain parenchyma was related to gestation and inborn delivery, and showed a small but significant decline over time. The lack of association between changes in survival rates and rates of cerebral haemorrhage may indicate that factors associated with both neonatal mortality and the incidence of cerebral haemorrhage may not be causally related as previously assumed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batton D. G., DeWitte D. B., Boal D. K., Nardis E. E., Maisels M. J. Incidence and severity of intraventricular hemorrhage: 1981-1984. Am J Perinatol. 1986 Oct;3(4):353–356. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-999896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leviton A., VanMarter L., Kuban K. C. Respiratory distress syndrome and intracranial hemorrhage: cause or association? Inferences from surfactant clinical trials. Pediatrics. 1989 Nov;84(5):915–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pharoah P. O., Alberman E. Annual statistical review. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Dec;63(12):1511–1515. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.12.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pharoah P. O., Cooke T., Cooke R. W., Rosenbloom L. Birthweight specific trends in cerebral palsy. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Jun;65(6):602–606. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.6.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip A. G., Allan W. C., Tito A. M., Wheeler L. R. Intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm infants: declining incidence in the 1980s. Pediatrics. 1989 Nov;84(5):797–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymonowicz W., Yu V. Y., Walker A., Wilson F. Reduction in periventricular haemorrhage in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1986 Jul;61(7):661–665. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.7.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


