Abstract
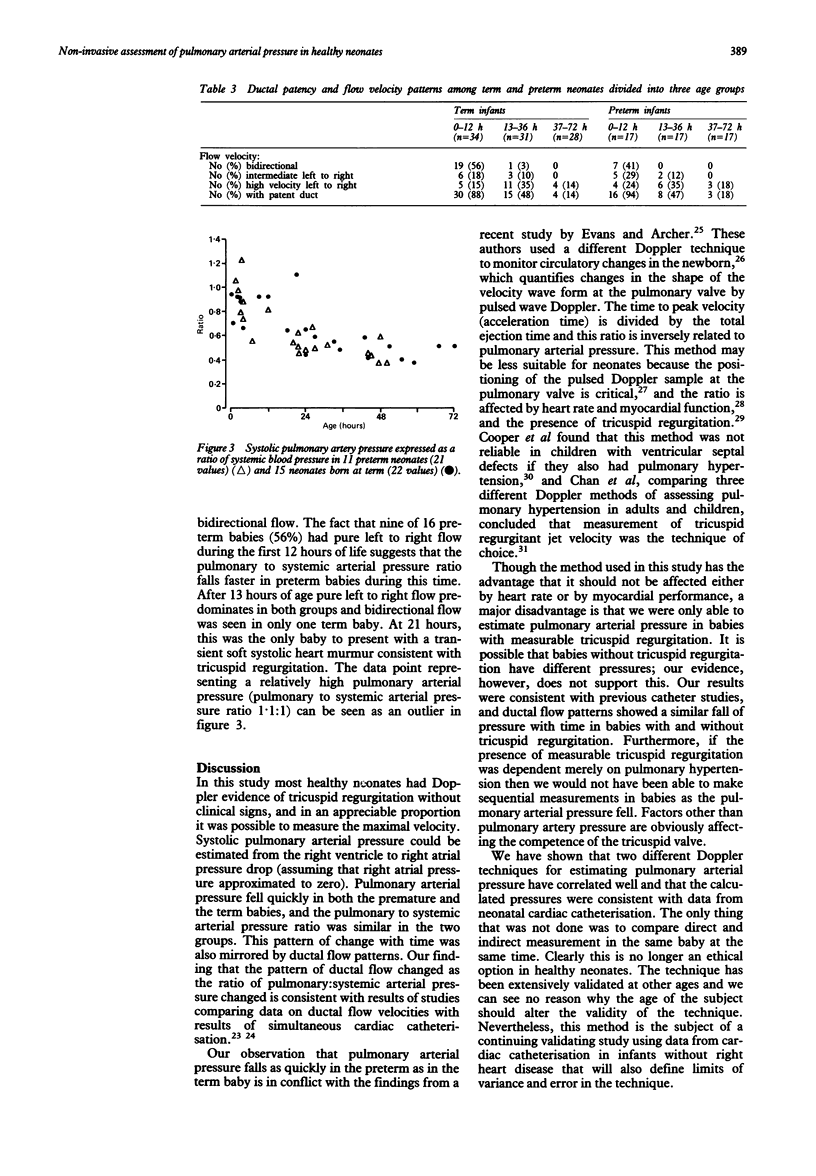
Doppler echocardiograms were carried out on 51 healthy babies three times during the first 72 hours of life to estimate pulmonary arterial systolic pressure by measuring regurgitant tricuspid jet velocity and applying the Bernoulli equation. Tricuspid regurgitation was detected at some stage in all preterm babies and most of those born at full term. Pulmonary arterial pressure could be measured from peak regurgitant velocity in babies with pansystolic regurgitation. The incidence of pansystolic regurgitation among 34 term babies at 0-12, 13-36, and 32-72 hours of age was 22, 27, and 19%, and in 17 preterm babies (within the same age groups) was 53, 50, and 31%, respectively. Estimates of pulmonary artery pressure in the term babies were in accord with known catheter values. Pressure fell rapidly during the first day in all 51 babies. The ratio of pulmonary:systemic arterial pressure was comparable between the two groups throughout. Ductal flow patterns mirrored the fall in this ratio with age--bidirectional flow was associated with a ratio of between 0.88:1 and 1.22:1 and high velocity left to right flow with a ratio of between 0.49:1 and 0.66:1. Both these techniques are noninvasive ways of assessing neonatal pulmonary arterial pressure.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger M., Haimowitz A., Van Tosh A., Berdoff R. L., Goldberg E. Quantitative assessment of pulmonary hypertension in patients with tricuspid regurgitation using continuous wave Doppler ultrasound. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1985 Aug;6(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(85)80172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucciarelli R. L., Nelson R. M., Egan E. A., Eitzman D. V., Gessner I. H. Transient tricuspid insufficiency of the newborn: a form of myocardial dysfunction in stressed newborns. Pediatrics. 1977 Mar;59(3):330–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K. L., Currie P. J., Seward J. B., Hagler D. J., Mair D. D., Tajik A. J. Comparison of three Doppler ultrasound methods in the prediction of pulmonary artery pressure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1987 Mar;9(3):549–554. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(87)80047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie P. J., Seward J. B., Chan K. L., Fyfe D. A., Hagler D. J., Mair D. D., Reeder G. S., Nishimura R. A., Tajik A. J. Continuous wave Doppler determination of right ventricular pressure: a simultaneous Doppler-catheterization study in 127 patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1985 Oct;6(4):750–756. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(85)80477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
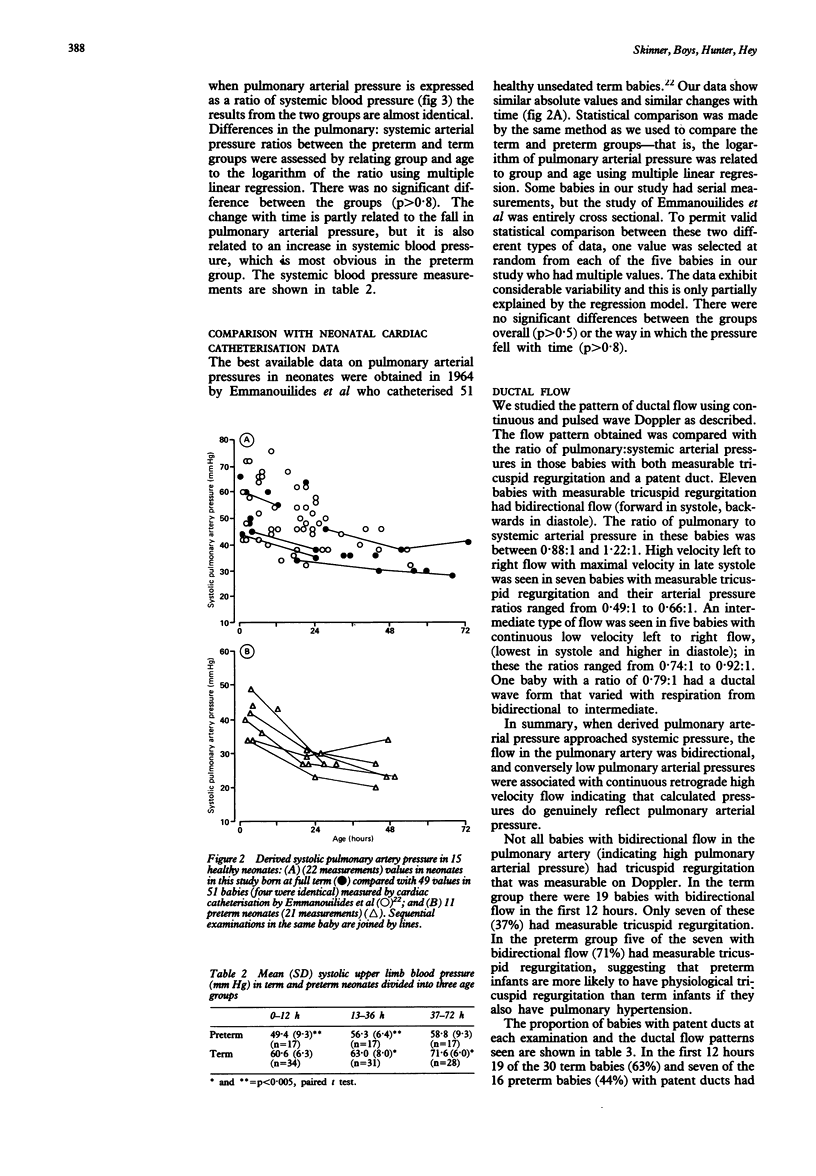
- EMMANOUILIDES G. C., MOSS A. J., DUFFIE E. R., Jr, ADAMS F. H. PULMONARY ARTERIAL PRESSURE CHANGES IN HUMAN NEWBORN INFANTS FROM BIRTH TO 3 DAYS OF AGE. J Pediatr. 1964 Sep;65:327–333. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80395-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans N. J., Archer L. N. Postnatal circulatory adaptation in healthy term and preterm neonates. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Jan;65(1 Spec No):24–26. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.1_spec_no.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewillig M., Dumoulin M., Van der Hauwaert L. G. Transient neonatal tricuspid regurgitation: a Doppler echocardiographic study of three cases. Br Heart J. 1988 Nov;60(5):446–451. doi: 10.1136/hrt.60.5.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatle L., Angelsen B. A., Tromsdal A. Non-invasive assessment of aortic stenosis by Doppler ultrasound. Br Heart J. 1980 Mar;43(3):284–292. doi: 10.1136/hrt.43.3.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatle L., Brubakk A., Tromsdal A., Angelsen B. Noninvasive assessment of pressure drop in mitral stenosis by Doppler ultrasound. Br Heart J. 1978 Feb;40(2):131–140. doi: 10.1136/hrt.40.2.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holen J., Aaslid R., Landmark K., Simonsen S. Determination of pressure gradient in mitral stenosis with a non-invasive ultrasound Doppler technique. Acta Med Scand. 1976;199(6):455–460. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1976.tb06763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston A. B., Lim M. K., Doig W. B., Gnanapragasam J., Coleman E. N., Jamieson M. P., Pollock J. C. Doppler flow characteristics in the assessment of pulmonary artery pressure in ductus arteriosus. Br Heart J. 1989 Oct;62(4):284–290. doi: 10.1136/hrt.62.4.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston A. B., Lim M. K., Doig W. B., Reid J. M., Coleman E. N. Doppler assessment of the interventricular pressure drop in patients with ventricular septal defects. Br Heart J. 1988 Jul;60(1):50–56. doi: 10.1136/hrt.60.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley J. R., Guntheroth W. G. Pansystolic murmur in the newborn: tricuspid regurgitation versus ventricular septal defect. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Oct;63(10 Spec No):1172–1174. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.10_spec_no.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabatake A., Inoue M., Asao M., Masuyama T., Tanouchi J., Morita T., Mishima M., Uematsu M., Shimazu T., Hori M. Noninvasive evaluation of pulmonary hypertension by a pulsed Doppler technique. Circulation. 1983 Aug;68(2):302–309. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.68.2.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostucki W., Vandenbossche J. L., Friart A., Englert M. Pulsed Doppler regurgitant flow patterns of normal valves. Am J Cardiol. 1986 Aug 1;58(3):309–313. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(86)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. L., Heymann M. A., Kitterman J. A., Gregory G. A., Phibbs R. H., Rudolph A. M. Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1976 Oct;89(4):626–630. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80405-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney L. T., Coryell K. G., Lauer R. M. The newborn transitional circulation: a two-dimensional Doppler echocardiographic study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1985 Sep;6(3):623–629. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(85)80123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musewe N. N., Smallhorn J. F., Benson L. N., Burrows P. E., Freedom R. M. Validation of Doppler-derived pulmonary arterial pressure in patients with ductus arteriosus under different hemodynamic states. Circulation. 1987 Nov;76(5):1081–1091. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.76.5.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panidis I. P., Ross J., Mintz G. S. Effect of sampling site on assessment of pulmonary artery blood flow by Doppler echocardiography. Am J Cardiol. 1986 Nov 15;58(11):1145–1147. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(86)90146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller M. D., Rice M. J., McDonald R. W. Tricuspid regurgitation in newborn infants with respiratory distress: echo-Doppler study. J Pediatr. 1987 May;110(5):760–764. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serwer G. A., Cougle A. G., Eckerd J. M., Armstrong B. E. Factors affecting use of the Doppler-determined time from flow onset to maximal pulmonary artery velocity for measurement of pulmonary artery pressure in children. Am J Cardiol. 1986 Aug 1;58(3):352–356. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(86)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraishi H., Yanagisawa M. Pulsed Doppler echocardiographic evaluation of neonatal circulatory changes. Br Heart J. 1987 Feb;57(2):161–167. doi: 10.1136/hrt.57.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjaerpe T., Hatle L. Noninvasive estimation of systolic pressure in the right ventricle in patients with tricuspid regurgitation. Eur Heart J. 1986 Aug;7(8):704–710. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a062126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez de Prada J. A., Ruano J., Martin-Duran R., Larman M., Zueco J., Ortiz de Murua J. A., Torres A., Figueroa A. Noninvasive determination of pulmonary arterial systolic pressure by continuous wave Doppler. Int J Cardiol. 1987 Aug;16(2):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0167-5273(87)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yock P. G., Popp R. L. Noninvasive estimation of right ventricular systolic pressure by Doppler ultrasound in patients with tricuspid regurgitation. Circulation. 1984 Oct;70(4):657–662. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.70.4.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Yoshikawa J., Shakudo M., Akasaka T., Jyo Y., Takao S., Shiratori K., Koizumi K., Okumachi F., Kato H. Color Doppler evaluation of valvular regurgitation in normal subjects. Circulation. 1988 Oct;78(4):840–847. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.78.4.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M., Cottom D. Arterial and venous blood pressure responses during a reduction in blood volume and hypoxia and hypercapnia in infants during the first two days of life. Pediatrics. 1966 May;37(5):733–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]