Abstract
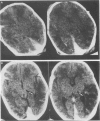
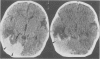
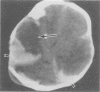
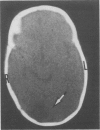
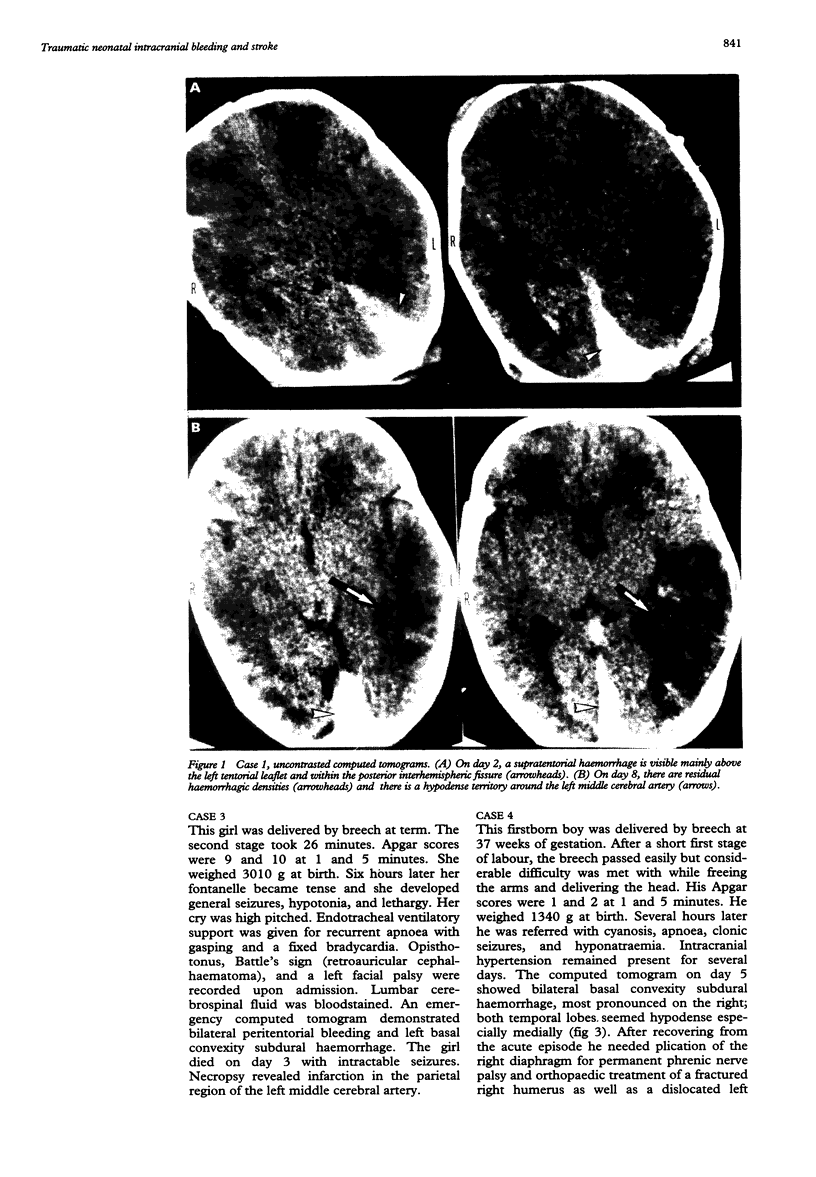
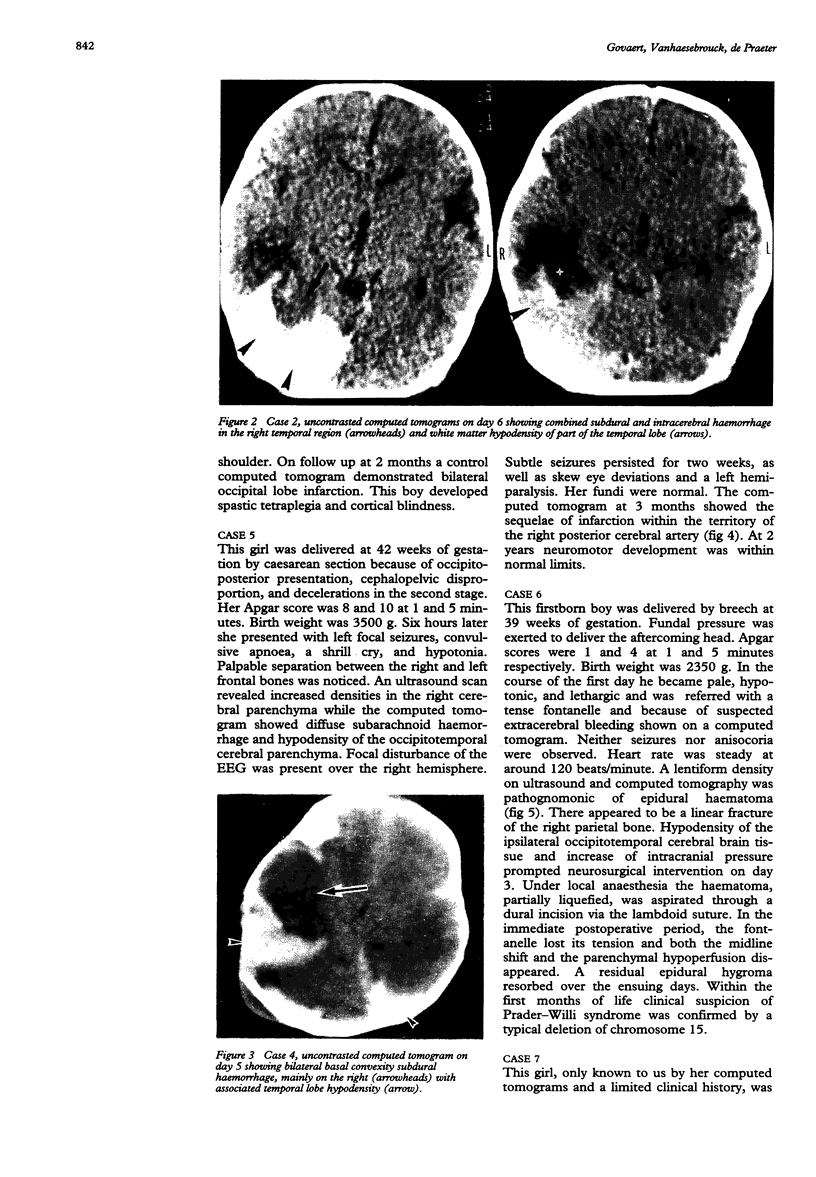
Ischaemia within the regions supplied by vertebral and posterior cerebral arteries has been described as a complication of birth injury, either by direct trauma or by compression from a herniated temporal uncus. Ischaemia within the territory of the middle cerebral artery has been documented after a stretch injury of the vessel's elastica interna. From a series of seven personal observations on birth trauma and related cerebral stroke, we describe three neonates with the uncal herniation type of occipital stroke and four infants with hypoperfusion of the middle cerebral artery or one of its major branches. In three of the latter a basal convexity subdural haemorrhage probably induced the ischaemia, whereas in the other it was associated with haemorrhagic contusion of the parietal lobe. Experimental work and reports on older children support the idea that vasospasm due to surrounding extravasated blood can be one of the responsible mechanisms. Both forceps delivery and difficult vacuum extraction can be implicated in this supratentorial injury, leading to permanent neurological damage in at least half of the survivors in this series.
Full text
PDF
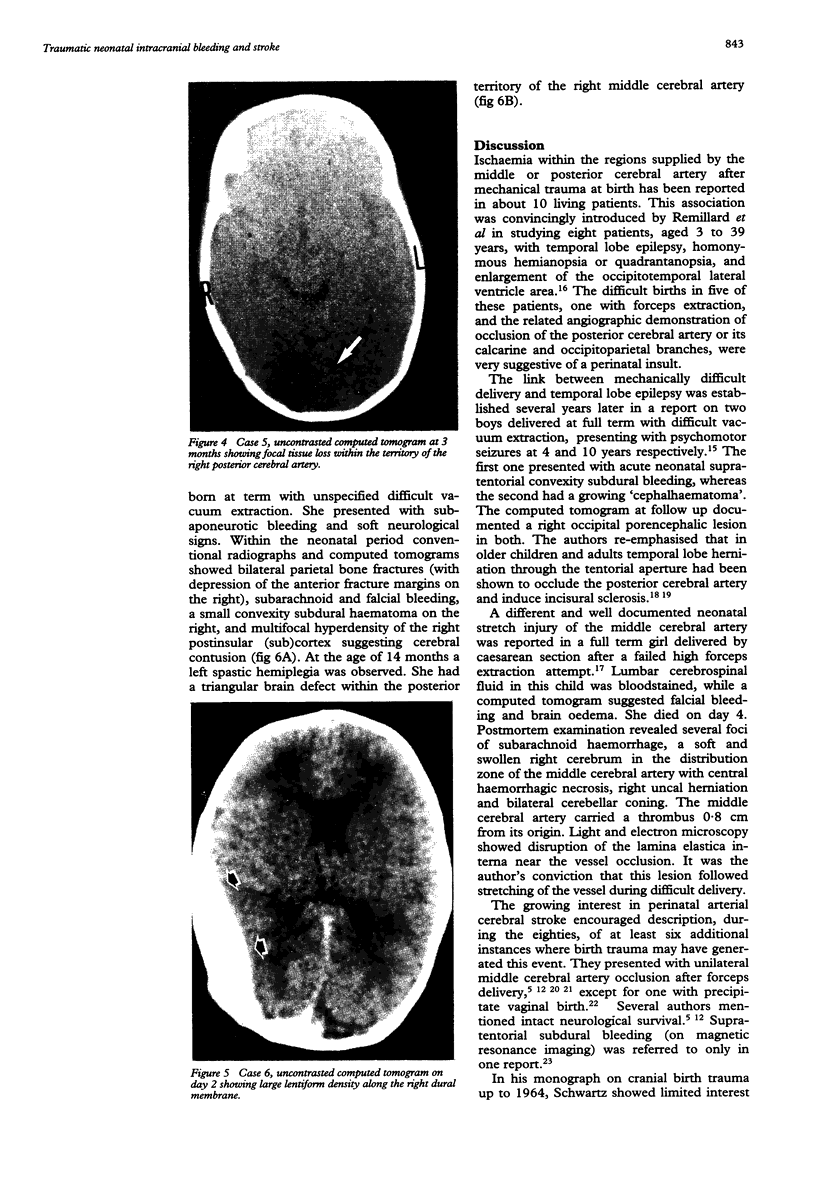
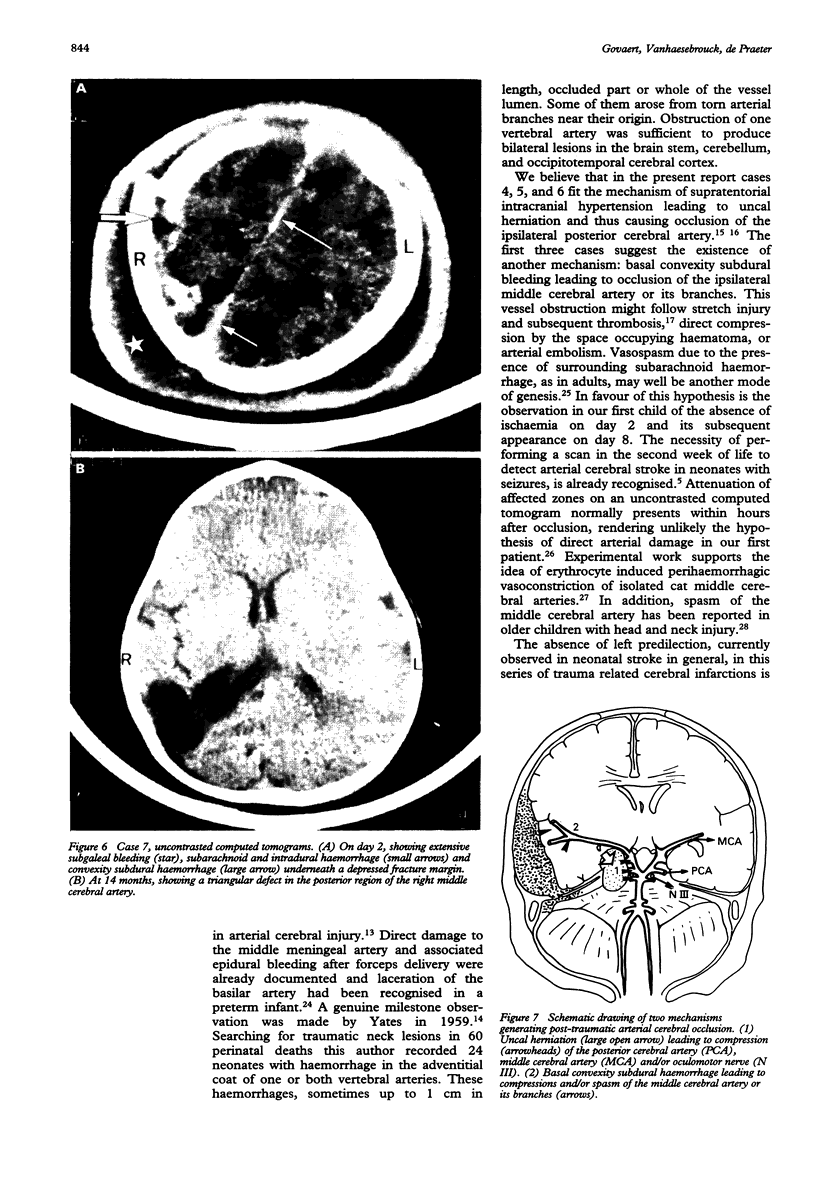

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barmada M. A., Moossy J., Shuman R. M. Cerebral infarcts with arterial occlusion in neonates. Ann Neurol. 1979 Dec;6(6):495–502. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman P. H., Banker B. Q. Neonatal meningitis. A clinical and pathological study of 29 cases. Pediatrics. 1966 Jul;38(1):6–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy R., Malin S., Laraque D., Baumgart S., Younkin D. Focal motor seizures heralding stroke in full-term neonates. Am J Dis Child. 1985 Jun;139(6):601–606. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1985.02140080071035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deonna T., Prod'hom L. S. Temporal lobe epilepsy and hemianopsia in childhood of perinatal origin. An overlooked and potentially treatable disease? Report of two cases, one with a demonstrable etiology. Neuropadiatrie. 1980 Feb;11(1):85–90. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1071379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EARLE K. M., BALDWIN M., PENFIELD W. Incisural sclerosis and temporal lobe seizures produced by hippocampal herniation at birth. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1953 Jan;69(1):27–42. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1953.02320250033003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Lou H. C., Tvede K. On the pathogenesis of regional cerebral ischemia in intracranial hemorrhage: a causal influence of potassium? Pediatr Res. 1986 May;20(5):478–480. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198605000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANTZEN E., JACOBSEN H. H., THERKELSEN J. Cerebral artery occlusions in children due to trauma to the head and neck. A report of 6 cases verified by cerebral angiography. Neurology. 1961 Aug;11:695–700. doi: 10.1212/wnl.11.8.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenichel G. M., Webster D. L., Wong W. K. Intracranial hemorrhage in the term newborn. Arch Neurol. 1984 Jan;41(1):30–34. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1984.04050130036018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halsey A. B., Stoddard R. A. Neonatal cerebral infarction. J Pediatr. 1984 Jun;104(6):957–958. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80511-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halsey A. B., Stoddard R. A. Neonatal cerebral infarction. J Pediatr. 1984 Jun;104(6):957–958. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80511-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanigan W. C., Morgan A. M., Stahlberg L. K., Hiller J. L. Tentorial hemorrhage associated with vacuum extraction. Pediatrics. 1990 Apr;85(4):534–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A., Martin D. J., Daneman A., Fitz C. R. Focal ischemic cerebral injury in the newborn: diagnosis by ultrasound and correlation with computed tomographic scan. Pediatrics. 1983 May;71(5):790–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klesh K. W., Murphy T. F., Scher M. S., Buchanan D. E., Maxwell E. P., Guthrie R. D. Cerebral infarction in persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Am J Dis Child. 1987 Aug;141(8):852–857. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1987.04460080038023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDENBERG R. Compression of brain arteries as pathogenetic factor for tissue necroses and their areas of predilection. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1955 Jul;14(3):223–243. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195507000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S. R., Abroms I. F., Marshall P. C., Rosquete E. E. Seizures and cerebral infarction in the full-term newborn. Ann Neurol. 1985 Apr;17(4):366–370. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannino F. L., Trauner D. A. Stroke in neonates. J Pediatr. 1983 Apr;102(4):605–610. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani J. F., Gerber G. J. 'Idiopathic' neonatal cerebral infarction. Am J Dis Child. 1984 Apr;138(4):359–362. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1984.02140420025010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ment L. R., Duncan C. C., Ehrenkranz R. A. Perinatal cerebral infarction. Semin Perinatol. 1987 Apr;11(2):142–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ment L. R., Duncan C. C., Ehrenkranz R. A. Perinatal cerebral infarction. Ann Neurol. 1984 Nov;16(5):559–568. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine J., Davies H., Gamsu H. R. Multiple idiopathic emboli in a full term neonate. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1989 Jul;78(4):644–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1989.tb17956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raybaud C. A., Livet M. O., Jiddane M., Pinsard N. Radiology of ischemic strokes in children. Neuroradiology. 1985;27(6):567–578. doi: 10.1007/BF00340853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remillard G. M., Ethier R., Andermann F. Temporal lobe epilepsy and perinatal occlusion of the posterior cerebral artery. A syndrome analogous to infantile hemiplegia and a demonstrable etiology in some patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology. 1974 Nov;24(11):1001–1009. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.11.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roessmann U., Miller R. T. Thrombosis of the middle cerebral artery associated with birth trauma. Neurology. 1980 Aug;30(8):889–892. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.8.889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roodhooft A. M., Parizel P. M., Van Acker K. J., Deprettere A. J., Van Reempts P. J. Idiopathic cerebral arterial infarction with paucity of symptoms in the full-term neonate. Pediatrics. 1987 Sep;80(3):381–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YATES P. O. Birth trauma to the vertebral arteries. Arch Dis Child. 1959 Oct;34:436–441. doi: 10.1136/adc.34.177.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]