Abstract
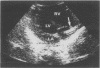
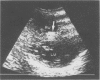
A newborn is described in whom the use of a central venous line was complicated by septicaemia and by intracardiac thrombus formation with tricuspid valve insufficiency and heart failure. Besides antibiotics, treatment consisted of tissue type plasminogen activator (tPA) for three days. This treatment resulted in the disappearance of the thrombus and the tricuspid insufficiency. No adverse effects were noted. Treatment with tPA should be considered in intracardiac thrombus formation with rapidly progressive heart failure in the neonate.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crabbe S. J., Cloninger C. C. Tissue plasminogen activator: a new thrombolytic agent. Clin Pharm. 1987 May;6(5):373–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaplane D., Scott J. P., Riggs T. W., Silverman B. L., Hunt C. E. Urokinase therapy for a catheter-related right atrial thrombus. J Pediatr. 1982 Jan;100(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80258-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy L. A., Drummond W. H., Knight M. E., Millsaps M. M., Williams J. L. Successful treatment of neonatal aortic thrombosis with tissue plasminogen activator. J Pediatr. 1990 May;116(5):798–801. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82675-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy M., Benson L. N., Burrows P. E., Bentur Y., Strong D. K., Smith J., Johnson D., Jacobson S., Koren G. Tissue plasminogen activator for the treatment of thromboembolism in infants and children. J Pediatr. 1991 Mar;118(3):467–472. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82170-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Sherry S. Thrombolytic therapy: current status (1). N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1512–1520. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel G. J., O'Loughlin J. E., Edelson P. J. Neonatal Staphylococcus epidermidis right-sided endocarditis: description of five catheterized infants. Pediatrics. 1988 Aug;82(2):234–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. S., Tresch D. D., Brooks H. L., Lepley D., Olinger G. N., Bonchek L. I., Johnson G. Operative approach to endocarditis. Am Heart J. 1984 Sep;108(3 Pt 1):561–566. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90424-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyles L. A., Pierpont M. E., Steiner M. E., Hesslein P. S., Smith C. M., 2nd Fibrinolysis by tissue plasminogen activator in a child with pulmonary embolism. J Pediatr. 1990 May;116(5):801–804. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82676-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt B., Zipursky A. Thrombotic disease in newborn infants. Clin Perinatol. 1984 Jun;11(2):461–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schollin J., Bjarke B., Wesström G. Infective endocarditis in Swedish children. II. Location, major complications, laboratory findings, delay of treatment, treatment and outcome. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1986 Nov;75(6):999–1004. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1986.tb10330.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Geme J. W., 3rd, Harris M. C. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal infection in the neonate. Clin Perinatol. 1991 Jun;18(2):281–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton B. F., Baltimore R. S., Clemens J. D. Changing spectrum of infective endocarditis in children. Analysis of 26 cases, 1970-1979. Am J Dis Child. 1984 Aug;138(8):720–725. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1984.02140460012006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]