Abstract
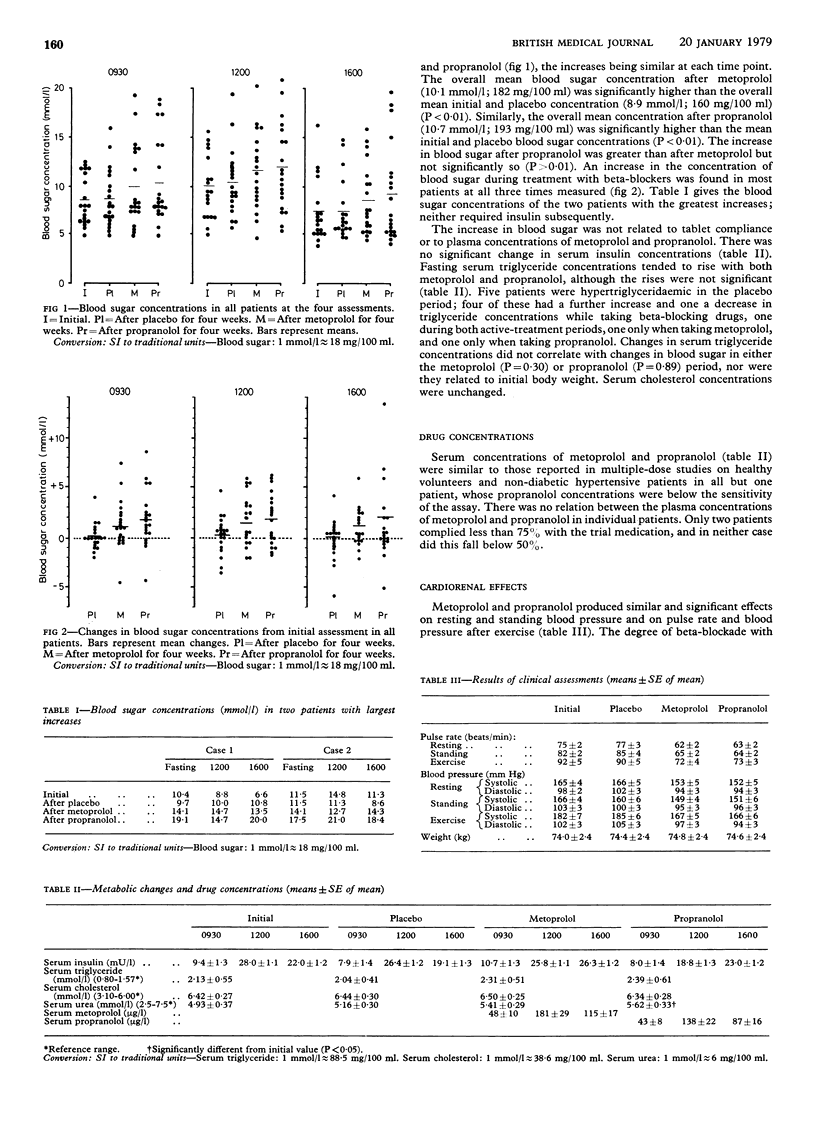
The effects on diabetic control of the relative cardioselective beta-blocker metoprolol and the non-selective drug propranolol were compared in 20 hypertensive diabetic patients receiving diet alone or diet and oral hypoglycaemic agents. Each drug was given for one month in a double-blind, cross-over study. Fasting, noon, and mid-afternoon blood sugar concentrations rose by 1.0-1.5 mmol/l (18-27 mg/100 ml). The rise with propranolol was not significantly greater than with metoprolol. In a few patients the rise was clinically important. The small overall change observed in diabetic control should not deter the use of beta-blockers in non-insulin-dependent diabetics, provided control is carefully monitored at the onset of treatment.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson E. A., Arky R. A., Woeber K. A. Effects of propranolol on the hormonal and metabolic responses to insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Lancet. 1966 Dec 24;2(7478):1386–1388. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90422-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berglund G., Sannerstedt R., Andersson O., Wedel H., Wilhelmsen L., Hansson L., Sivertsson R., Wikstrand J. Coronary heart-disease after treatment of hypertension. Lancet. 1978 Jan 7;1(8054):1–5. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90356-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R., Efendić S. Effect of adrenergic blocking agents on insulin response to glucose infusion in man. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 Feb;69(2):335–346. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0690335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deacon S. P., Barnett D. Comparison of atenolol and propranolol during insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Br Med J. 1976 Jul 31;2(6030):272–273. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6030.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen P. H., Riess W. Simplified method for the determination of oxprenolol and other beta-receptor-blocking agents in biological fluids by gas-liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1976 Jun 9;121(1):72–75. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)82299-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIZZLE J. E. THE TWO-PERIOD CHANGE-OVER DESIGN AN ITS USE IN CLINICAL TRIALS. Biometrics. 1965 Jun;21:467–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgeland A., Hjermann I., Leren P., Holme I. Possible metabolic side effects of beta-adrenergic blocking drugs. Br Med J. 1978 Apr 1;1(6116):828–828. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6116.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. J., Kohner E. M., Petrie A., Dollery C. T. Deterioration of glucose tolerance in hypertensive patients on prolonged diuretic treatment. Lancet. 1976 Mar 13;1(7959):564–566. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loubatières A., Mariani M. M., Sorel G., Savi L. The action of beta-adrenergic blocking and stimulating agents on insulin secretion. Characterization of the type of beta receptor. Diabetologia. 1971 Jun;7(3):127–132. doi: 10.1007/BF01212541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt D. G., Shanks R. G., Prichard B. N. The clinical pharmacology of beta adrenergic blocking drugs. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1976 Oct;11(1):21–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EULER U. S., LUFT R. Effect of insulin on urinary excretion of adrenalin and noradrenalin; studies in ten healthy subjects and in six cases of acromegaly. Metabolism. 1952 Nov;1(6):528–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waal-Manning H. J. Metabolic effects of beta-adrenoreceptor blockers. Drugs. 1976;11(Suppl 1):121–126. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197600111-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. C., Porte D., Jr Neural control of the endocrine pancreas. Physiol Rev. 1974 Jul;54(3):596–619. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.3.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


