Abstract
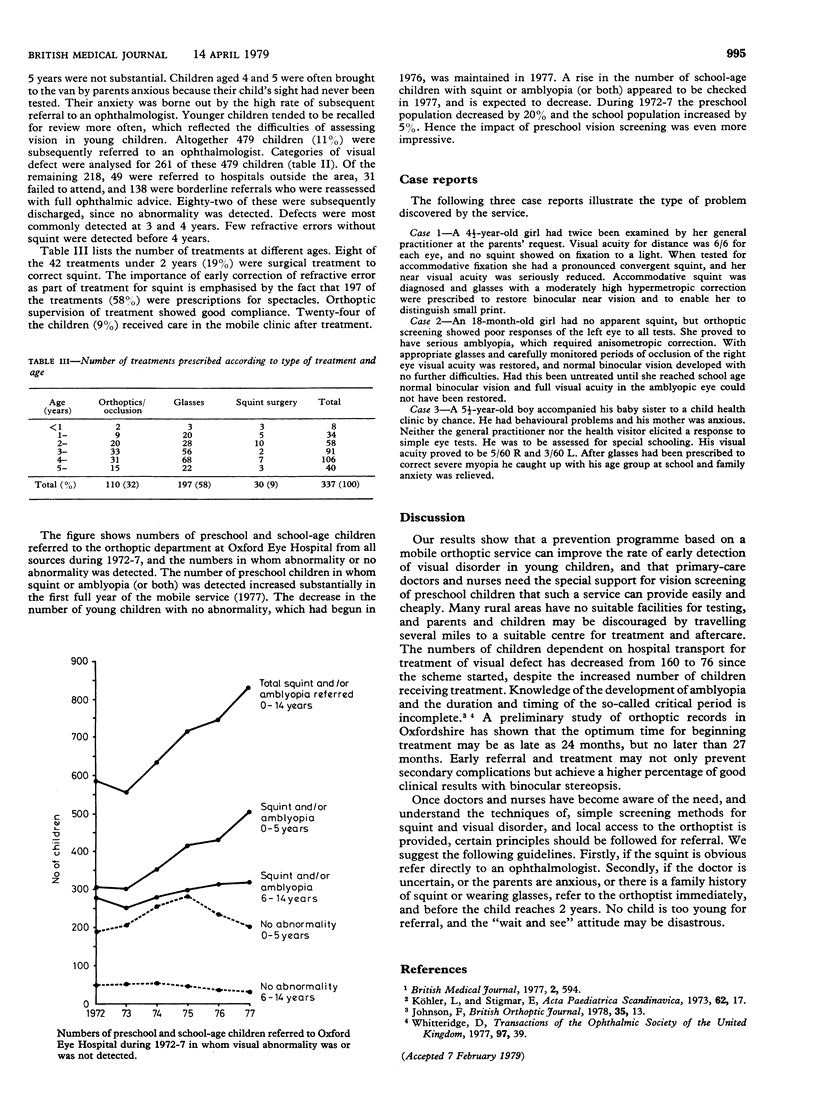
A mobile orthoptic service was begun in 1976. General practitioners, clinic doctors, and health visitors referred 4544 preschool children to the service in 18 months. Of the children referred, no defect was detected in 3138 (69%), 927 (20%) were recalled for a second assessment within 12 months, and 479 (11%) were referred for treatment. Out of 261 who received treatment in Oxford, 24 (9%) received aftercare. Benefits of the service included a 25% decrease during 1976-7 in inappropriate referrals of preschool children to the specialist hospital. The chance of inappropriate referral was reduced by a factor of 30 if a child was referred to the mobile service instead of to the eye hospital. A prevention programme such as the mobile orthoptic service can improve the rate of detection of visual disorder in young children, while providing the support needed by primary-care doctors and nurses for visual screening of preschool children easily and cheaply.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Köhler L., Stigmar G. Vision screening of four-year-old children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1973 Jan;62(1):17–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1973.tb08060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


