Abstract
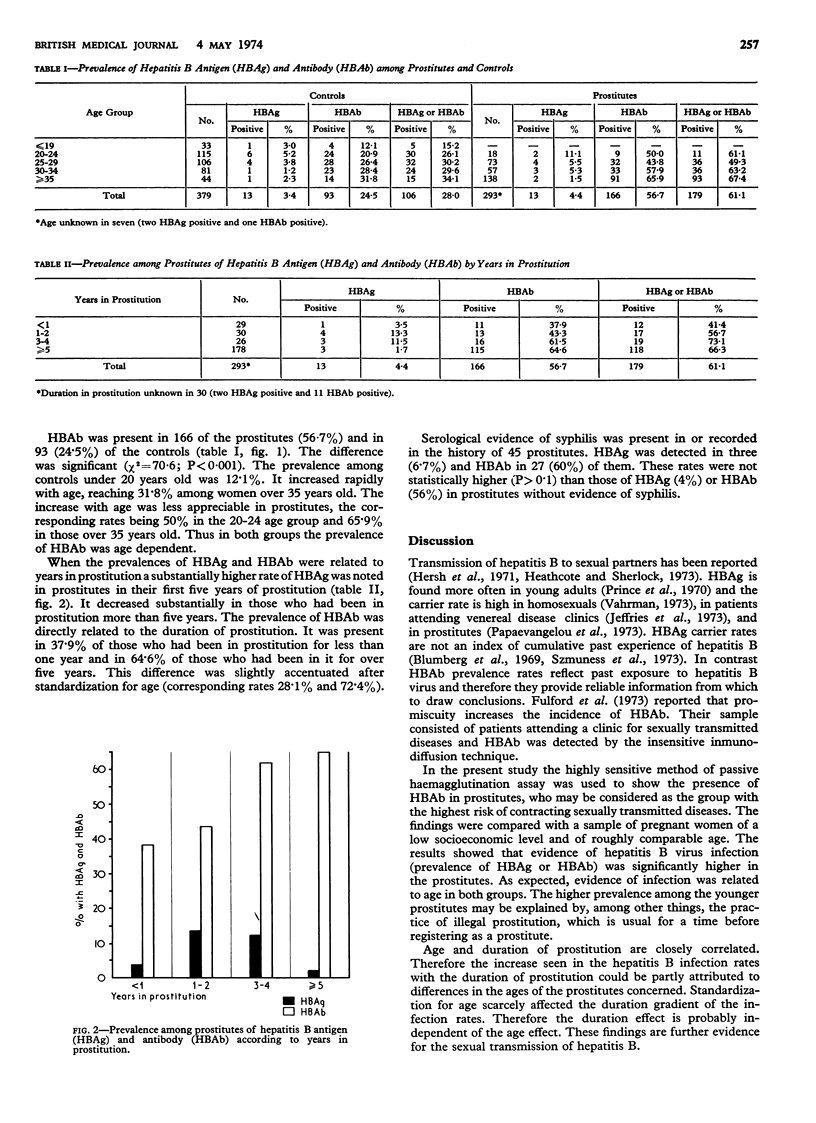
We investigated the prevalence of hepatitis B antigen (HBAg) and antibody (HBAb) in 293 prostitutes and in 379 pregnant women of similar age and of low socioeconomic level, who served as controls. HBAg was found in 4·4% of prostitutes and 3·4% of controls. The prevalence of HBAb was significantly higher (P <0·001) in prostitutes (56·7%) than in controls (24·5%). The prevalence of HBAb was clearly age-dependent in both groups. Evidence of hepatitis B virus infection significantly increased with the number of years in prostitution. The evidence of increased infection rates among prostitutes and their distribution support the hypothesis that hepatitis B infection is sexually transmitted.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg B. S., Sutnick A. I., London W. T. Australia antigen and hepatitis. JAMA. 1969 Mar 10;207(10):1895–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart Y. E. Australia antigen and heaptitis: a review. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Jul;24(5):394–403. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.5.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulford K. W., Dane D. S., Catterall R. D., Woof R., Denning J. V. Australia antigen and antibody among patients attending a clinic for sexually transmitted diseases. Lancet. 1973 Jun 30;1(7818):1470–1473. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91810-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heathcote J., Sherlock S. Spread of acute type-B hepatitis in London. Lancet. 1973 Jun 30;1(7818):1468–1470. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91809-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh T., Melnick J. L., Goyal R. K., Hollinger F. B. Nonparenteral transmission of viral hepatitis type B (Australia antigen-associated serum hepatitis). N Engl J Med. 1971 Dec 9;285(24):1363–1364. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197112092852408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffries D. J., James W. H., Jefferiss F. J., MacLeod K. G., Willcox R. R. Australia (hepatitis-associated) antigen in patients attending a venereal disease clinic. Br Med J. 1973 May 26;2(5864):455–456. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5864.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papaevangelou G. J., Kourea T., Tsoukas S. Hepatitis associated antigen in acute viral hepatitis in Greece. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1971;37(5):361–367. doi: 10.1159/000162337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesendorfer F., Krassnitzky O., Wewalka F. Immunelektrophoretischer Nachweis von "Hepatitis-Associated-Antigen" (Au-SH-Antigen. Klin Wochenschr. 1970 Jan 1;48(1):58–59. doi: 10.1007/BF01486135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M. An antigen detected in the blood during the incubation period of serum hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):814–821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Hargrove R. L., Szmuness W., Cherubin C. E., Fontana V. J., Jeffries G. H. Immunologic distinction between infectious and serum hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1970 Apr 30;282(18):987–991. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197004302821801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REITMAN S., FRANKEL S. A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957 Jul;28(1):56–63. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/28.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vahrman J. Spread of acute type-B hepatitis in London. Lancet. 1973 Jul 21;2(7821):157–157. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Shulman N. R. Hemagglutination assay for antigen and antibody associated with viral hepatitis. Science. 1970 Oct 16;170(3955):332–333. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3955.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


