Abstract
A series of experiments has been carried out with single doses of simple analgesics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using a consistent polyad design. This method proved to be both valid and useful. Pain relief scores were a better measure of the effectiveness of analgesics than preference.
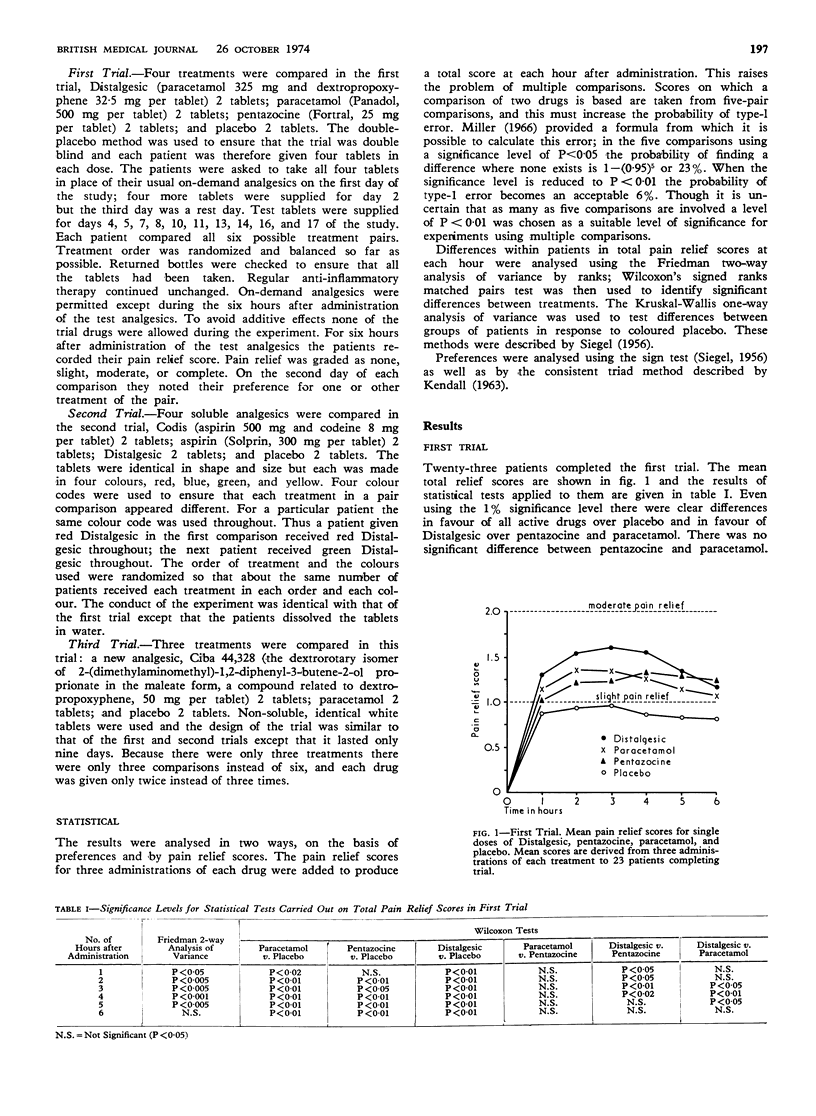
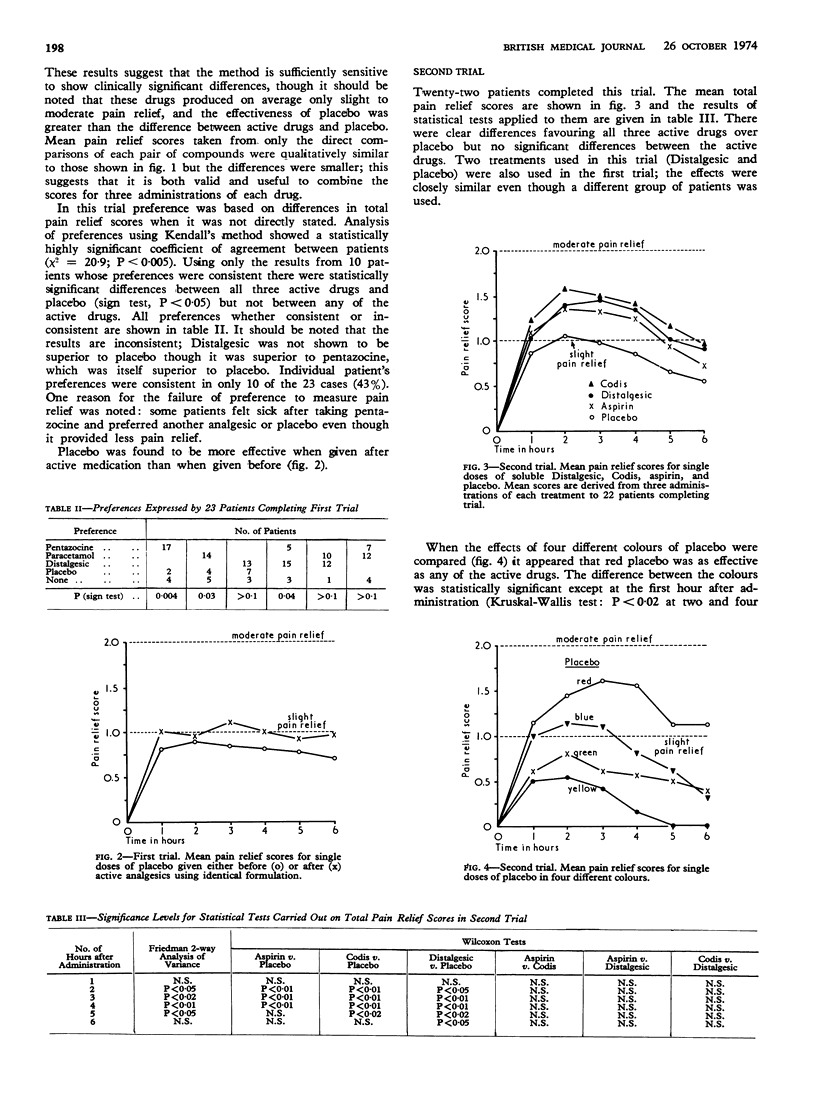
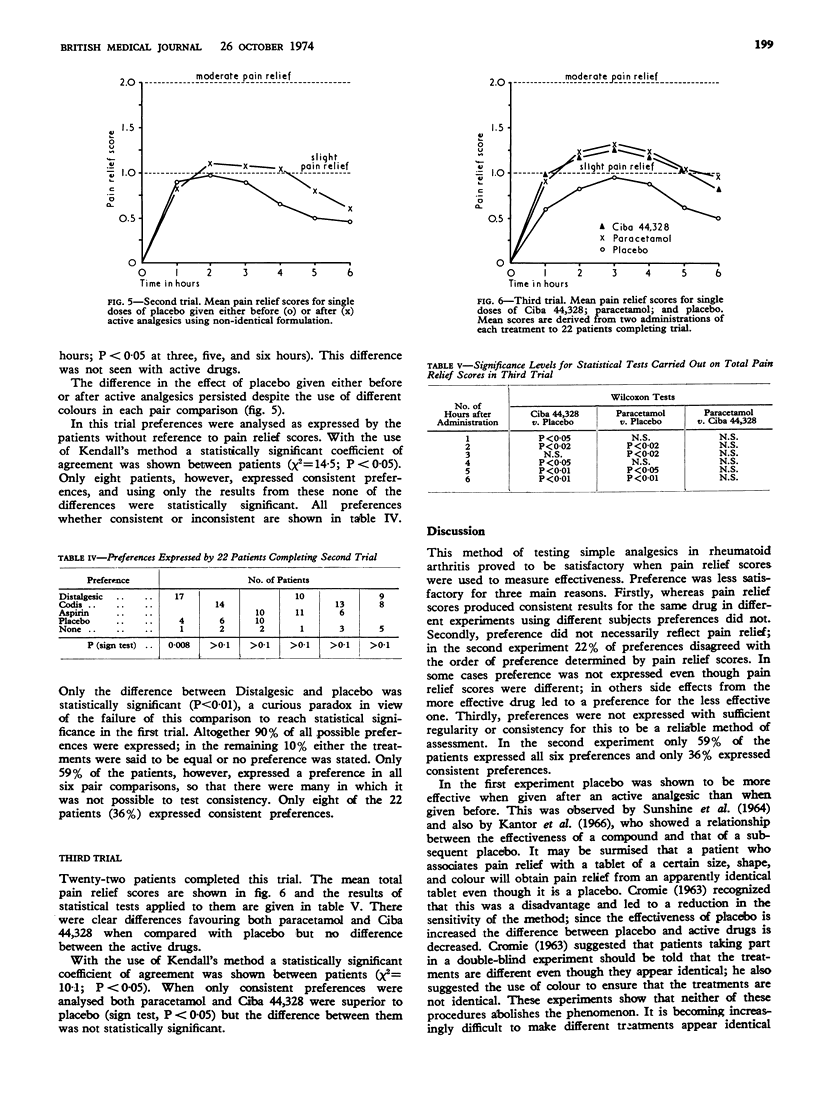
Aspirin, Codis, and Distalgesic were the most effective analgesics tested, with paracetamol, pentazocine, and Ciba 44,328 intermediate between these agents and placebo. Placebo given after an active analgesic was more effective than when given before; this phenomenon was not abolished by telling the patients that apparently identical tablets were, in fact, different or by making them different in colour. The effectiveness of soluble placebo depended on its colour, red being the most effective.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CROMIE B. W. THE FEET OF CLAY OF THE DOUBLE-BLIND TRIAL. Lancet. 1963 Nov 9;2(7315):994–997. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90693-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huskisson E. C., Hart F. D. The use of indomethacin and aloxiprin at night. Practitioner. 1972 Feb;208(244):248–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor T. G., Sunshine A., Laska E., Meisner M., Hopper M. Oral analgesic studies: pentazocine hydrochloride, codeine, aspirin, and placebo and their influence on response to placebo. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1966 Jul-Aug;7(4):447–454. doi: 10.1002/cpt196674447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moertel C. G., Ahmann D. L., Taylor W. F., Schwartau N. A comparative evaluation of marketed analgesic drugs. N Engl J Med. 1972 Apr 13;286(15):813–815. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197204132861504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUNSHINE A., LASKA E., MEISNER M., MORGAN S. ANALGESIC STUDIES OF INDOMETHACIN AS ANALYZED BY COMPUTER TECHNIQUES. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1964 Nov-Dec;5:699–707. doi: 10.1002/cpt196456part1699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


