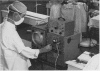
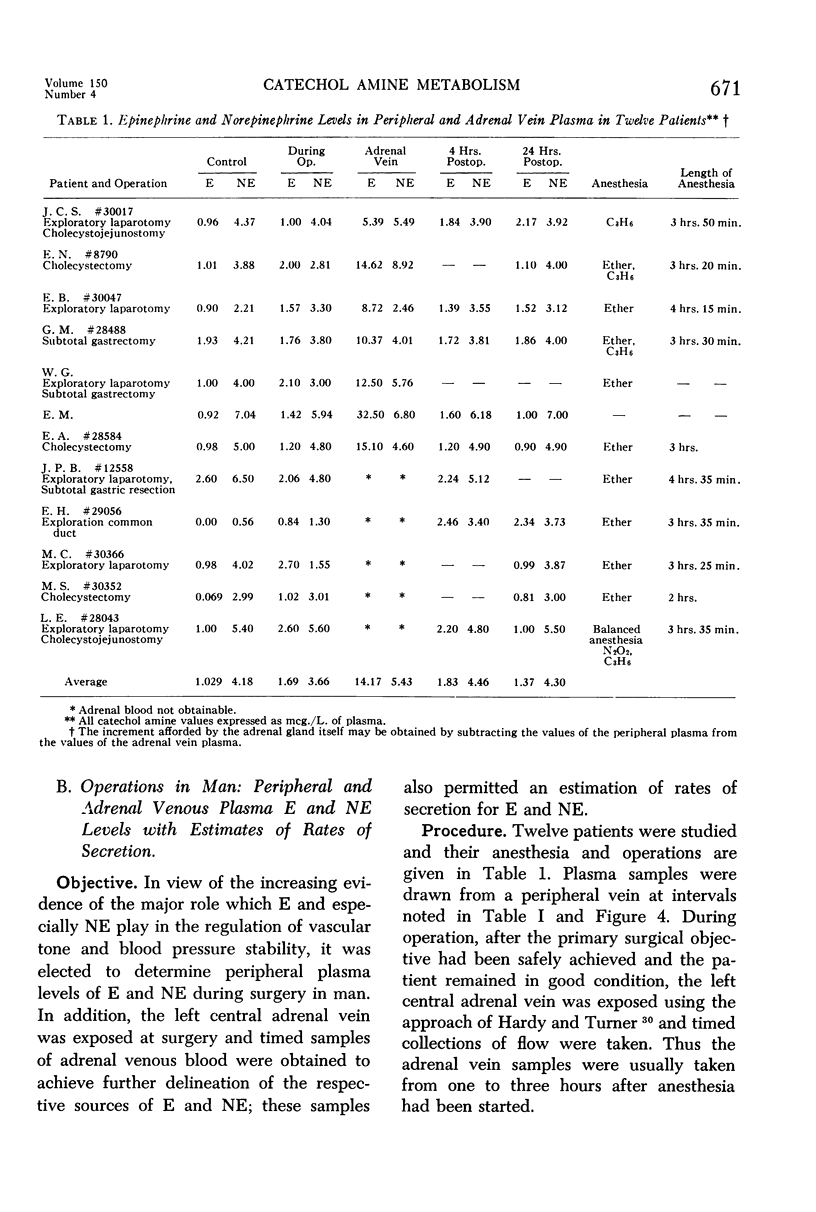
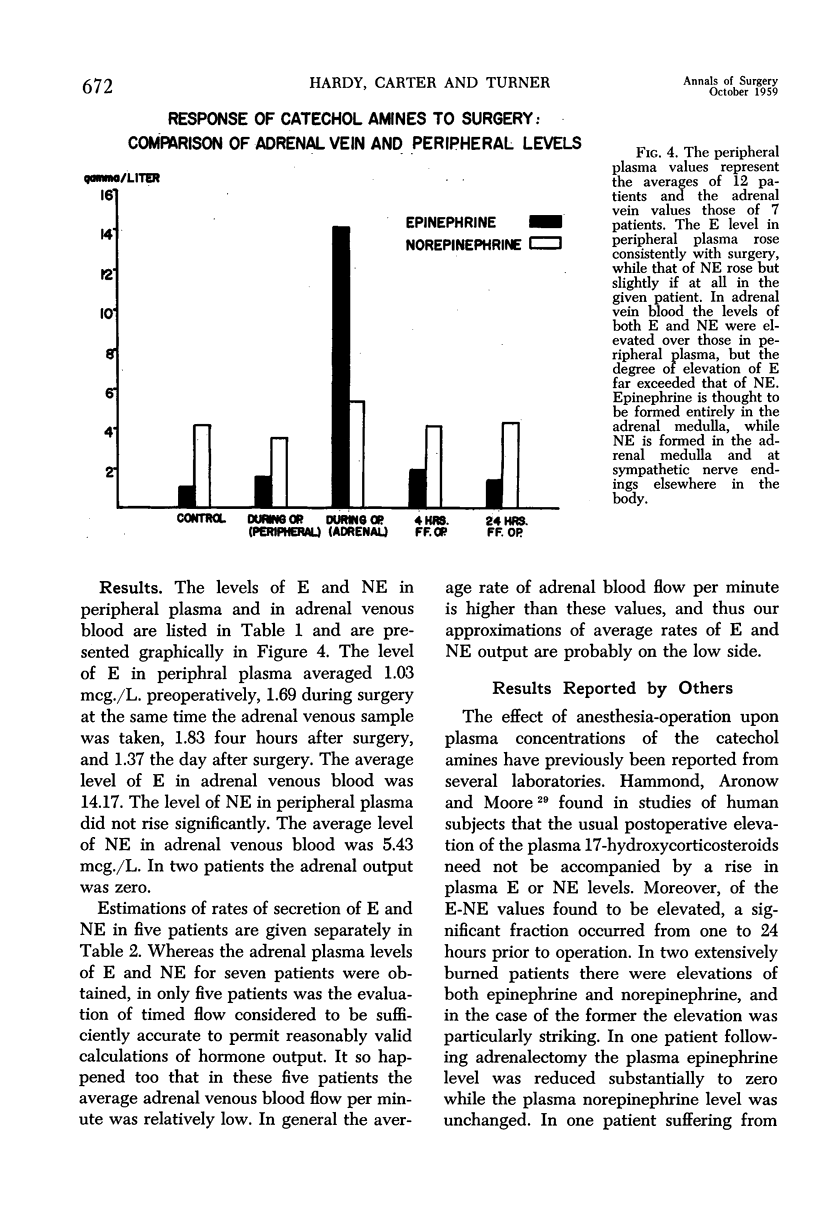
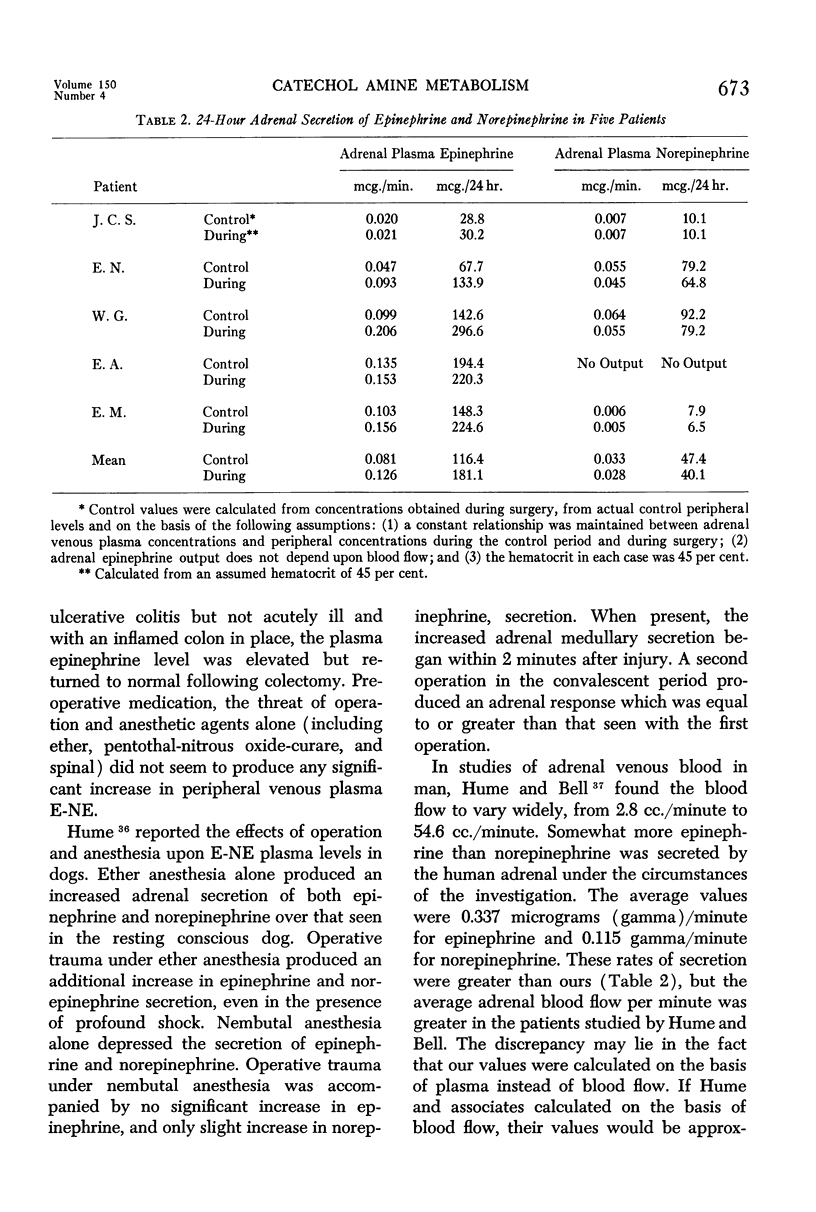
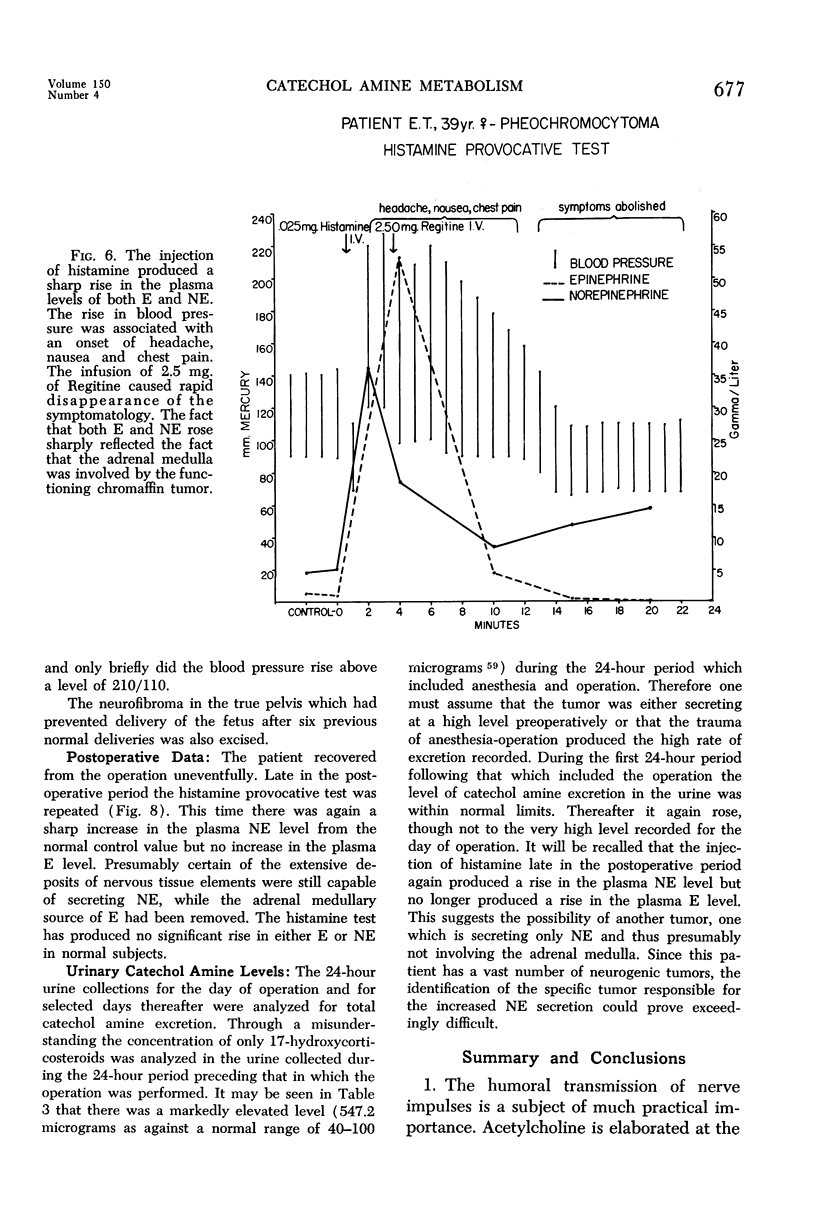
Full text
PDF


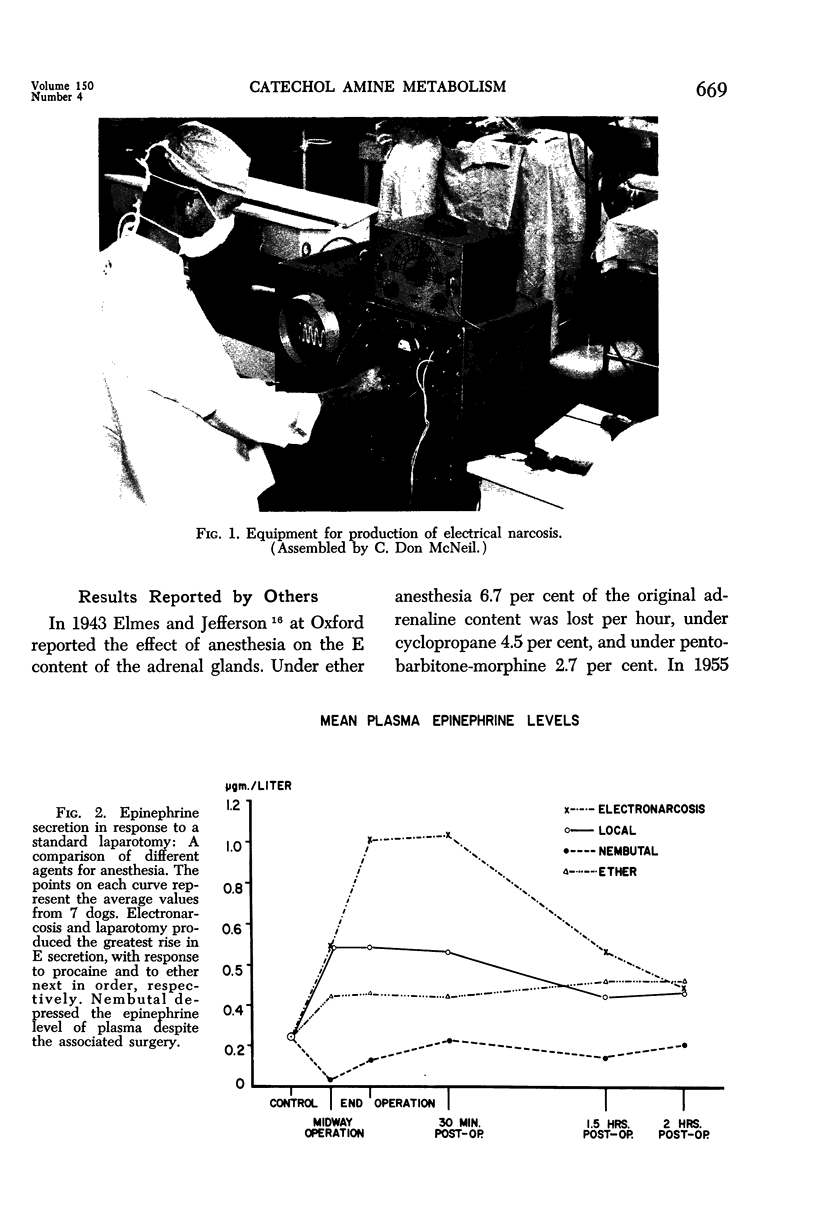
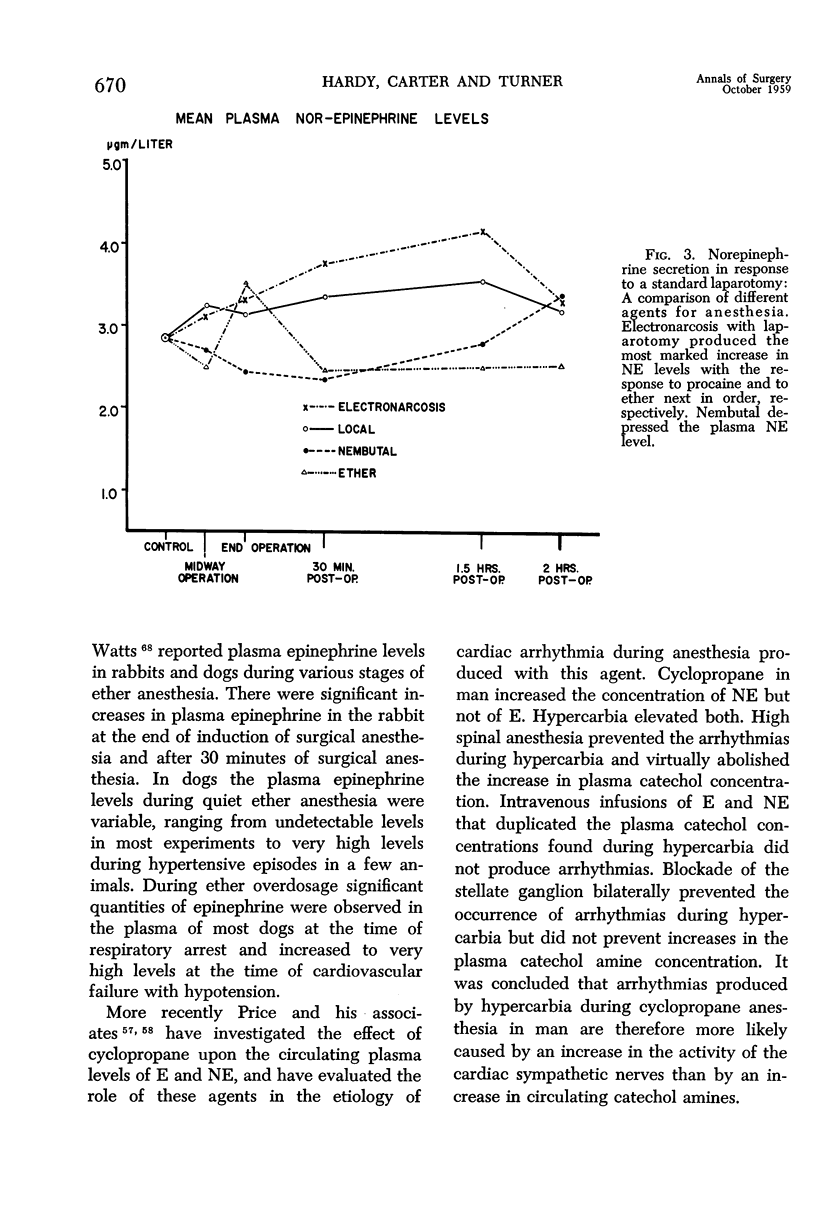






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN M. S., CONE T. E., Jr, PEARSON H. A. Pheochromocytoma in children; report of three familial cases in two unrelated families. Pediatrics. 1957 Jan;19(1):44–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARONOW L., HAMMOND W. G., MOORE F. D. Studies in surgical endocrinology III. Plasma concentrations of epinephrine and norepinephrine in anesthesia, trauma and surgery, as measured by a modification of the method of Weil-Malherbe and Bone. Ann Surg. 1956 Oct;144(4):715–732. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195610000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barger G., Dale H. H. Chemical structure and sympathomimetic action of amines. J Physiol. 1910 Oct 11;41(1-2):19–59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1910.sp001392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONE T. E., Jr Recurrent pheochromocytoma; report of a case in a previously treated child. Pediatrics. 1958 Jun;21(6):994–999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUPLAND R. E. The prenatal development of the abdominal para-aortic bodies in man. J Anat. 1952 Oct;86(4):357–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAESCHNER C. W., MOYER J. H., ABLE L. W. Pheochromocytoma in a four-year-old child: renal hemodynamic, pharmacologic, and radiographic studies. J Pediatr. 1954 Aug;45(2):141–152. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(54)80136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DILLER W. F., KILPATRICK R. Adrenaline in hyperthyroidism and insulin hypoglycaemia. Br Med J. 1958 Oct 4;2(5100):823–825. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5100.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIS S. The metabolic effects of epinephrine and related amines. Pharmacol Rev. 1956 Dec;8(4):485–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T. R. The action of adrenalin. J Physiol. 1905 Jul 13;32(5-6):401–467. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1905.sp001093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmes P. C., Jefferson A. A. The effect of anaesthesia on the adrenaline content of the suprarenal glands. J Physiol. 1942 Nov 30;101(3):355–361. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1942.sp003990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLUSHIEN A. S., MANSUY M. M., LITTMAN D. S. Pheochromocytoma; its relationship to the neurocutaneous syndromes. Am J Med. 1953 Mar;14(3):318–327. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(53)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDENBERG M. Adrenal medullary function. Am J Med. 1951 May;10(5):627–641. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(51)90332-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDENBERG M., SERLIN I., EDWARDS T., RAPPORT M. M. Chemical screening methods for the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. I. Nor-epinephrine and epinephrine in human urine. Am J Med. 1954 Mar;16(3):310–327. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(54)90349-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODALL M., KIRSHNER N. Biosynthesis of epinephrine and norepinephrine by sympathetic nerves and ganglia. Circulation. 1958 Mar;17(3):366–371. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.17.3.366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBERG R. E., GARDNER L. I. Pheochromocytoma in father and son: report of the eighth known affected kindred. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1959 Mar;19(3):351–362. doi: 10.1210/jcem-19-3-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUYTON A. C., GILLESPIE W. M., Jr Constant infusion of epinephrine; rate of epinephrine secretion and destruction in the body. Am J Physiol. 1951 May;165(2):319–327. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.165.2.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDY J. D., TURNER M. D. Hydrocortisone secretion in man: studies of adrenal vein blood. Surgery. 1957 Jul;42(1):194–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEALEY F. H., Jr, MEKELATOS C. J. Pheochromocytoma and neurofibromatosis; report of a case. N Engl J Med. 1958 Mar 13;258(11):540–543. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195803132581106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HICKLER R. B., WELLS R. E., Jr, TYLER H. R., HAMLIN J. T., 3rd Plasma catechol amine and electroencephalographic responses to acute postural change; evidence of a deficient pressor amine response in postural hypotension. Am J Med. 1959 Mar;26(3):410–423. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90249-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILLARP N. A., HOKFELT B. Evidence of adrenaline and noradrenaline in separate adrenal medullary cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1953 Dec 31;30(1):55–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1954.tb01074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUME D. E., BELL C. C., Jr The secretion of epinephrine nor-epinephrine, and corticosteroid in the adrenal venous blood of the human. Surg Forum. 1958;9:6–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUME D. M. The secretion of epinephrine, nor-epinephrine and corticosteroids in the adrenal venous blood of the dog following single and repeated trauma. Surg Forum. 1957;8:111–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTCHISON G. B., EVANS J. A., DAVIDSON D. C. Pitfalls in the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. Ann Intern Med. 1958 Feb;48(2):300–309. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-48-2-300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holton P. Noradrenaline in tumours of the adrenal medulla. J Physiol. 1949 Jun 15;108(4):525–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS H., MEDALIE M., POLITZER W. M. Noradrenaline-secreting neuroblastomata. Br Med J. 1959 Feb 14;1(5119):401–404. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5119.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELSALL A. R., ROSS E. J. Bilateral phaeochromocytoma in two sisters. Lancet. 1955 Aug 6;269(6884):273–274. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(55)92693-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOX J., SLESSOR A. Phaeochromocytoma and neurofibromatosis; adrenolytic effect of phentolamine and chlorpromazine. Lancet. 1955 Apr 16;268(6868):790–793. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(55)90486-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNUTSON R. C., REITMAN J. H., TICHY F. Y. The use of electrical current as an anesthetic agent. Anesthesiology. 1956 Nov-Dec;17(6):815–825. doi: 10.1097/00000542-195611000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOONCE D. H., POLLOCK B. E., GLASSY F. J. Bilateral pheochromocytoma associated with neurofibromatosis; death following aortography. Am Heart J. 1952 Dec;44(6):901–909. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(52)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KVALE W. F., MANGER W. M., PRIESTLEY J. T., ROTH G. M. Pheochromocytoma. Circulation. 1956 Oct;14(4 Pt 1):622–630. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.14.4.622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITCHFIELD J. W., PEART W. S. Phaeochromocytoma with normal excretion of adrenaline and noradrenaline. Lancet. 1956 Dec 22;271(6956):1283–1284. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)91435-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOPEZ J. F. Phenochromocytoma of the adrenal gland with granulosa cell tumor and neurofibromatosis: report of a case with fatal outcome following abdominal aortography. Ann Intern Med. 1958 Jan;48(1):187–199. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-48-1-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUND A., MOLLER K. O. Adrenaline concentration in the blood of human patients dying of adrenaline poisoning. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1958;14(4):363–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1958.tb02980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAIER H. C., HUMPHREYS G. H., 2nd Intrathoracic pheochromocytoma; including a case of multiple paragangliomas of the functional and nonfunctional type. J Thorac Surg. 1958 Nov;36(5):625–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANGAN G. F., Jr, MASON J. W. The fluorimetric measurement of plasma epinephrine and norepinephrine concentrations in man, monkey, and dog. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Mar;51(3):484–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANGER W. M., FLOCK E. V., BERKSON J., BOLLMAN J. L., ROTH G. M., BALDES E. J., JACOBS M. Chemical quantitation of epinephrine and norepinephrine in thirteen patients with pheochromocytoma. Circulation. 1954 Nov;10(5):641–652. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.10.5.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNEIL C. D., TURNER M. D., HARDY J. D. Electrical anesthesia: some metabolic observations and comparisons. Surg Forum. 1958;9:394–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRICE H. L., LURIE A. A., JONES R. E., PRICE M. L., LINDE H. W. Cyclopropane anesthesia. II. Epinephrine and norepinephrine in initiation of ventricular arrhythmias by carbon dioxide inhalation. Anesthesiology. 1958 Sep-Oct;19(5):619–630. doi: 10.1097/00000542-195809000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REUTTER F. W., ZILELI M. S., HAMLIN J. T., 3rd, THORN G. W., FRIEND D. G. Importance of detecting rapid changes in blood catechol amine levels in the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. N Engl J Med. 1957 Aug 15;257(7):323–325. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195708152570707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON J. A., RICHARDSON A. K., BRODIE O. J. Fluorimetric determination of epinephrine and norepinephrine in plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1956 May;47(5):832–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH G. M., HIGHTOWER N. C., Jr, BARKER N. W., PRIESTLEY J. T. Familial pheochromocytoma; report on three siblings with bilateral tumors. AMA Arch Surg. 1953 Jul;67(1):100–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMID A. C., DUSHANE J. W. Pheochromocytoma in children; report of case. AMA Am J Dis Child. 1955 Jul;90(1):81–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROM G., VON EULER U. S. Present status of diagnosis and treatment of pheochromocytoma. Circulation. 1957 Jan;15(1):5–13. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.15.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUZUKI T., TANAKA I., NINAGAWA C., NAKAMURA T., FUJISAKI S. Descending spinal pathway subserving the adrenaline secretion of the adrenal in dogs. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1958 Feb 25;67(2-3):293–298. doi: 10.1620/tjem.67.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EULER U. S. Adrenaline and noradrenaline; distribution and action. Pharmacol Rev. 1954 Mar;6(1):15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EULER U. S. Some aspects of the role of noradrenaline and adrenaline in circulation. Am Heart J. 1958 Sep;56(3):469–477. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(58)90286-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EULER U. S. The nature of adrenergic nerve mediators. Pharmacol Rev. 1951 Sep;3(3):247–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATTS D. T. Epinephrine in the circulating blood during ether anesthesia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1955 Jun;114(2):203–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIL-MALHERBE H., BONE A. D. The adrenergic amines of human blood. Lancet. 1953 May 16;1(6768):974–977. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)92117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIL-MALHERBE H., BONE A. D. The chemical estimation of adrenaline-like substances in blood. Biochem J. 1952 Jun;51(3):311–318. doi: 10.1042/bj0510311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEST G. B., SHEPHERD D. M., HUNTER R. B., MACGREGOR A. R. The function of the organs of Zuckerkandl. Clin Sci. 1953 Nov;12(4):317–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEST G. B. The comparative pharmacology of the suprarenal medulla. Q Rev Biol. 1955 Jun;30(2):116–137. doi: 10.1086/400758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG R. C., MURRAY W. A. Familial adrenal phaeochromocytoma with sustained hypertension. Can Med Assoc J. 1955 Apr 1;72(7):503–509. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]