Abstract
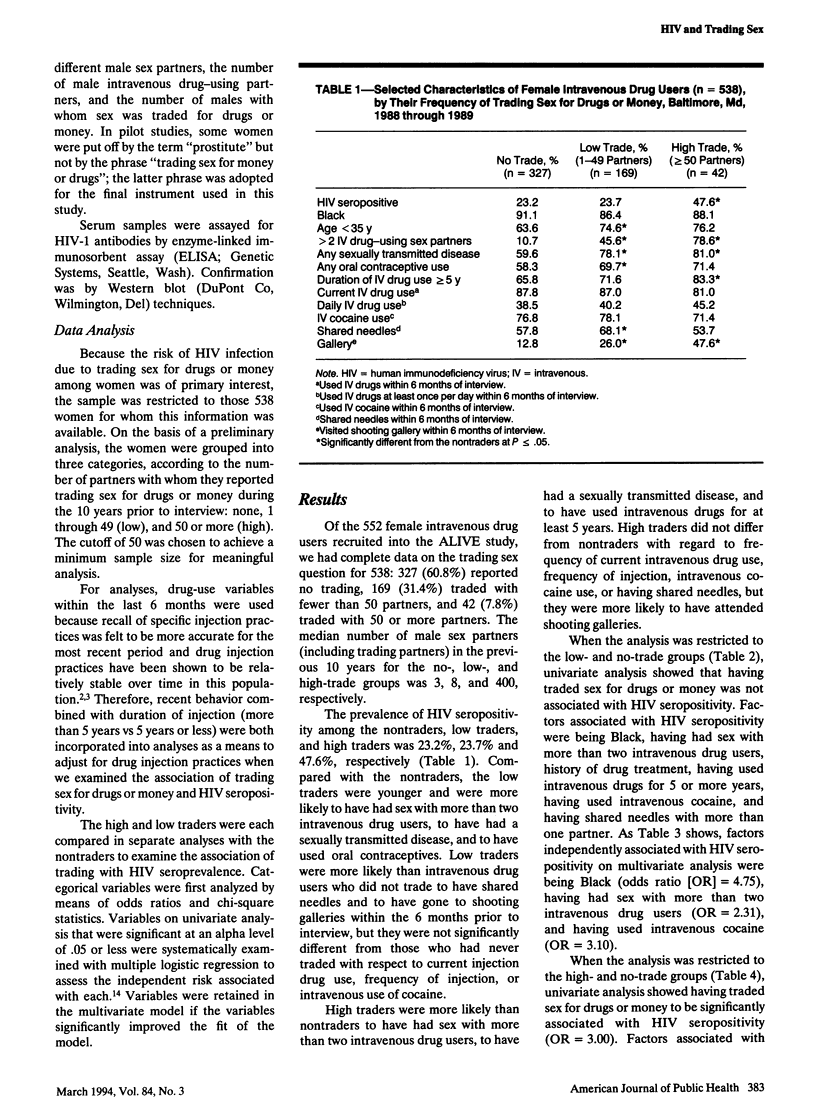
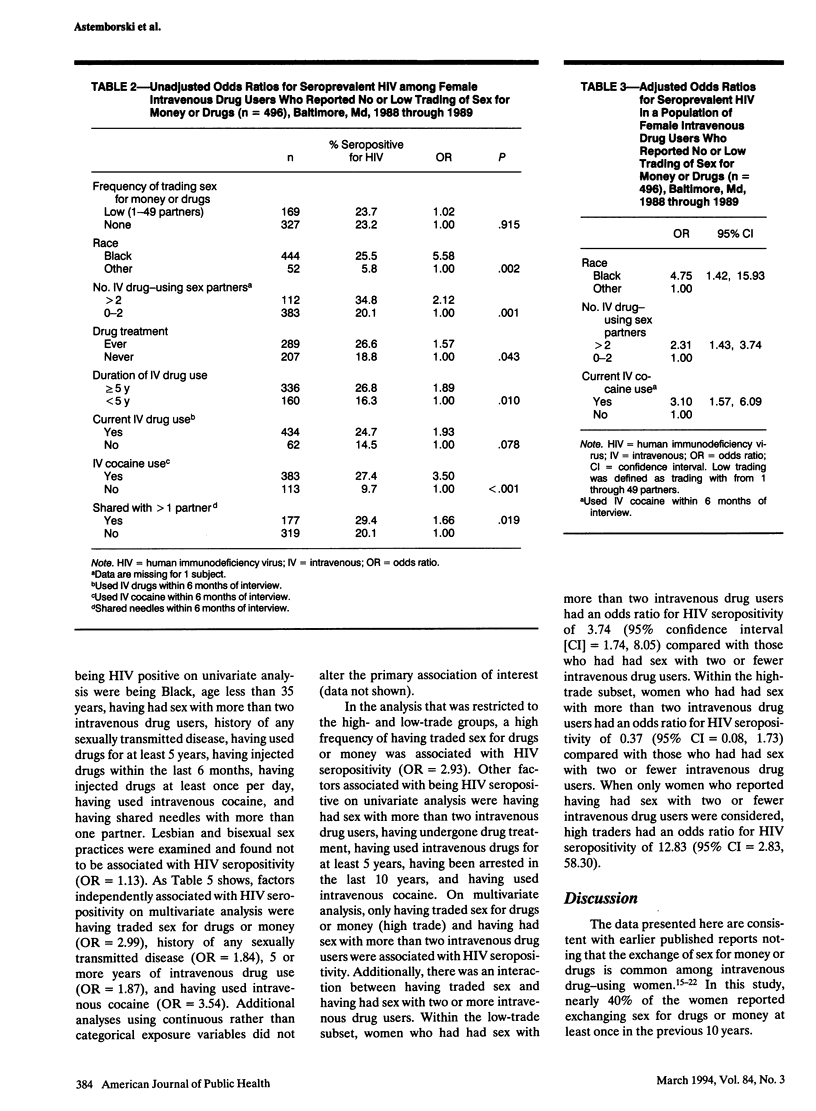
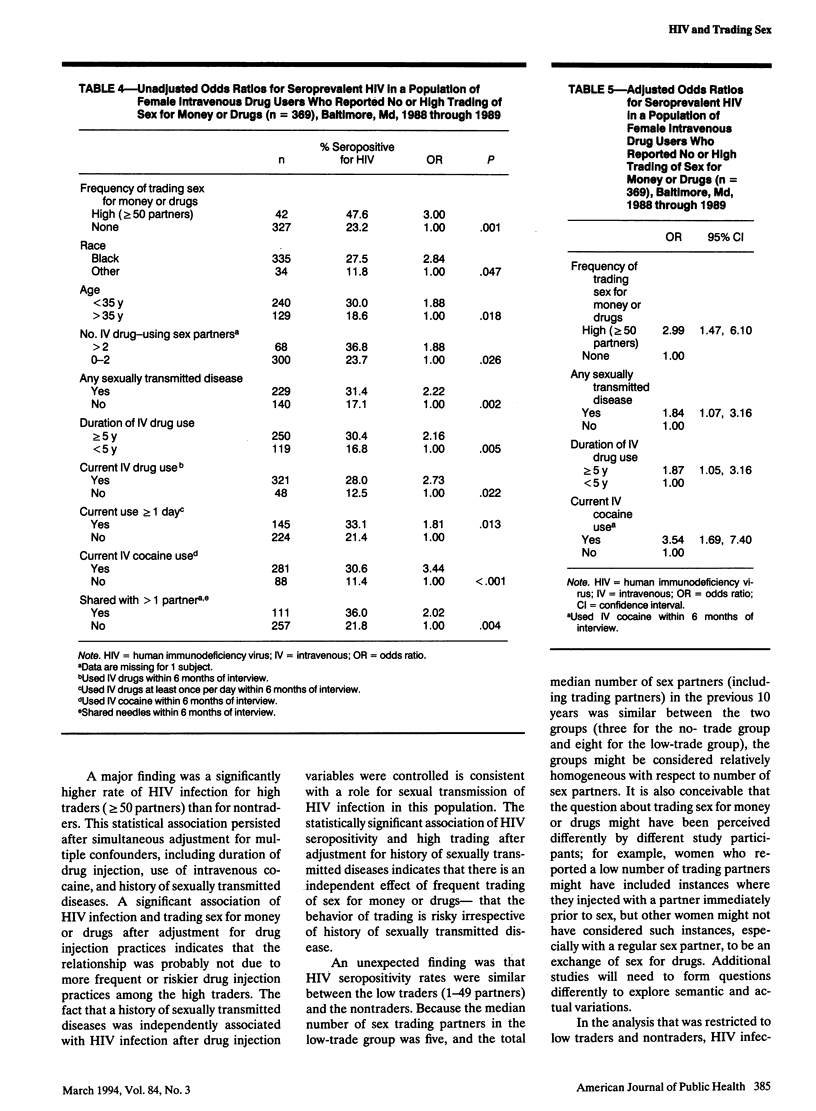
OBJECTIVES. Data from 538 women in a cohort study recruited in 1988-1989 were analyzed to determined whether trading sex for drugs or money was independently associated with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) seroprevalence in a population of female intravenous drug users. METHODS. The women were grouped according to the number of partners with whom they reported trading sex for drugs or money during the previous 10 years: none, 1 through 49 (low), or 50 or more (high); the prevalence of HIV seropositivity in the three groups was 23.2%, 23.7%, and 47.6%, respectively. Logistic regression was used to compare the low- and high-trade groups separately with the group that reported no trading. RESULTS. Low trading was not associated with seroprevalent HIV infection. In a multivariate model, high trading (compared with no trading) was significantly associated with HIV seropositivity after adjustment for cocaine use, history of sexually transmitted diseases, and duration of intravenous drug use. CONCLUSIONS. These data indicate that, among intravenous drug-using women, high levels of trading sex for drugs or money were independently associated with HIV infection. This group needs to be targeted for further intensive intervention.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony J. C., Vlahov D., Nelson K. E., Cohn S., Astemborski J., Solomon L. New evidence on intravenous cocaine use and the risk of infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Am J Epidemiol. 1991 Nov 15;134(10):1175–1189. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battjes R. J., Pickens R. W., Amsel Z., Brown L. S., Jr Heterosexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus among intravenous drug users. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1007–1011. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth R., Koester S., Brewster J. T., Weibel W. W., Fritz R. B. Intravenous drug users and AIDS: risk behaviors. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 1991 Sep;17(3):337–353. doi: 10.3109/00952999109027557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaisson R. E., Bacchetti P., Osmond D., Brodie B., Sande M. A., Moss A. R. Cocaine use and HIV infection in intravenous drug users in San Francisco. JAMA. 1989 Jan 27;261(4):561–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaisson R. E., Moss A. R., Onishi R., Osmond D., Carlson J. R. Human immunodeficiency virus infection in heterosexual intravenous drug users in San Francisco. Am J Public Health. 1987 Feb;77(2):169–172. doi: 10.2105/ajph.77.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiasson M. A., Stoneburner R. L., Hildebrandt D. S., Ewing W. E., Telzak E. E., Jaffe H. W. Heterosexual transmission of HIV-1 associated with the use of smokable freebase cocaine (crack). AIDS. 1991 Sep;5(9):1121–1126. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199109000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin K., DeHovitz J. A., Dillon S., McCormack W. M. HIV infection, genital ulcer disease, and crack cocaine use among patients attending a clinic for sexually transmitted diseases. Am J Public Health. 1991 Dec;81(12):1576–1579. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.12.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franceschi S., Tirelli U., Vaccher E., Serraino D., Crovatto M., De Paoli P., Diodato S., La Vecchia C., Decarli A., Monfardini S. Risk factors for HIV infection in drug addicts from the northeast of Italy. Int J Epidemiol. 1988 Mar;17(1):162–167. doi: 10.1093/ije/17.1.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland G. H., Klein R. S. Transmission of the human immunodeficiency virus. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 29;317(18):1125–1135. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710293171806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. K., Watters J. K. Sexual risk behavior among heterosexual intravenous drug users: ethnic and gender variations. AIDS. 1991 Jan;5(1):77–83. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199101000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmor M., Des Jarlais D. C., Cohen H., Friedman S. R., Beatrice S. T., Dubin N., el-Sadr W., Mildvan D., Yancovitz S., Mathur U. Risk factors for infection with human immunodeficiency virus among intravenous drug abusers in New York City. AIDS. 1987 May;1(1):39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. E., Vlahov D., Cohn S., Odunmbaku M., Lindsay A., Antohony J. C., Hook E. W., 3rd Sexually transmitted diseases in a population of intravenous drug users: association with seropositivity to the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). J Infect Dis. 1991 Sep;164(3):457–463. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.3.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolosi A., Leite M. L., Musicco M., Molinari S., Lazzarin A. Parenteral and sexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus in intravenous drug users: a study of seroconversion. The Northern Italian Seronegative Drug Addicts (NISDA) Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1992 Feb 1;135(3):225–233. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmaso S., Conti S., Sasse H. Drug use and HIV-1 infection: report from the Second Italian Multicenter Study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(6):607–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels J. F., Vlahov D., Anthony J. C., Chaisson R. E. Measurement of HIV risk behaviors among intravenous drug users. Br J Addict. 1992 Mar;87(3):417–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1992.tb01942.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A. J., Calsyn D. A., Whittaker S., Freeman G., Jr Sexual behaviors of intravenous drug users in treatment. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(10):938–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenbaum E. E., Hartel D., Selwyn P. A., Klein R. S., Davenny K., Rogers M., Feiner C., Friedland G. Risk factors for human immunodeficiency virus infection in intravenous drug users. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 28;321(13):874–879. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909283211306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirelli U., Vaccher E., Carbone A., De Paoli P., Santini G., Monfardini S. Heterosexual contact is not the predominant mode of HTLV-III transmission among intravenous drug abusers. JAMA. 1986 May 2;255(17):2289–2289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahov D., Muñoz A., Anthony J. C., Cohn S., Celentano D. D., Nelson K. E. Association of drug injection patterns with antibody to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 among intravenous drug users in Baltimore, Maryland. Am J Epidemiol. 1990 Nov;132(5):847–856. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. L. A model of the sexual relations of young i.v. drug users. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(2):192–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Hoek J. A., Coutinho R. A., van Haastrecht H. J., van Zadelhoff A. W., Goudsmit J. Prevalence and risk factors of HIV infections among drug users and drug-using prostitutes in Amsterdam. AIDS. 1988 Feb;2(1):55–60. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198802000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Hoek J. A., van Haastrecht H. J., Scheeringa-Troost B., Goudsmit J., Coutinho R. A. HIV infection and STD in drug addicted prostitutes in Amsterdam: potential for heterosexual HIV transmission. Genitourin Med. 1989 Jun;65(3):146–150. doi: 10.1136/sti.65.3.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


