Abstract
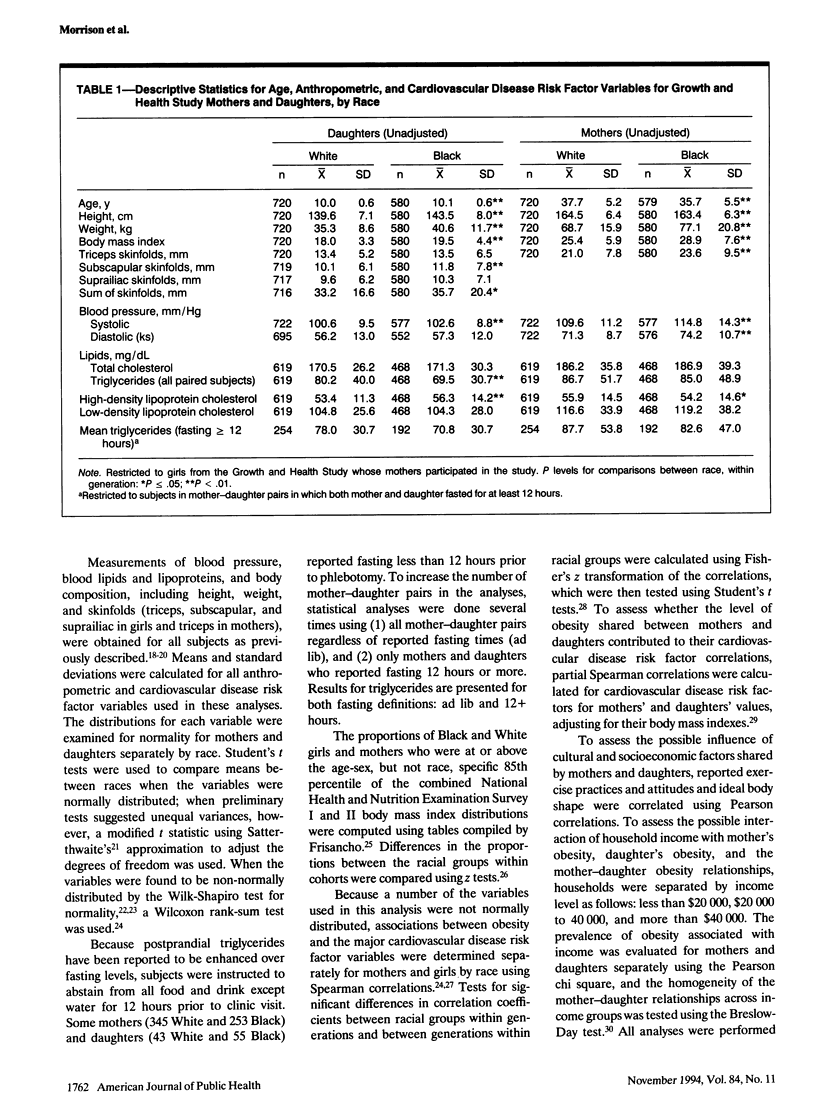
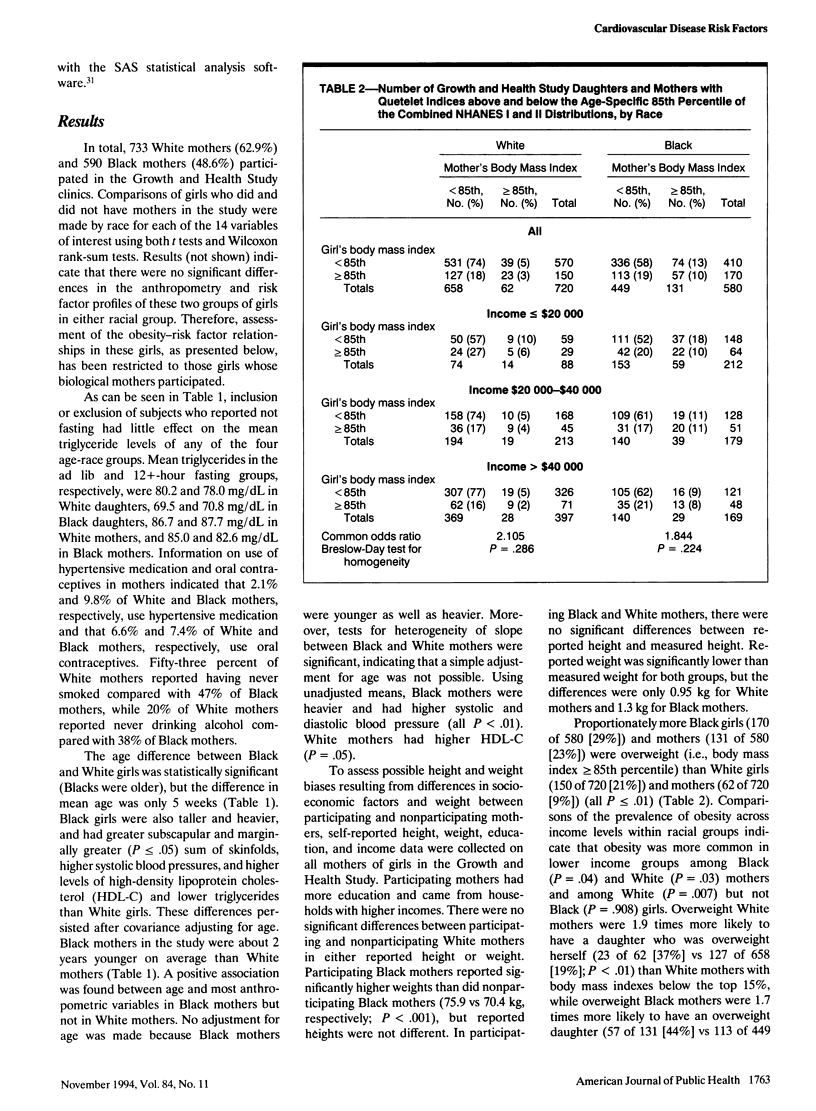
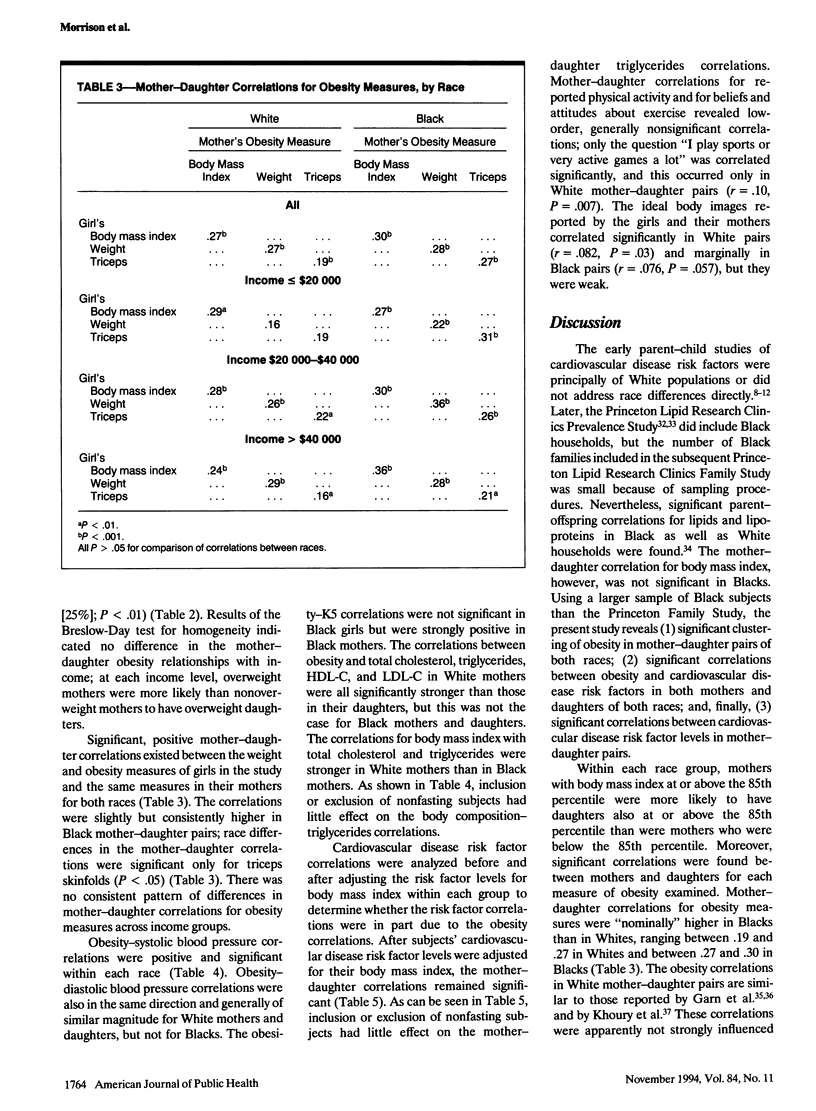
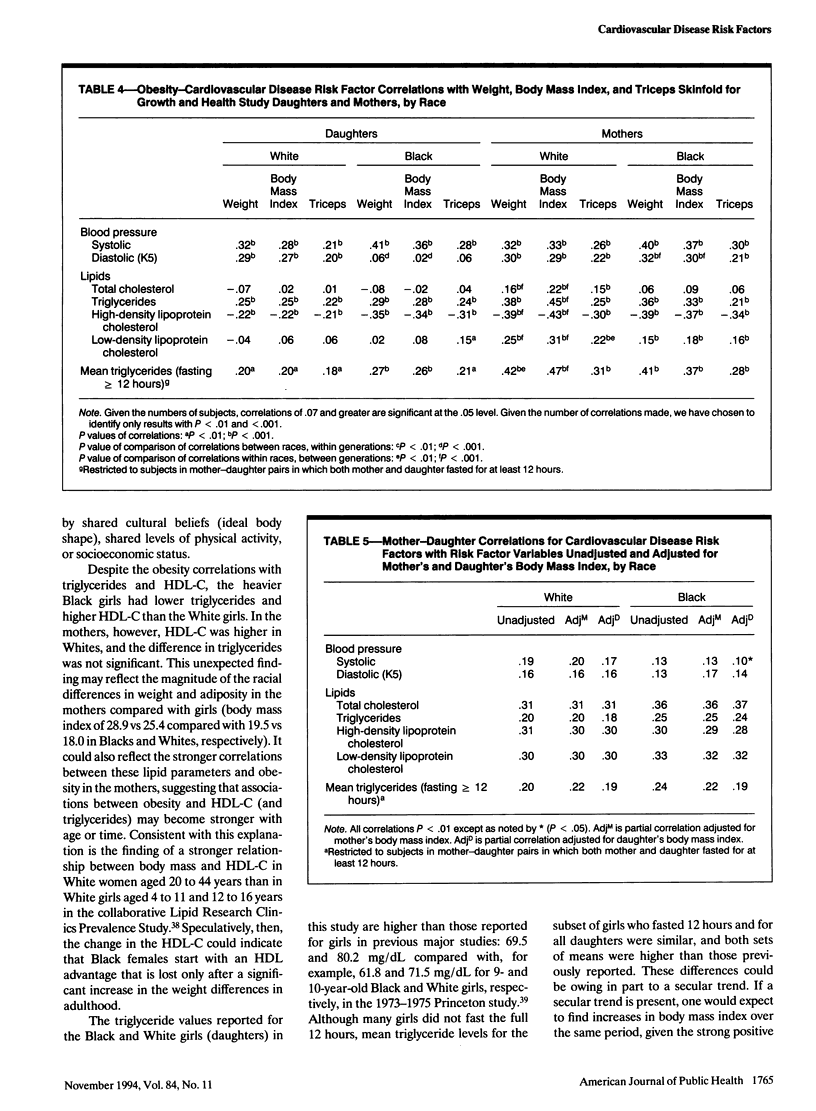
OBJECTIVES. This study sought to evaluate obesity as a potential explanatory factor for the increased relative risk for cardiovascular disease in Black compared with White women. METHODS. Familial associations for obesity and cardiovascular disease risk factors were assessed in 720 White and 580 Black mother-daughter pairs from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute's Growth and Health Study by using Pearson's chi square, Spearman's correlations, and partial correlations. RESULTS. Black girls and mothers were significantly heavier and had higher body mass indices than their White counterparts. In each racial group, significant, positive mother-daughter correlations existed for weight, body mass index, and triceps skinfolds, and for all cardiovascular disease risk factors. Obesity measures correlated positively with systolic blood pressure and triglycerides and inversely with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in girls and mothers of both races. Correlations between mothers and daughters for exercise and ideal body shape were weak and did not explain obesity associations. CONCLUSIONS. Intrafamilial associations of obesity, cardiovascular disease risk factors, and the obesity-cardiovascular disease risk factor relationship support the position that increased cardiovascular disease morbidity and mortality rates in Black women may be linked to excess obesity in Black women compared with White ones.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chase H. P., O'Quin R. J., O'Brien D. Screening for hyperlipidemia in childhood. JAMA. 1974 Dec 16;230(11):1535–1537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong D. M., DeLong E. R., Wood P. D., Lippel K., Rifkind B. M. A comparison of methods for the estimation of plasma low- and very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. The Lipid Research Clinics Prevalence Study. JAMA. 1986 Nov 7;256(17):2372–2377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher S., Epstein F. H., Kjelsberg M. O. Familial aggregation of factors associated with coronary heart disease. Circulation. 1966 Jun;33(6):911–924. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.33.6.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folsom A. R., Burke G. L., Byers C. L., Hutchinson R. G., Heiss G., Flack J. M., Jacobs D. R., Jr, Caan B. Implications of obesity for cardiovascular disease in blacks: the CARDIA and ARIC studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991 Jun;53(6 Suppl):1604S–1611S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/53.6.1604S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garn S. M., Bailey S. M., Solomon M. A., Hopkins P. J. Effect of remaining family members on fatness prediction. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Feb;34(2):148–153. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.2.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison R. J., Castelli W. P., Feinleib M., Kannel W. B., Havlik R. J., Padgett S. J., McNamara P. M. The association of total cholesterol, triglycerides and plasma lipoprotein cholesterol levels in first degree relatives and spouse pairs. Am J Epidemiol. 1979 Sep;110(3):313–321. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glueck C. J., Fallat R. W., Tsang R., Buncher C. R. Hyperlipemia in progeny of parents with myocardial infarction before age 50. Am J Dis Child. 1974 Jan;127(1):70–75. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110200072010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes C. G., Tyroler H. A., Cassel J. C. Family aggregation of blood pressure in Evans County, Georgia. Arch Intern Med. 1971 Dec;128(6):965–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennekens C. H., Jesse M. J., Klein B. E., Gourley J. E., Blumenthal S. Cholesterol among children of men with myocardial infarction. Pediatrics. 1976 Aug;58(2):211–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON B. C., EPSTEIN F. H., KJELSBERG M. O. DISTRIBUTIONS AND FAMILIAL STUDIES OF BLOOD PRESSURE AND SERUM CHOLESTEROL LEVELS IN A TOTAL COMMUNITY--TECUMSEH, MICHIGAN. J Chronic Dis. 1965 Feb;18:147–160. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(65)90098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannel W. B., Feinleib M., McNamara P. M., Garrison R. J., Castelli W. P. An investigation of coronary heart disease in families. The Framingham offspring study. Am J Epidemiol. 1979 Sep;110(3):281–290. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury P., Morrison J. A., Laskarzewski P. M., Glueck C. J. Parent-offspring and sibling body mass index associations during and after sharing of common household environments: the Princeton School District Family Study. Metabolism. 1983 Jan;32(1):82–89. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(83)90161-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. H., Borhani N. O., Kuller L. H. Validation of reported myocardial infarction mortality in blacks and whites. A report from the Community Cardiovascular Surveillance Program. Ann Epidemiol. 1990 Oct;1(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/1047-2797(90)90014-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. A., Barton B., Biro F. M., Sprecher D. L., Falkner F., Obarzanek E. Sexual maturation and obesity in 9- and 10-year-old black and white girls: the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Growth and Health Study. J Pediatr. 1994 Jun;124(6):889–895. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. A., Kelly K., Horvitz R., Khoury P., Laskarzewski P. M., Mellies M. J., Glueck C. J. Parent-offspring and sibling lipid and lipoprotein associations during and after sharing of household environments: the Princeton school district family study. Metabolism. 1982 Feb;31(2):158–166. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90129-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. A., Khoury P., Mellies M., Kelly K., Horvitz R., Glueck C. J. Lipid and lipoprotein distributions in black adults. The Cincinnati Lipid Research Clinic's Princeton School Study. JAMA. 1981 Mar 6;245(9):939–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. A., Laskarzewski P. M., Khoury P., Samuels S. J., Kelly K. K., Mellies M. J., Glueck C. J. Intrafamilial associations of cholesterol and triglyceride among related and unrelated household members. Clin Genet. 1980 Nov;18(5):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1980.tb02292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. A., deGroot I., Edwards B. K., Kelly K. A., Rauh J. L., Mellies M., Glueck C. J. Plasma cholesterol and triglyceride levels in 6,775 school children, ages 6--17. Metabolism. 1977 Nov;26(11):1199–1211. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(77)90112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEFER L. E., DRACHMAN S. R., STEINBERG A. G., ADLERSBERG D. Genetic studies on hypercholesteremia: frequency in a hospital population and in families of hypercholesteremic index patients. Am Heart J. 1953 Jul;46(1):99–116. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(53)90243-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamir I., Bojanower Y., Levtow O., Heldenberg D., Dickerman Z., Werbin B. Serum lipids and lipoproteins in children from families with early coronary heart disease. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Oct;47(255):808–810. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.255.808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Itallie T. B. Health implications of overweight and obesity in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Dec;103(6 ):983–988. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-6-983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber L. S., Srinivasan S. R., Wattigney W. A., Berenson G. S. Tracking of serum lipids and lipoproteins from childhood to adulthood. The Bogalusa Heart Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1991 May 1;133(9):884–899. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deGroot I., Morrison J. A., Kelly K. A., Rauh J. L., Mellies M. J., Edwards B. K., Glueck C. J. Lipids in schoolchildren 6 to 17 years of age: upper normal limits. Pediatrics. 1977 Oct;60(4):437–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


