Abstract
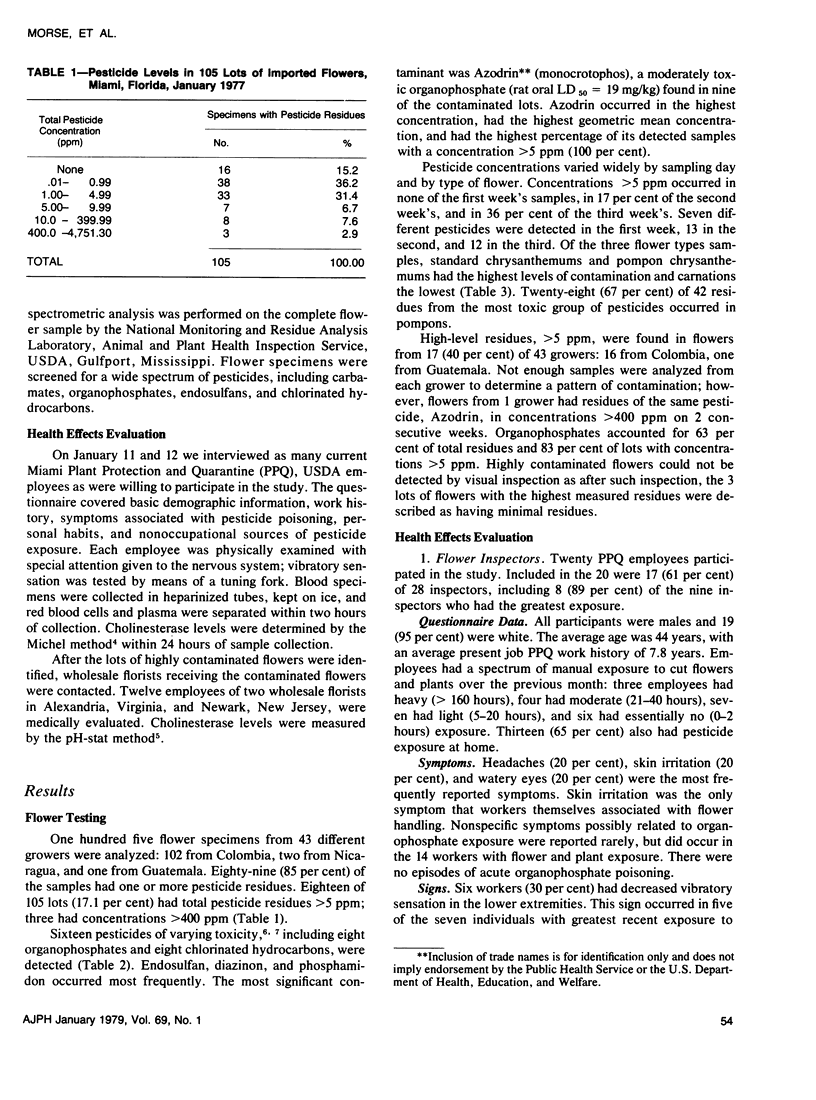
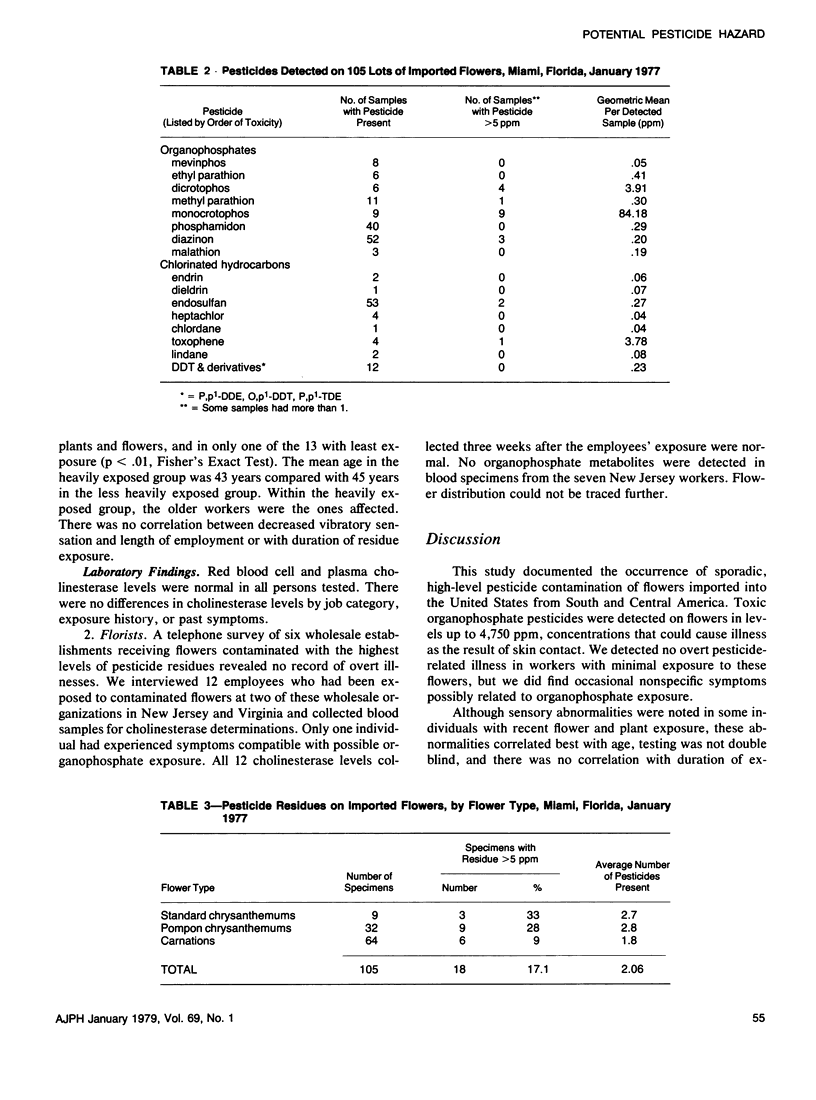
Following reports of ten cases of possible organophosphate pesticide poisoning in florists exposed to pesticide residues on cut flowers, we conducted a prospective random-sample survey to determine residual pesticide levels on flowers imported into the United States via Miami, Florida. A sample of all flowers imported into Miami on three days in January 1977 showed that 18 (17.7 per cent) of 105 lots contained pesticide residue levels greater than 5 ppm, and that three lots had levels greater than 400 ppm. Azodrin (monocrotophos) was the most important contaminant with levels of 7.7--4,750 ppm detected in nine lots. We examined 20 quarantine workers in Miami and 12 commercial florists exposed to contaminated flowers. Occasional nonspecific symptoms compatible with possible organophosphate exposure were noted, but we found no abnormalities in plasma or red blood cell cholinesterase levels. This study documents a previously unrecognized potential source of occupational pesticide exposure and suggests that safety standards should be set for residue levels on cut flowers.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cavanagh J. B. Peripheral neuropathy caused by chemical agents. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol. 1973 Nov;2(3):365–417. doi: 10.3109/10408447309082021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaines T. B. Acute toxicity of pesticides. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1969 May;14(3):515–534. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(69)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabb D. P., Whitfield F. Determination of cholinesterase by an automated pH stat method. Arch Environ Health. 1967 Aug;15(2):147–154. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1967.10664895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


