Abstract
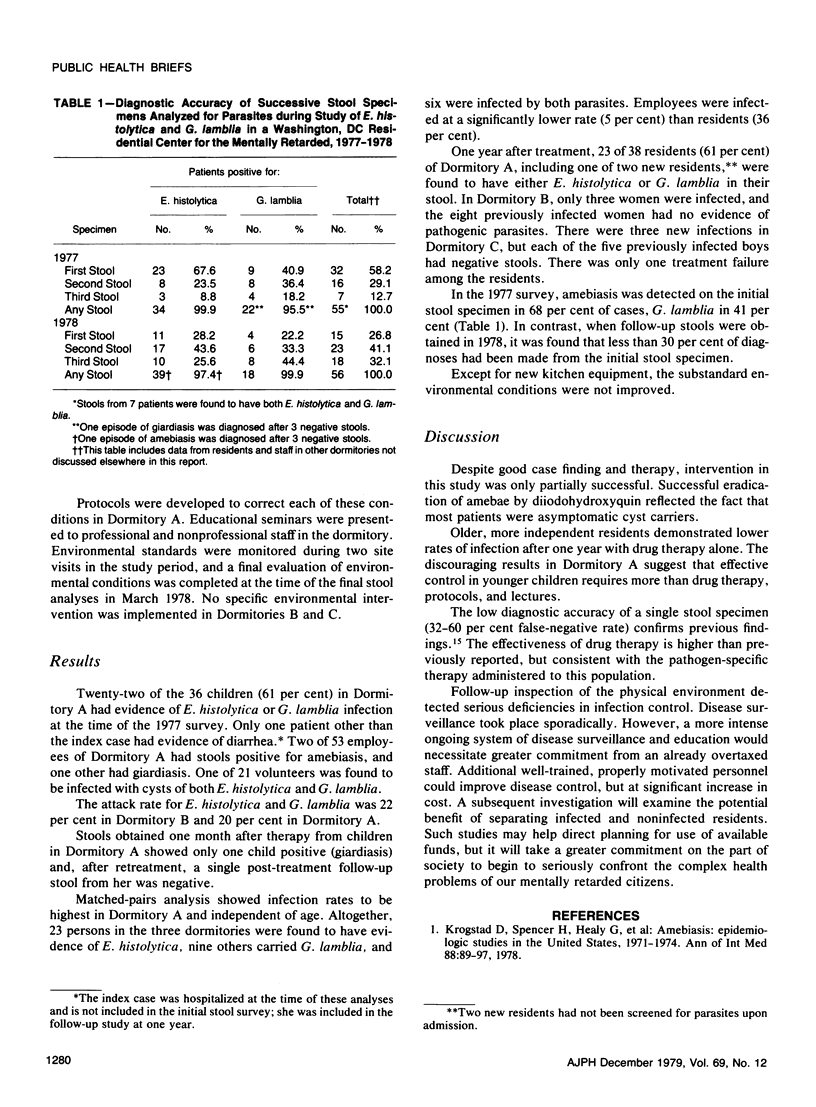
Asymptomatic infection with either Entameba histolytica or Giardia lamblia was found in 61 per cent of the residents of a dormitory in an institution for the mentally retarded; two other dormitories had rates of 20 per cent and 22 per cent. Drug therapy was successfully undertaken in all three dormitories, and environmental improvements were introduced in the heavily infected dormitory. A one-year follow-up showed a reduction in parasitic disease in two dormitories but, in the most heavily infected dormitory, infection had returned to pretreatment levels.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLAGG W., SCHLOEGEL E. L., MANSOUR N. S., KHALAF G. I. A new concentration technic for the demonstration of protozoa and helminth eggs in feces. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1955 Jan;4(1):23–28. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1955.4.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROOKE M. M. EPIDEMIOLOGY AND CONTROL OF AMEBIASIS IN INSTITUTIONS FOR THE MENTALLY RETARDED. Am J Ment Defic. 1963 Sep;68:187–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROOKE M. M. EPIDEMIOLOGY OF AMEBIASIS. Am J Gastroenterol. 1964 Apr;41:371–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROOKE M. M., WILCOX D. E., KAISER R. L., MELVIN D. M. Investigation of factors associated with the decline of intestinal protozoa in a Kansas mental institution. Am J Hyg. 1962 Jul;76:52–60. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS R. B. Prevalence of amebiasis in the United States and Canada. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1961 Mar;10:172–184. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1961.10.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evins M. B. Public health nursing in California State Hospitals for the mentally retarded. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1968 May;58(5):949–956. doi: 10.2105/ajph.58.5.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GHOLZ L. M. Long term prophylactic control of amebiasis and shigellosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1962 Jul;11:452–454. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1962.11.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy G. R. Laboratory diagnosis of amebiasis. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1971 May;47(5):478–493. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEFFERY G. M. A three-year epidemiologic study of intestinal parasites in a selected group of mental patients. Am J Hyg. 1960 Jan;71:1–8. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Spencer H. C., Jr, Healy G. R., Gleason N. N., Sexton D. J., Herron C. A. Amebiasis: epidemiologic studies in the United States, 1971-1974. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jan;88(1):89–97. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWLESS D. K. A rapid permanent-mount stain technic for the diagnosis of the intestinal protozoa; a preliminary report. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1953 Nov;2(6):1137–1138. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1953.2.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAPERO J. J., LAWLESS D. K. The MIF stain-preservation technic for the identification of intestinal protozoa. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1953 Jul;2(4):613–619. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1953.2.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandars D. F., Bianchi G. N. Amoebiasis in Australia. 2. An epidemic in an institution for mental defectives and observations on the therapeutic effectiveness of "intestopan" and "humatin". Med J Aust. 1970 Feb 7;1(6):261–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoeli M., Most H., Hammond J., Scheinesson G. P. Parasitic infections in a closed community. Results of a 10-year survey in Willowbrook State School. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1972;66(5):764–776. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(72)90091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


