Abstract
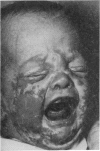
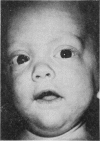
A 2-month-old preterm boy who developed symptomatic zinc deficiency while being exclusively breast fed is described. Oral zinc supplements induced a complete remission but mucosal 65Zn uptake studies and metabolic balances conducted before and after withdrawal of the supplements excluded the diagnosis of acrodermatitis enteropathica. By age 12 months the boy was well and no longer required zinc supplements. Other possible causes of this patient's symptomatic zinc deficiency are discussed and these should be considered in the immediate and long-term management of preterm infants.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggett P. J., Harries J. T. Current status of zinc in health and disease states. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Dec;54(12):909–917. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.12.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton D. J., Muller D. P., Aggett P. J., Harries J. T. A defect in zinc uptake by jejunal biopsies in acrodermatitis enteropathica. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 May;56(5):505–507. doi: 10.1042/cs0560505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox T. M., Peters T. J. Uptake of iron by duodenal biopsy specimens from patients with iron-deficiency anaemia and primary haemochromatosis. Lancet. 1978 Jan 21;1(8056):123–124. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauncey M. J., Shaw J. C., Urman J. The absorption and retention of magnesium, zinc, and copper by low birth weight infants fed pasteurized human breast milk. Pediatr Res. 1977 Oct;11(10 Pt 1):1033–1039. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197710000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkin R. I., Schulman J. D., Schulman C. B., Bronzert D. A. Changes in total, nondiffusible, and diffusible plasma zinc and copper during infancy. J Pediatr. 1973 May;82(5):831–837. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meret S., Henkin R. I. Simultaneous direct estimation by atomic absorption spectrophotometry of copper and zinc in serum, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chem. 1971 May;17(5):369–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siimes M. A., Vuori E., Kuitunen P. Breast milk iron--a declining concentration during the course of lactation. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Jan;68(1):29–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb04425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivasubramanian K. N., Henkin R. I. Behavioral and dermatologic changes and low serum zinc and copper concentrations in two premature infants after parenteral alimentation. J Pediatr. 1978 Nov;93(5):847–851. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuori E. A longitudinal study of manganese in human milk. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Jul;68(4):571–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb05057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson E. M. Trace elements in foetal and early postnatal development. Proc Nutr Soc. 1974 Dec;33(3):275–284. doi: 10.1079/pns19740050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]