Abstract
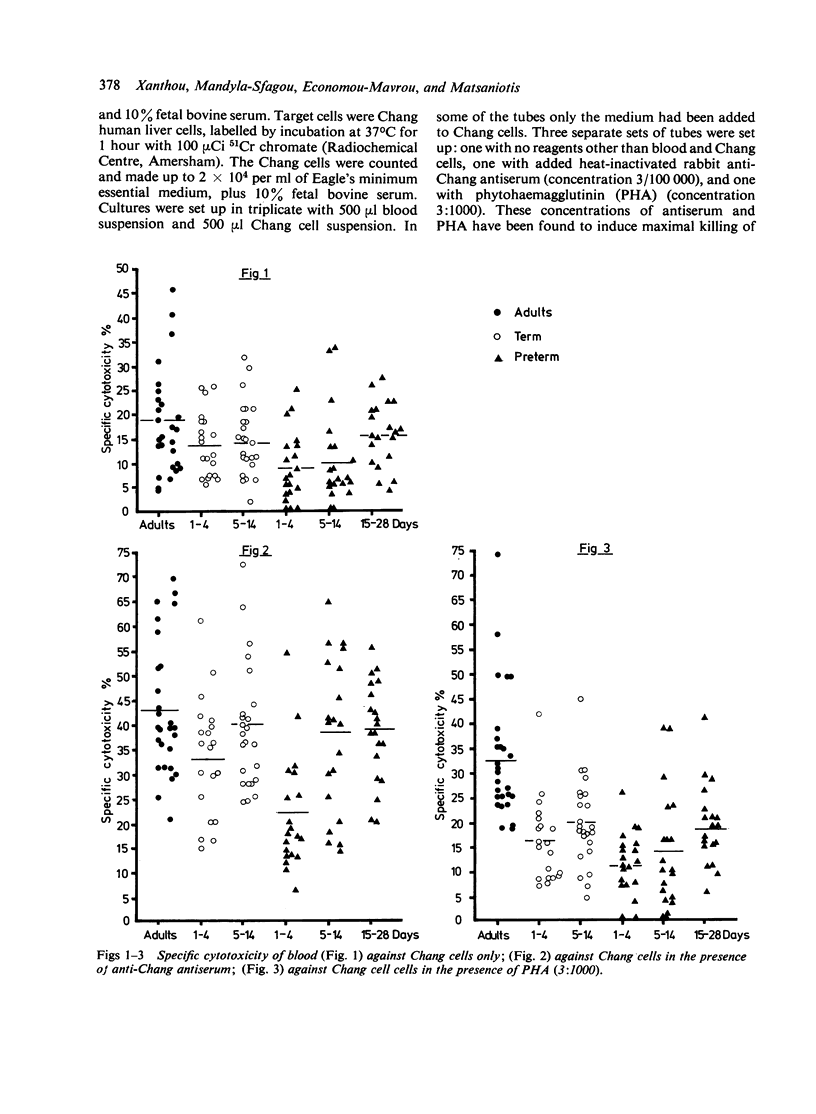
Antibody-dependent, phytohaemagglutinin-induced, and spontaneous cytotoxicity was studied in 44 term and 60 preterm newborn babies, all of whom were healthy and of normal weight for gestational age. Twenty-seven adults were used as controls. Antibody-dependent cytotoxicity was low in term babies particularly in the preterm ones during the first 4 days of life, but soon rose to adult levels. Phytohaemagglutinin-induced cytotoxicity was low both in term and preterm babies compared with adult levels, and remained lower throughout the neonatal period although it began to rise. Spontaneous cytotoxicity was lower in preterm babies than in term ones during the first 2 weeks of life, and lower too than in adults. These findings indicate decreased cytotoxic ability of neonatal leucocytes especially during the first 4 days of postnatal life particularly in preterm babies, suggesting either lack of effector cells or that the cells are functionally immature.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adinolfi M. Levels of wo components of complement (C'4 and C'3) in human fetal and newborn sera. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1970 Jun;12(3):306–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld P., Johansson A. Contact areas of cytotoxic lymphocytes and target cells. An electron microscopic study. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Aug;94(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90533-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. C., Waller C., Wood J., Aynsley-Green A., Yu V. Lymphocyte subpopulations in the blood of newborn infants. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Dec;18(4):469–482. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. C., Lieber E., Fudenberg H. H. In vitro cytolysis by human fetal lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1970 Oct;1(4):455–458. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattwyler R. J., Tomasi T. B. Inhibition of sensitization of T-cells by alpha-fetoprotein. Int J Cancer. 1975 Dec 15;16(6):942–945. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dossett J. H. Microbial defenses of the child and man. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1972 May;19(2):355–372. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)32705-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A. H., Hudson L., Shen L., Roitt I. M. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity due to a "null" lymphoid cell. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 28;242(117):111–113. doi: 10.1038/newbio242111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLM G., PERLMANN P., WERNER B. PHYTOHAEMAGGLUTININ-INDUCED CYTOTOXIC ACTION OF NORMAL LYMPHOID CELLS ON CELLS IN TISSUE CULTURE. Nature. 1964 Aug 22;203:841–843. doi: 10.1038/203841a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg A., Hallberg T. Evolution of three lymphocyte markers in newborn, preterm infants. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1977;55(1-6):102–111. doi: 10.1159/000231916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg T., Hallberg A. Lymphocyte markers in newborn infants. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1976 Dec;84C(6):477–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S. T cell mediated cytolysis: consideration of the role of a soluble mediator. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1975 Apr;17(4):231–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay H. D., Bonnard G. D., West W. H., Herberman R. B. A functional comparison of human Fc-receptor-bearing lymphocytes active in natural cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2058–2066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Shaban S. S., Starr S. E., Wood P. A., Nahmias A. J. Human neonatal and maternal monocyte-macrophage and lymphocyte-mediated antibody-dependent cytotoxicity to cells infected with herpes simplex. J Pediatr. 1978 Aug;93(2):206–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80497-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovchik J. C., Hong R. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytolysis (ADCC): analyses and projections. Prog Allergy. 1977;22:1–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Bonnard G. D., Sordat B., Zawodnik S. A. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity: heterogeneity of effector cells in human peripheral blood. Scand J Immunol. 1975 Sep;4(5-6):487–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02654.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan I. C. Antibody in the induction and inhibition of lymphocyte cytotoxicity. Transplant Rev. 1972;13:67–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz E. Multiple target cell killing by the cytolytic T lymphocyte and the mechanism of cytotoxicity. Transplantation. 1976 Jan;21(1):5–11. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197601000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnachie P. R., Rachelefsky G., Stiehm E. R., Terasaki P. I. Antibody-dependent lymphocyte killer function and age. Pediatrics. 1973 Dec;52(6):795–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H., Wigzell H. Lymphocyte mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Induction and inhibition by humoral antibody and nature of effector cells. Transplant Rev. 1972;13:91–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Milgrom H., Wood P. A., Nahmias A. J. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to target cells infected with herpes simplex viruses: functional adequacy in the neonate. Pediatrics. 1977 Jan;59(1):22–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller C. A., Campbell A. C., MacLennan I. C. Two populations of lymphocytes involved in phytohaemagglutinin-induced cytotoxicity of a dividing target cell. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(8):931–939. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisloff F., Froland S. S., Michaelsen T. E. Characterization of subpopulations of human lymphoid cells participating in phytohemagglutinin and concanavalin A-induced cytotoxicity. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1974;47(4):488–497. doi: 10.1159/000231243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthou M., Agathopoulos A., Sakellariou A., Economou-Mavrou C., Tsingoglou S., Matsaniotis N. Serum levels of lysozyme in term and preterm newborns. Arch Dis Child. 1975 Apr;50(4):304–307. doi: 10.1136/adc.50.4.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthou M. Leucocyte blood picture in healthy full-term and premature babies during neonatal period. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Apr;45(240):242–249. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.240.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


