Abstract
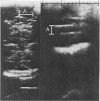
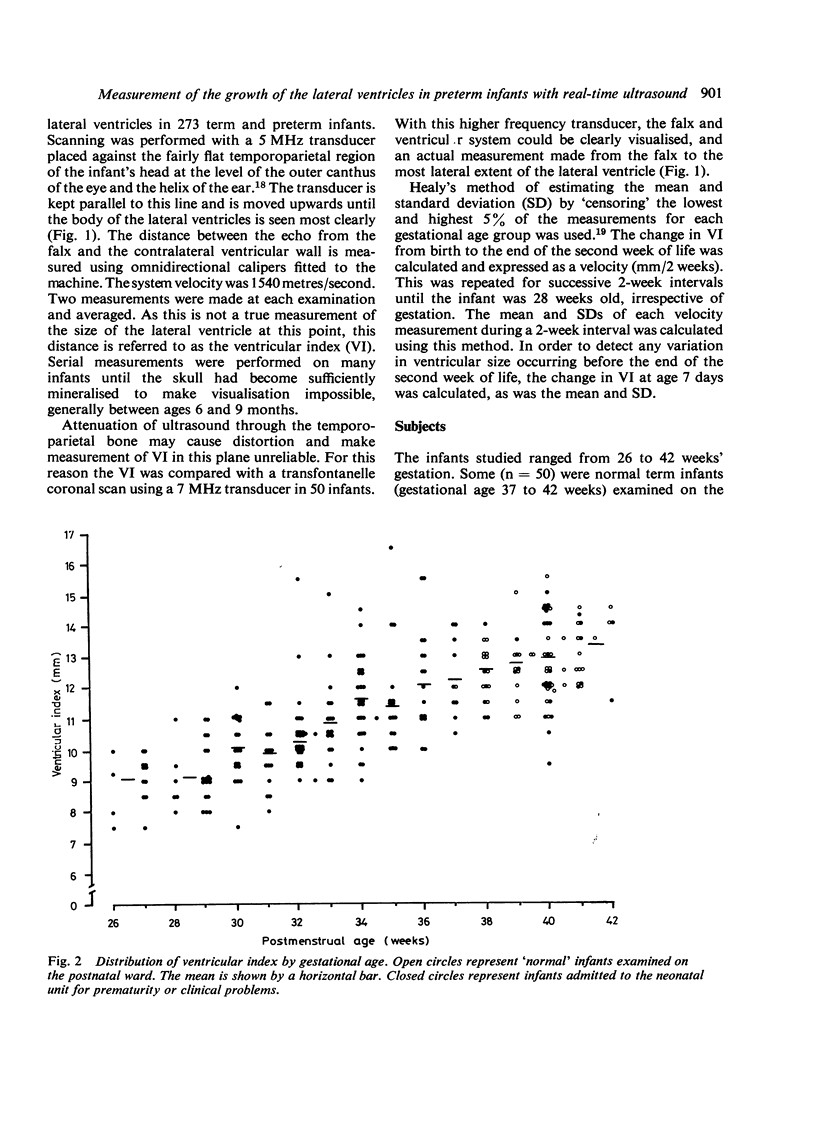
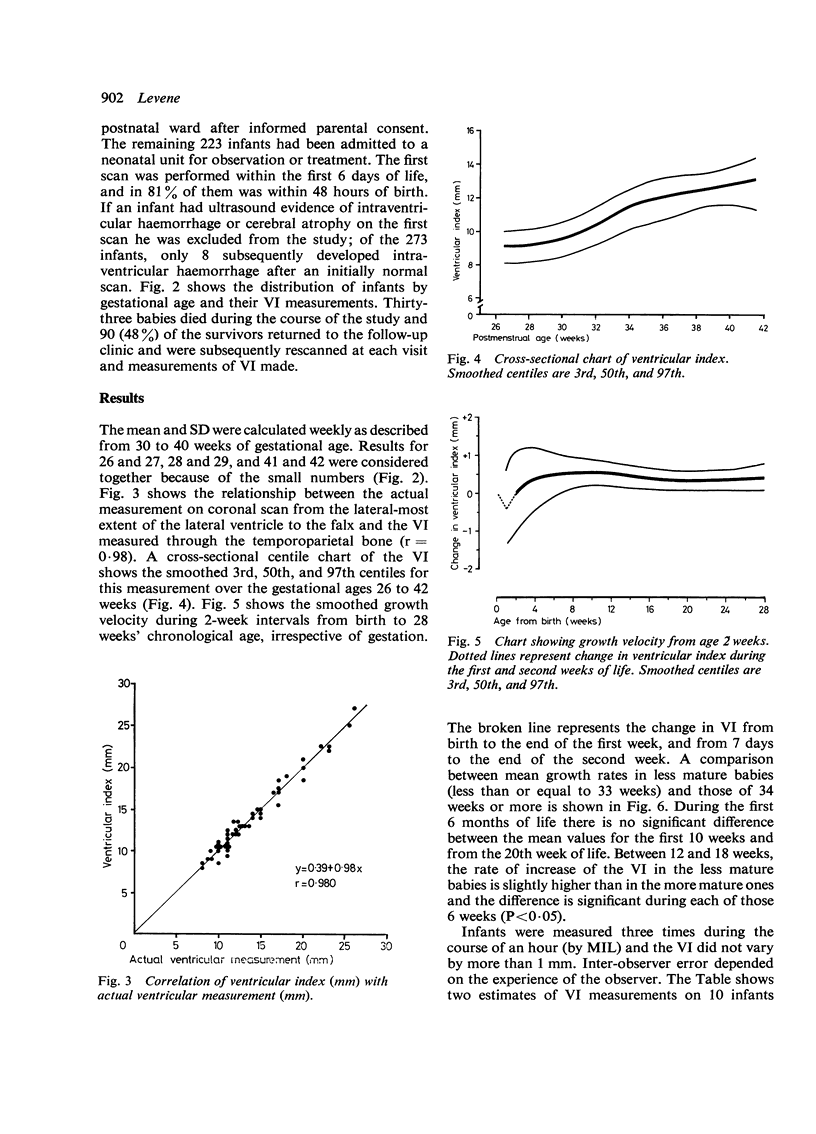
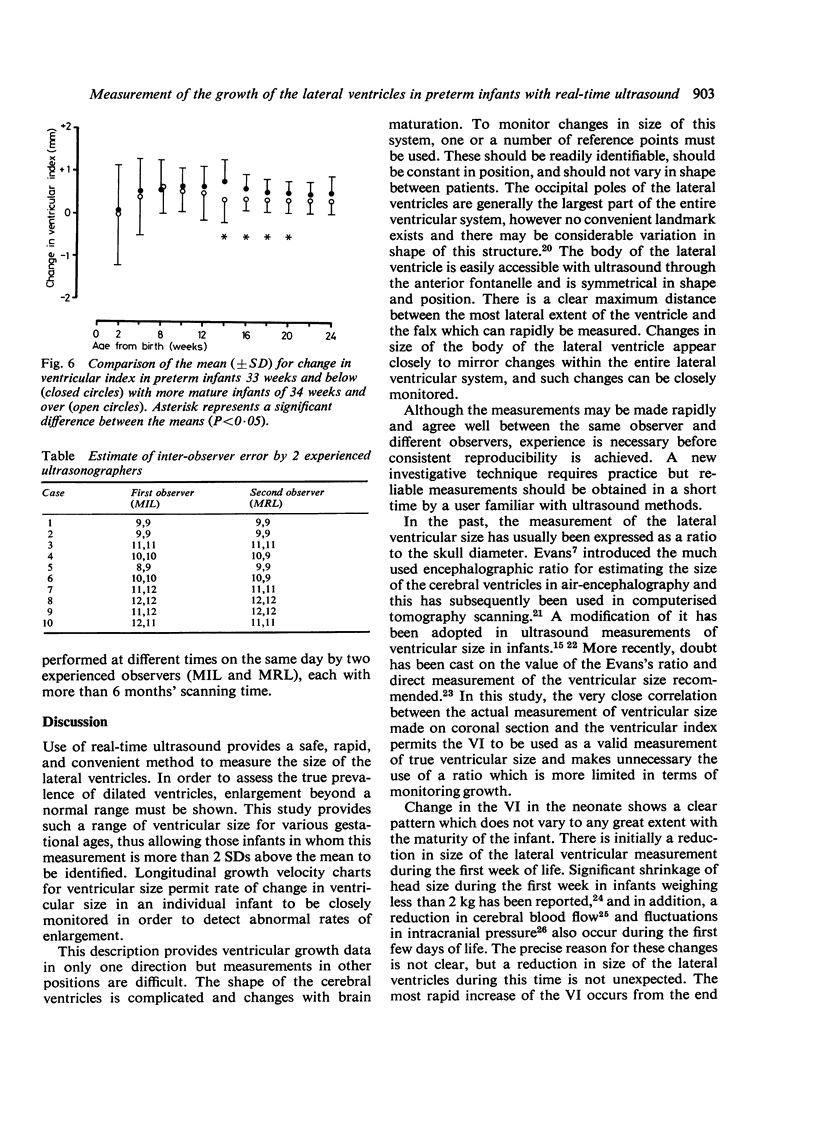
Real-time ultrasound was used to make exact measurements from the lateral wall of the body of the lateral ventricle to the falx (the ventricular index) in 273 infants of varying gestational ages. The measurement performed in an axial plane through the temporoparietal bone correlated closely with an actual measurement made in coronal plane in 50 infants. A cross-sectional centile chart was drawn up of the normal range for this measurement from 27 to 42 weeks' postmenstrual age. A further chart showing the rate of change of the ventricular index allowed growth of the ventricles to be assessed in a longitudinal manner. Use of these charts permits early detection of hydrocephalus or dilated ventricles secondary to cerebral atrophy.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Denkhaus H., Winsberg F. Ultrasonic measurement of the fetal ventricular system. Radiology. 1979 Jun;131(3):781–787. doi: 10.1148/131.3.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dill R. Echoencephalographische Normalwerte des kindlichen Ventrikelsystems in den verschiedenen Altersgruppen. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1971 Sep;119(9):496–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donn S. M., Philip A. G. Early increase in intracranial pressure in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 1978 Jun;61(6):904–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuyama Y., Miyao M., Ishizu T., Maruyama H. Developmental changes in normal cranial measurements by computed tomography. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1979 Aug;21(4):425–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1979.tb01645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumme T. Die Breite der 3. Hirnkammer vom Frühgeborenen bis ins 10. Dezennium. Eine eindimensional-echoencephalographische Studie an 1841 neurologisch unauffälligen Probanden. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr Grenzgeb. 1977 Apr;45(4):223–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumme T., Frömmel G., Meese W. Postnatale echoencephalographische Untersuchungen bei Frühgeborenen. Neuropadiatrie. 1971 Oct;3(2):155–170. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1091808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumme T., Meese W., Frömmel G. Echoencephalographische kontrolluntersuchungen an frühgeborenen während der ersten 18 lebensmonate. Neuropadiatrie. 1974 Aug;5(3):243–249. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1091706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyldensted C. Measurements of the normal ventricular system and hemispheric sulci of 100 adults with computed tomography. Neuroradiology. 1977 Dec 31;14(4):183–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00496982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn F. J., Rim K. Frontal ventricular dimensions on normal computed tomography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1976 Mar;126(3):593–596. doi: 10.2214/ajr.126.3.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson J., Levander B., Liliequist B. Size of the intracerebral ventricles as measured with computer tomography, encephalography and echoventriculography. Acta Radiol Suppl. 1975;346:98–106. doi: 10.1177/0284185175016s34611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. L., Mack L. A., Rumack C. M., Frost M., Rashbaum C. B-mode echoencephalography in the normal and high risk infant. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979 Sep;133(3):375–381. doi: 10.2214/ajr.133.3.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. L., Rumack C. M. Ultrasonic evaluation of the neonatal brain. Radiol Clin North Am. 1980 Apr;18(1):117–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAST R. J., TOMPSETT D. H. Casts of the cerebral ventricles. Br J Surg. 1953 May;40(164):525–543. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004016403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene M. I., Wigglesworth J. S., Dubowitz V. Cerebral structure and intraventricular haemorrhage in the neonate: a real-time ultrasound study. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Jun;56(6):416–424. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.6.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombroso C. T., Erba G., Yogo T. Two-dimensional ultrasonography: a method to study normal and abnormal ventricles. Pediatrics. 1968 Jul;42(1):157–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidich T. P., Epstein F., Lin J. P., Kricheff I. I., Hochwald G. M. Evaluation of pediatric hydrocephalus by computed tomography. Radiology. 1976 May;119(2):337–345. doi: 10.1148/119.2.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oigaard A. Changes in ventricular size during pneumoencephalography. Neuroradiology. 1971 Nov;3(1):8–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00346110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape K. E., Blackwell R. J., Cusick G., Sherwood A., Houang M. T., Thorburn R. J., Reynolds E. O. Ultrasound detection of brain damage in preterm infants. Lancet. 1979 Jun 16;1(8129):1261–1264. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92227-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner M. S., Wodraska G., Adapon B. D. Newer ultrasound techniques in the evaluation of neurologic disorders. Radiol Clin North Am. 1974 Aug;12(2):283–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J., Hirsch N. J., Corbet A. J., Rudolph A. J. Postnatal head shrinkage in small infants. Pediatrics. 1977 Apr;59(4):619–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpert S. M. The ventricular size on computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1977 Apr;1(2):222–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz L. M. The Evans ratio for ventricular size: a calculation error. Neuroradiology. 1979 Aug 15;18(2):81–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00344827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]