Abstract
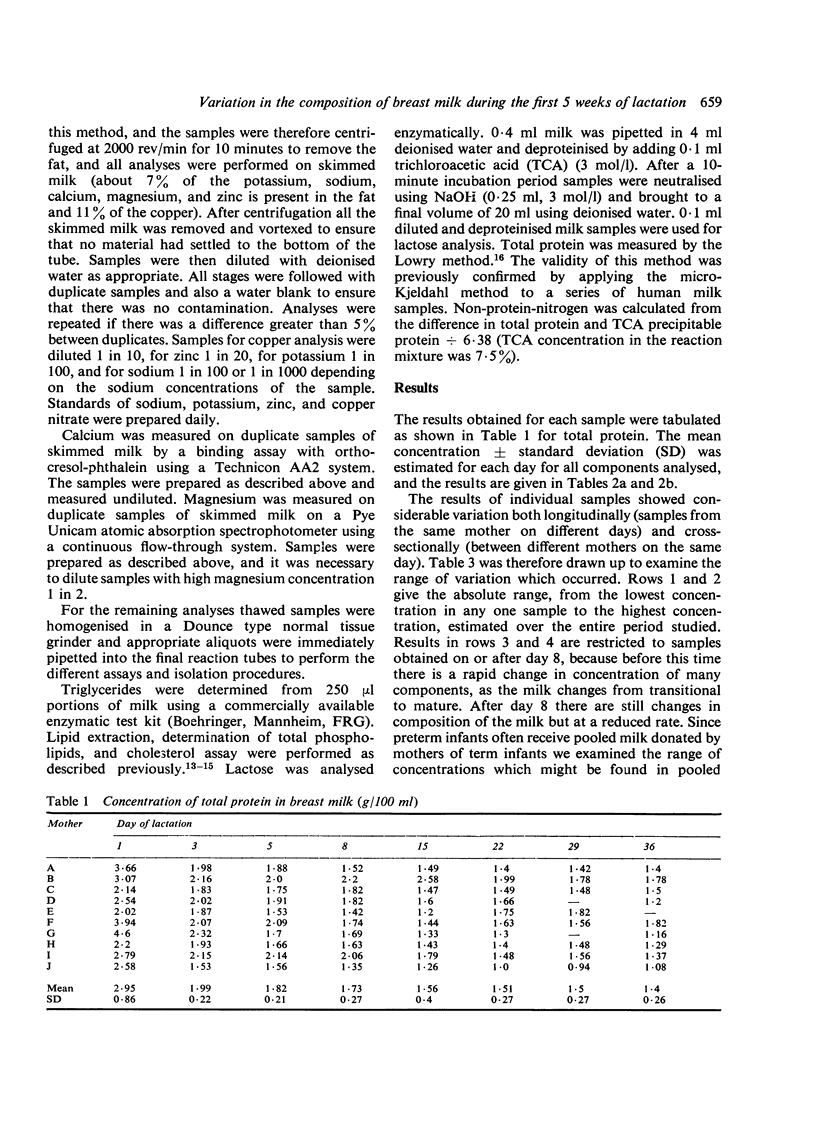
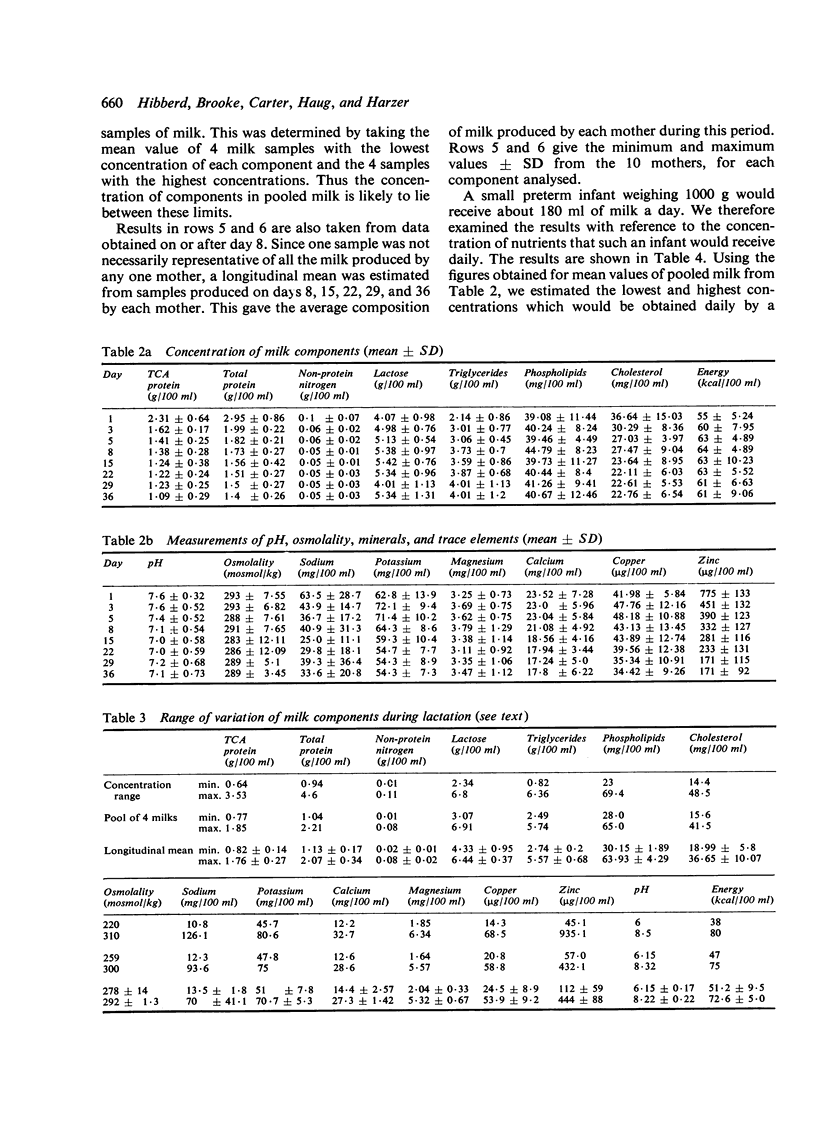
Milk samples were collected from 10 mothers by a standardised technique with complete expression of both breasts at each feed for 24 hours. Samples were obtained at 8 intervals during the first 36 days of lactation. Analyses were performed for trichloroacetic acid-precipitable protein, total protein, lactose, triglycerides, phospholipids, cholesterol, energy, sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, copper, pH, and osmolality. The results give a comprehensive picture of the development of milk composition from transitional to mature milk. The most striking feature of the results was the high degree of variation observed both between samples from the same mother and between samples from different mothers on the same day of lactation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlow B., Santulli T. V., Heird W. C., Pitt J., Blanc W. A., Schullinger J. N. An experimental study of acute neonatal enterocolitis--the importance of breast milk. J Pediatr Surg. 1974 Oct;9(5):587–595. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(74)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrie H., Martin E., Ansell C. Milk for babies. Lancet. 1975 Jun 14;1(7920):1330–1331. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92330-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. P. Adequacy of expressed breast milk for early growth of preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Apr;52(4):296–301. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.4.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. B., Walker B. E. Direct determination of zinc in whole blood, plasma and urine by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Dec;26(3):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman A. R., Finberg L. Breast milk for term and premature infants--optimal nutrition? Semin Perinatol. 1979 Oct;3(4):397–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomon S. J., Ziegler E. E., Vázquez H. D. Human milk and the small premature infant. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Apr;131(4):463–467. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1977.02120170089018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentner P. R., Bauer M., Dieterich I. Thin-layer chromatography of phospholipids. Separation of major phospholipid classes of milk without previous isolation from total lipid extracts. J Chromatogr. 1981 Feb 6;206(1):200–204. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)82628-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. H., Fisher C., Bhattacharya S., Goddard P., Baum J. D. Drip breast milk: it's composition, collection and pasteurization. Early Hum Dev. 1977 Dec;1(3):227–245. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(77)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson L. A., Winberg J. Breast milk and defence against infection in the newborn. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Dec;47(256):845–848. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.256.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER D. S., PAYNE P. R. A ballistic bomb calorimeter. Br J Nutr. 1959;13:501–508. doi: 10.1079/bjn19590064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picciano M. F., Guthrie H. A. Copper, iron, and zinc contents of mature human milk. Am J Clin Nutr. 1976 Mar;29(3):242–254. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/29.3.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Räihä N. C., Heinonen K., Rassin D. K., Gaull G. E. Milk protein quantity and quality in low-birthweight infants: I. Metabolic responses and effects on growth. Pediatrics. 1976 May;57(5):659–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens L. H. Appraisal of the state of nutrition of babies of low birth weight. 1. Current status. Aust Paediatr J. 1970 Mar;6(1):70–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan L. A., Weber C. W., Kemberling S. R. Longitudinal changes in the mineral content of human milk. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Nov;32(11):2301–2306. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.11.2301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDDOWSON E. M., SPRAY C. M. Chemical development in utero. Arch Dis Child. 1951 Jun;26(127):205–214. doi: 10.1136/adc.26.127.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


