Abstract
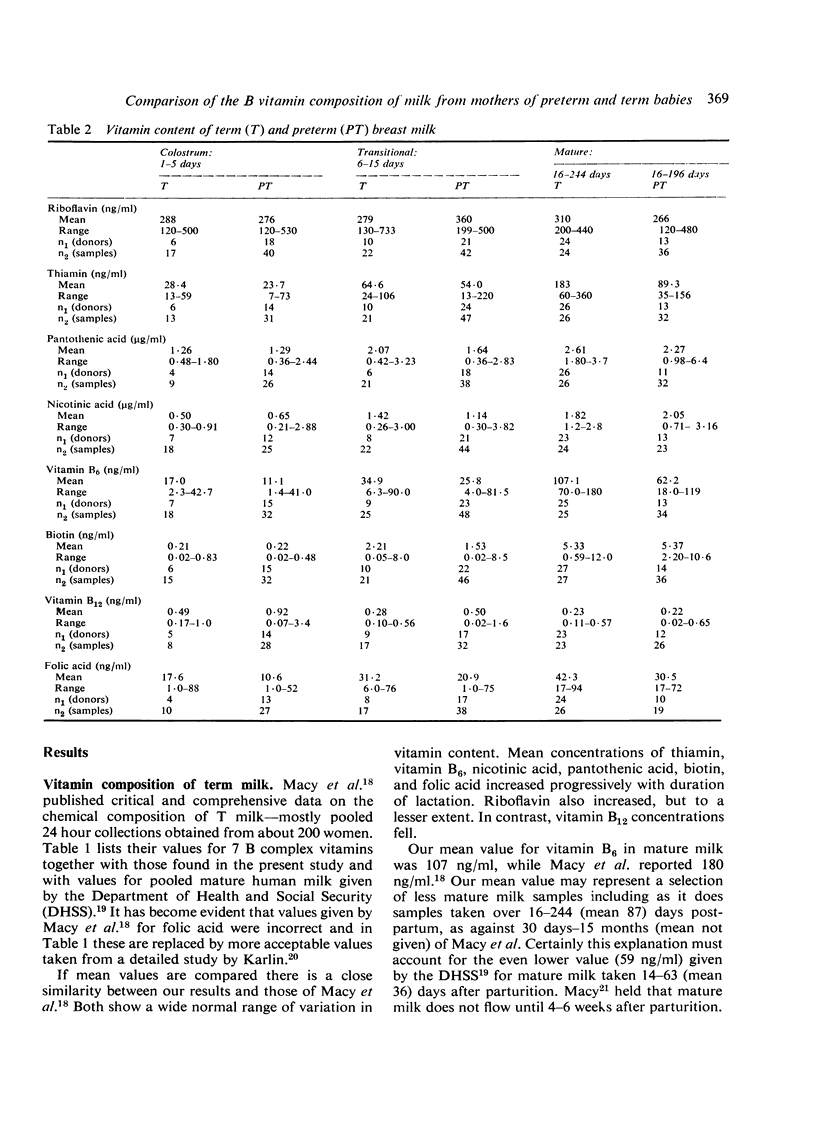
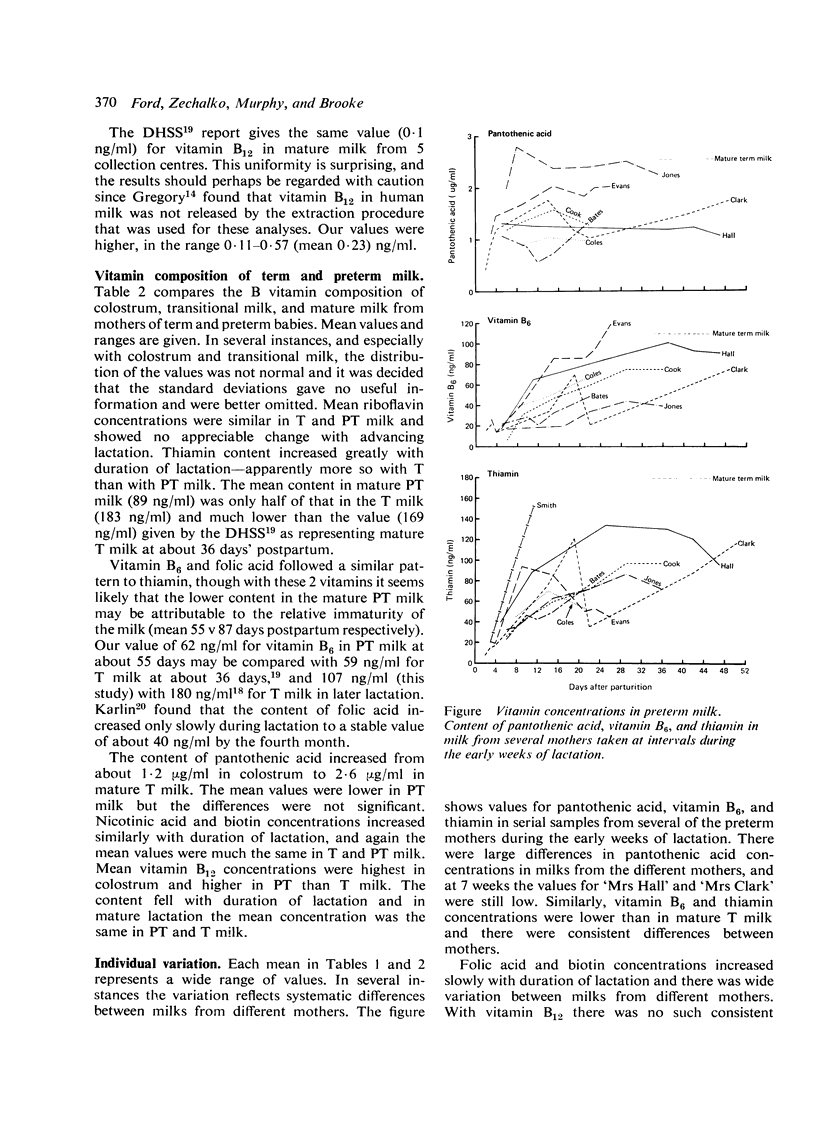
Samples of milk were taken at intervals during lactation from 35 mothers of term and 26 mothers of preterm infants and assayed for 8 B complex vitamins. Both term and preterm milks varied widely in vitamin content between mothers. Mean concentrations of thiamin, vitamin B6, nicotinic acid, pantothenic acid, biotin, and folic acid increased progressively over several weeks after parturition but vitamin B12 concentrations declined generally and riboflavin values showed little change. Preterm milk was not richer in vitamins than term milk of the corresponding stage of lactation and it appeared that intake of B vitamins differed widely among preterm infants given their own mothers' milk. These infants may have meagre body reserves and an increased need for vitamins, and breast milk whether from their own mother or from the milk bank may not meet their needs. There is a strong case for supplementing breast milk given to preterm babies with the B complex vitamins.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AINLEY N. J. Megaloblastic anaemia of pregnancy and the puerperium. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1961 Apr;68:254–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1961.tb02718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson S. A., Bryan M. H., Anderson G. H. Human milk: difference in nitrogen concentration in milk from mothers of term and premature infants. J Pediatr. 1978 Jul;93(1):67–69. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80602-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. P. Adequacy of expressed breast milk for early growth of preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Apr;52(4):296–301. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.4.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek J. Plasma and red cell folate values in newborn infants and their mothers in relation to gestational age. J Pediatr. 1980 Aug;97(2):288–292. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80497-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomon S. J., Ziegler E. E., Vázquez H. D. Human milk and the small premature infant. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Apr;131(4):463–467. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1977.02120170089018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGORY M. E. The microbiological assay of vitamin B12 in the milk different animal species. Br J Nutr. 1954;8(4):340–347. doi: 10.1079/bjn19540051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. J., David R. J., Bauman L., Tomarelli R. M. Nutritional composition of milk produced by mothers delivering preterm. J Pediatr. 1980 Apr;96(4):641–644. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80729-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. J., Geller J., Tomarelli R. M. Composition of breast milk from mothers of preterm infants. Pediatrics. 1981 Oct;68(4):490–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V. The assay and nature of folic acid activity in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jan;40:81–91. doi: 10.1172/JCI104240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibberd C., Brooke O. G., Carter N. D., Wood C. A comparison of protein concentrations and energy in breast milk from preterm and term mothers. J Hum Nutr. 1981 Jun;35(3):189–198. doi: 10.3109/09637488109143311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin R. Etude sur les taux d'acide folique du lait humain et du lait bovin. Int Z Vitaminforsch. 1967;37(3):334–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissileff H. R., Pi-Sunyer F. X., Thornton J., Smith G. P. C-terminal octapeptide of cholecystokinin decreases food intake in man. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Feb;34(2):154–160. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemons J. A., Moye L., Hall D., Simmons M. Differences in the composition of preterm and term human milk during early lactation. Pediatr Res. 1982 Feb;16(2):113–117. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198202000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Räihä N. C., Heinonen K., Rassin D. K., Gaull G. E. Milk protein quantity and quality in low-birthweight infants: I. Metabolic responses and effects on growth. Pediatrics. 1976 May;57(5):659–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanler R. J., Oh W. Composition of breast milk obtained from mothers of premature infants as compared to breast milk obtained from donors. J Pediatr. 1980 Apr;96(4):679–681. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80738-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strelling M. K., Blackledge G. D., Goodall H. B., Walker C. H. Megaloblastic anaemia and whole-blood folate levels in premature infants. Lancet. 1966 Apr 23;1(7443):898–900. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91576-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


