Abstract
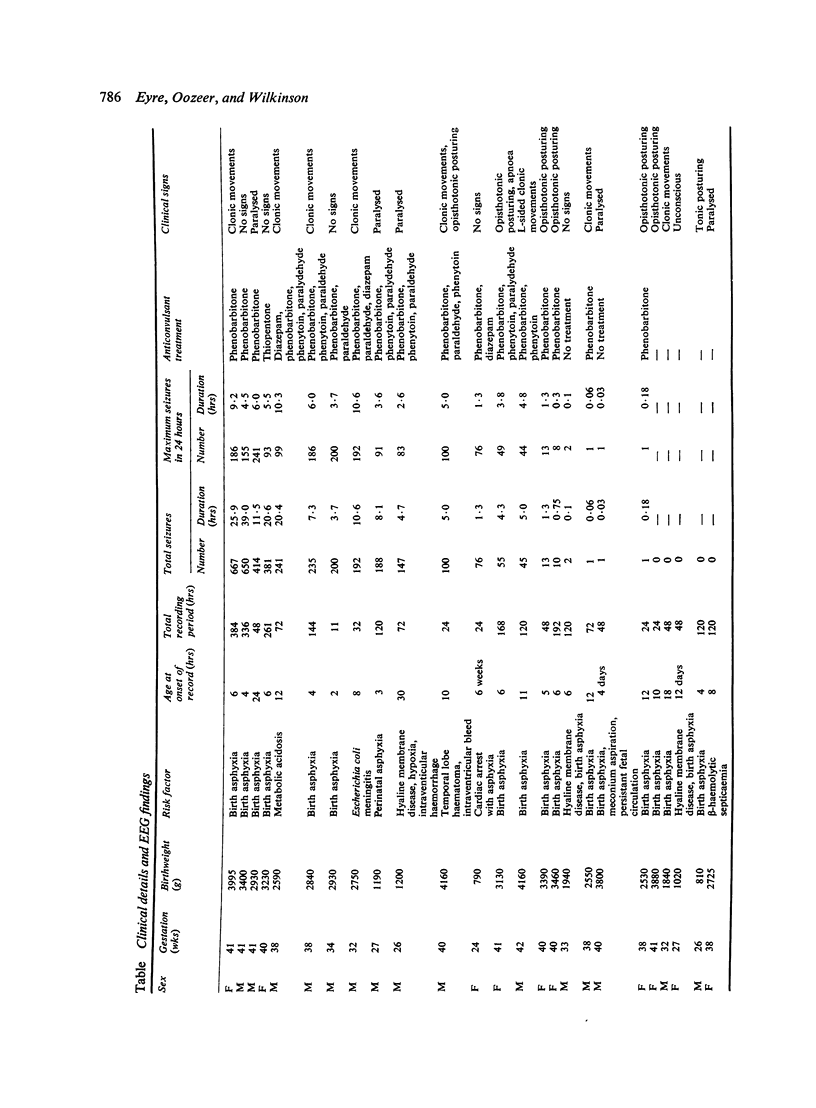
Clinical diagnosis of neonatal seizure is difficult and repeated seizures may be unrecognised. To assist in early diagnosis we recorded continuously the electroencephalogram (EEG) of very sick newborns while intensive care continued. In 25 babies at high risk of seizure a continuous record of two channels of EEG, ECG, and respiration was made for periods varying from 11 hours to 16 days. The method employed produced an EEG largely free of movement and electrical artefact which was analysed rapidly using a visual display unit. Electroencephalographic seizure activity was recorded in 20 babies, and continuous monitoring of the EEG allowed earlier recognition of seizure than was possible with clinical observation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURKE J. B. The prognostic significance of neonatal convulsions. Arch Dis Child. 1954 Aug;29(146):342–345. doi: 10.1136/adc.29.146.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. K., Cockburn F., Forfar J. O. Clinical and chemical correlates in convulsions of the newborn. Lancet. 1972 Jan 15;1(7742):135–139. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90694-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAIG W. S. Convulsive movements occurring in the first 10 days of life. Arch Dis Child. 1960 Aug;35:336–344. doi: 10.1136/adc.35.182.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis J. Neonatal convulsions: aetiology, late neonatal status and long-term outcome. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1978 Apr;20(2):143–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1978.tb15199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson M., Zetterström R. Neonatal convulsions. Incidence and causes in the Stockholm area. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Nov;68(6):807–811. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb08216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre J. A., Oozeer R. C., Wilkinson A. R. Continuous electroencephalographic recording to detect seizures in paralysed newborn babies. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Mar 26;286(6370):1017–1018. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6370.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS R., TIZARD J. P. The electroencephalogram in neonatal convulsions. J Pediatr. 1960 Oct;57:501–520. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(60)80078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen J. H., Lee D. Sequelae of neonatal convulsions. Study of 112 infants. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Jul;48(7):542–546. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.7.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lou H. C., Friis-Hansen B. Arterial blood pressure elevations during motor activity and epileptic seizures in the newborn. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Nov;68(6):803–806. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb08215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lou H. C., Lassen N. A., Friis-Hansen B. Impaired autoregulation of cerebral blood flow in the distressed newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1979 Jan;94(1):118–121. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80373-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B. S., Brierley J. B. Neuronal loss and gliosis in the hippocampus following repetitive epileptic seizures induced in adolescent baboons by allylglycine. Brain Res. 1972 Dec 24;48:361–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits E. D., Holden K. R., Freeman J. M. Neonatal seizures. II. A multivariate analysis of factors associated with outcome. Pediatrics. 1982 Aug;70(2):177–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ment L. R., Freedman R. M., Ehrenkranz R. A. Neonates with seizures attributable to perinatal complications: computed tomographic evaluation. Am J Dis Child. 1982 Jun;136(6):548–550. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1982.03970420072016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plum F., Posner J. B., Troy B. Cerebral metabolic and circulatory responses to induced convulsions in animals. Arch Neurol. 1968 Jan;18(1):1–13. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00470310015001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose A. L., Lombroso C. T. A study of clinical, pathological, and electroencephalographic features in 137 full-term babies with a long-term follow-up. Pediatrics. 1970 Mar;45(3):404–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt F., Roth J. G., Engel R. C. The usefulness of electroencephalography in curarized newborns. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1981 Feb;51(2):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(81)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasterlain C. G. Breakdown of brain polysomes in status epilepticus. Brain Res. 1972 Apr 14;39(1):278–284. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90807-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasterlain C. G. Does anoxemia play a role in the effects of neonatal seizures on brain growth? An experimental study in the rat. Eur Neurol. 1979;18(4):222–229. doi: 10.1159/000115080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasterlain C. G. Effects of neonatal status epilepticus on rat brain development. Neurology. 1976 Oct;26(10):975–986. doi: 10.1212/wnl.26.10.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasterlain C. G. Inhibition of cerebral protein synthesis by epileptic seizures without motor manifestations. Neurology. 1974 Feb;24(2):175–180. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.2.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasterlain C. G. Mortality and morbidity from serial seizures. An experimental study. Epilepsia. 1974 Jun;15(2):155–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1974.tb04939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasterlain C. G., Plum F. Vulnerability of developing rat brain to electroconvulsive seizures. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jul;29(1):38–45. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490250056006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe K., Hara K., Miyazaki S., Kuroyanagi M., Asano S., Kondo K., Kuno K., Jose H., Iwase K. Electroclinical studies of seizures in the newborn. Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn. 1977;31(3):383–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.1977.tb02625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



