Abstract
The perinatal histories of 50 very low birthweight infants weighing 1500 g, or less, with necrotizing enterocolitis were compared with those of the remaining 325 very low birthweight infants who were admitted to this hospital during a four year study period. Many factors previously reported to be associated with necrotizing enterocolitis were found with equal frequency in both groups of babies. The only adverse factor which was more frequently present in patients with necrotizing enterocolitis was hypothermia on admission to hospital. Those infants who developed severe necrotizing enterocolitis also had a higher incidence of polycythaemia. A further controlled study which examined feeding practices showed that the timing, type, and volume of milk feeding were not different in infants with necrotizing enterocolitis and matched controls. Prematurity is clearly the greatest risk factor which predisposes to the development of necrotizing enterocolitis and most of the factors previously implicated in the aetiology may simply represent the descriptive characteristics of a population of sick, very low birthweight infants.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Book L. S., Herbst J. J., Jung A. L. Comparison of fast- and slow-feeding rate schedules to the development of necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr. 1976 Sep;89(3):463–466. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80552-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunton G. L., Durbin G. M., McIntosh N., Shaw D. G., Taghizadeh A., Reynolds E. O., Rivers R. P., Urman G. Necrotizing enterocolitis. Controlled study of 3 years' experience in a neonatal intensive care unit. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Oct;52(10):772–777. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.10.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyal F., Sagi E., Arad I., Avital A. Necrotising enterocolitis in the very low birthweight infant: expressed breast milk feeding compared with parenteral feeding. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Apr;57(4):274–276. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.4.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz I. D., 3rd, L'heureux P., Engel R. R., Hunt C. E. Necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr. 1975 Feb;86(2):259–263. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80485-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman H. I. Feeding and necrotizing enterocolitis. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Jun;134(6):553–555. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130180011004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinan M., Schaberg D., Bruhn F. W., Richardson C. J., Fox W. W. Epidemic occurrence of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Am J Dis Child. 1979 Jun;133(6):594–597. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1979.02130060034005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson D. O., Oh W. Necrotizing enterocolitis and hyperviscosity in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1977 Mar;90(3):458–461. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80716-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison M. W., Connell R. S., Campbell J. R., Webb M. C. Microcirculatory changes in the gastrointestinal tract of the hypoxic puppy: an electron microscope study. J Pediatr Surg. 1975 Oct;10(5):599–608. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(75)90362-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliegman R. M., Fanaroff A. A. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: a nine-year experience. Am J Dis Child. 1981 Jul;135(7):603–607. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1981.02130310009005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliegman R. M., Pittard W. B., Fanaroff A. A. Necrotizing enterocolitis in neonates fed human milk. J Pediatr. 1979 Sep;95(3):450–453. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80534-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leake R. D., Thanopoulos B., Nieberg R. Hyperviscosity syndrome associated with necrotizing enterocolitis. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Oct;129(10):1192–1194. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120470042011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriartey R. R., Finer N. N., Cox S. F., Phillips H. J., Theman A., Stewart A. R., Ulan O. A. Necrotizing enterocolitis and human milk. J Pediatr. 1979 Feb;94(2):295–296. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80848-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., Shelton J. D., Guinan M. E. Necrotizing enterocolitis: a prospective multicenter investigation. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Jul;112(1):113–123. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sántulli T. V., Schullinger J. N., Heird W. C., Gongaware R. D., Wigger J., Barlow B., Blanc W. A., Berdon W. E. Acute necrotizing enterocolitis in infancy: a review of 64 cases. Pediatrics. 1975 Mar;55(3):376–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibboel D., van Nie C. J., Molenaar J. C. The effects of temporary general hypoxia and local ischemia on the development of the intestines: an experimental study. J Pediatr Surg. 1980 Feb;15(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(80)80404-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., del Portillo M., Schmidt E., Feldman R. A., Kanto W. P., Jr Risk factors for necrotizing enterocolitis in infants weighing more than 2,000 grams at birth: a case-control study. Pediatrics. 1983 Jan;71(1):19–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth F. H., Goldberg K. E., Lubchenco L. O. Neonatal hyperviscosity: I. Incidence. Pediatrics. 1979 Jun;63(6):833–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. Y., James B., Hendry P., MacMahon R. A. Total parenteral nutrition in very low birthweight infants: a controlled trial. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Sep;54(9):653–661. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.9.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
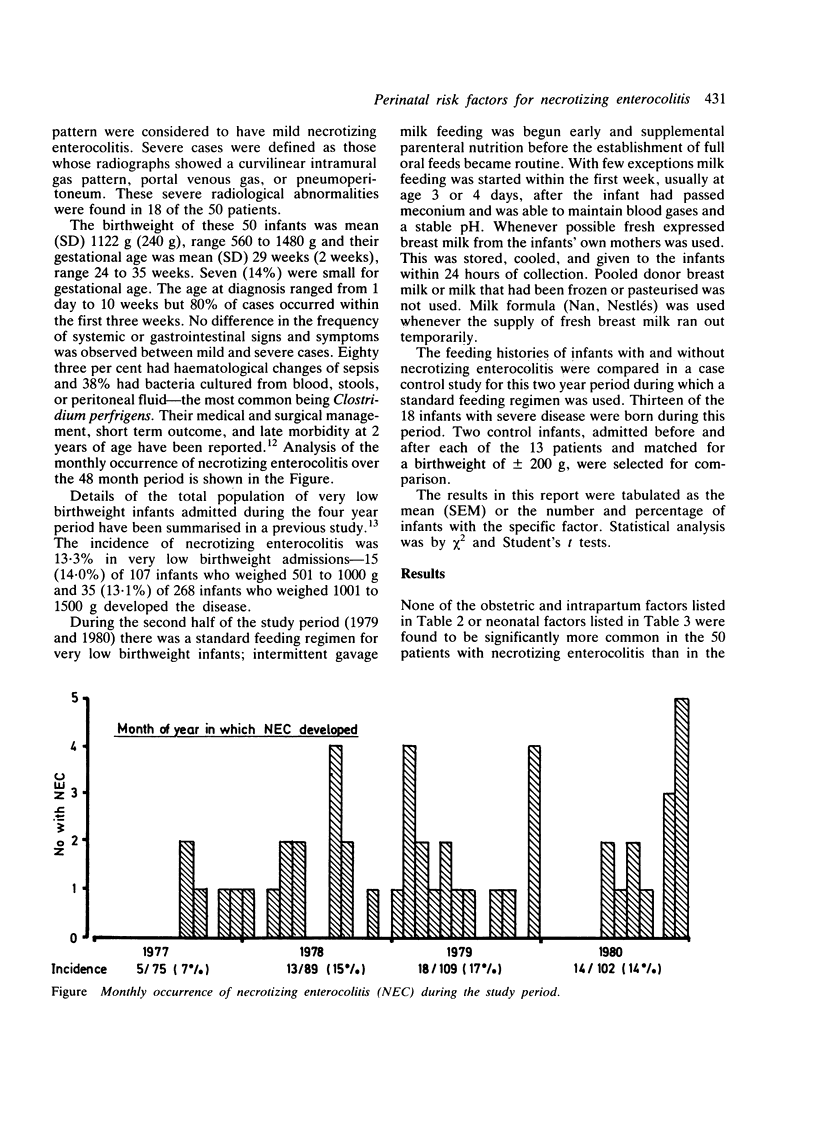
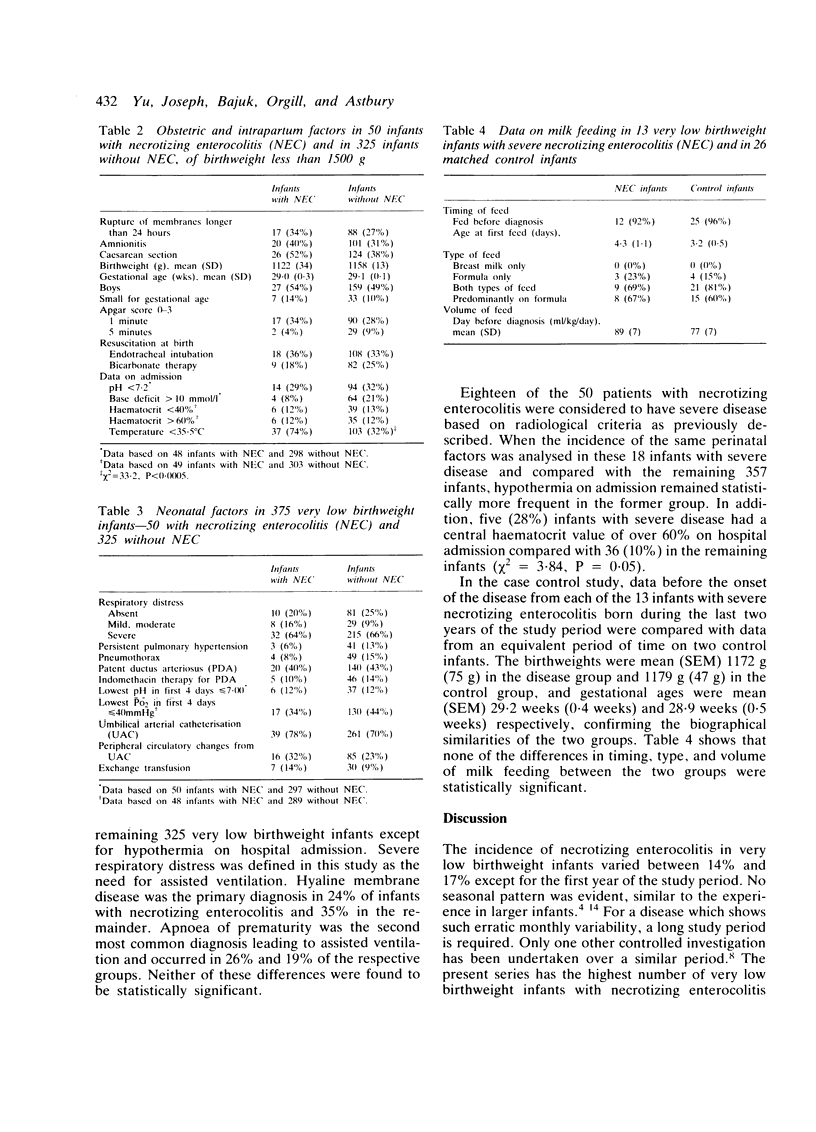
- Yu V. Y., Tudehope D. I., Gill G. J. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: 1. Clinical aspects. Med J Aust. 1977 May 7;1(19):685–688. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1977.tb131028.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. Y., Tudehope D. I. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: 2. Perinatal risk factors. Med J Aust. 1977 May 7;1(19):688–693. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1977.tb131029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. Y., Zhao S. M., Bajuk B. Results of intensive care for 375 very low birthweight infants. Aust Paediatr J. 1982 Sep;18(3):188–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1982.tb02025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


