Abstract
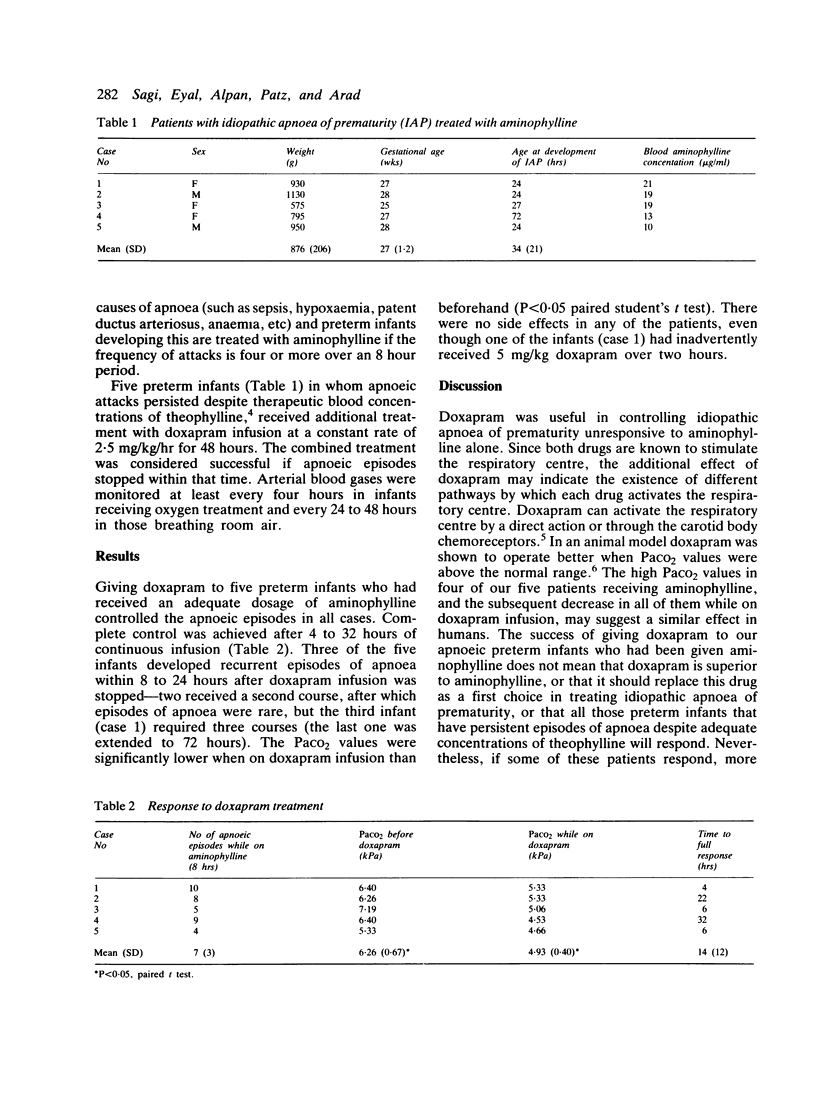
Doxapram infusion was given to five preterm infants in whom therapeutic concentrations of theophylline had failed to control episodes of apnoea. Doxapram successfully controlled the apnoea, the arterial blood PCO2 value decreased significantly, and no side effects were reported.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bopp P., Drummond G., Fisher J., Milic-Emili J. Effect of doxapram on control of breathing in cats. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1979 May;26(3):191–195. doi: 10.1007/BF03006980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P. K., Moore J. The use of doxapram in the newborn. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1973 Nov;80(11):1002–1006. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1973.tb02965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon D. C., Gotay F., Stein I. M., Rogers M. C., Todres I. D., Moylan F. M. Prevention of apnea and bradycardia in low-birthweight infants. Pediatrics. 1975 May;55(5):589–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. C., Ward J. W. Analeptics. Pharmacol Ther B. 1977;3(1):123–165. doi: 10.1016/0306-039x(77)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


