Full text
PDF
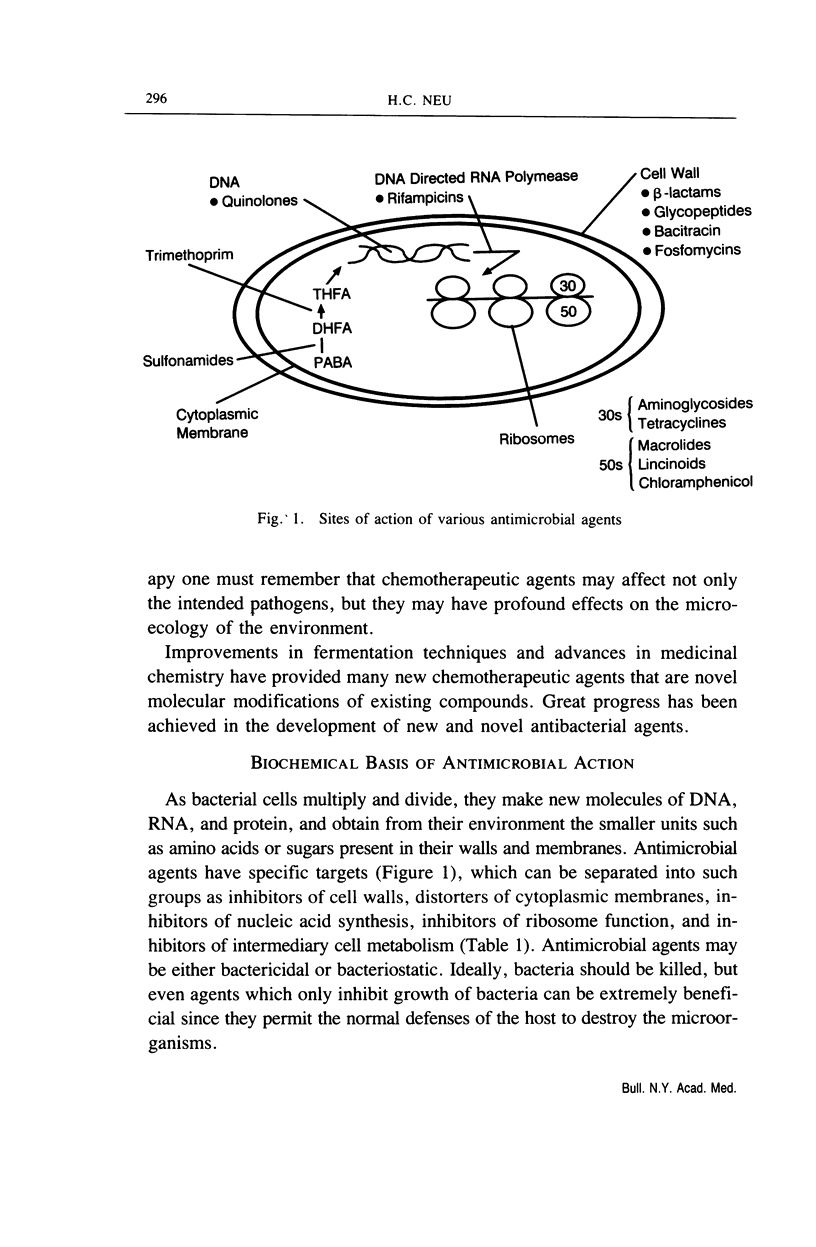



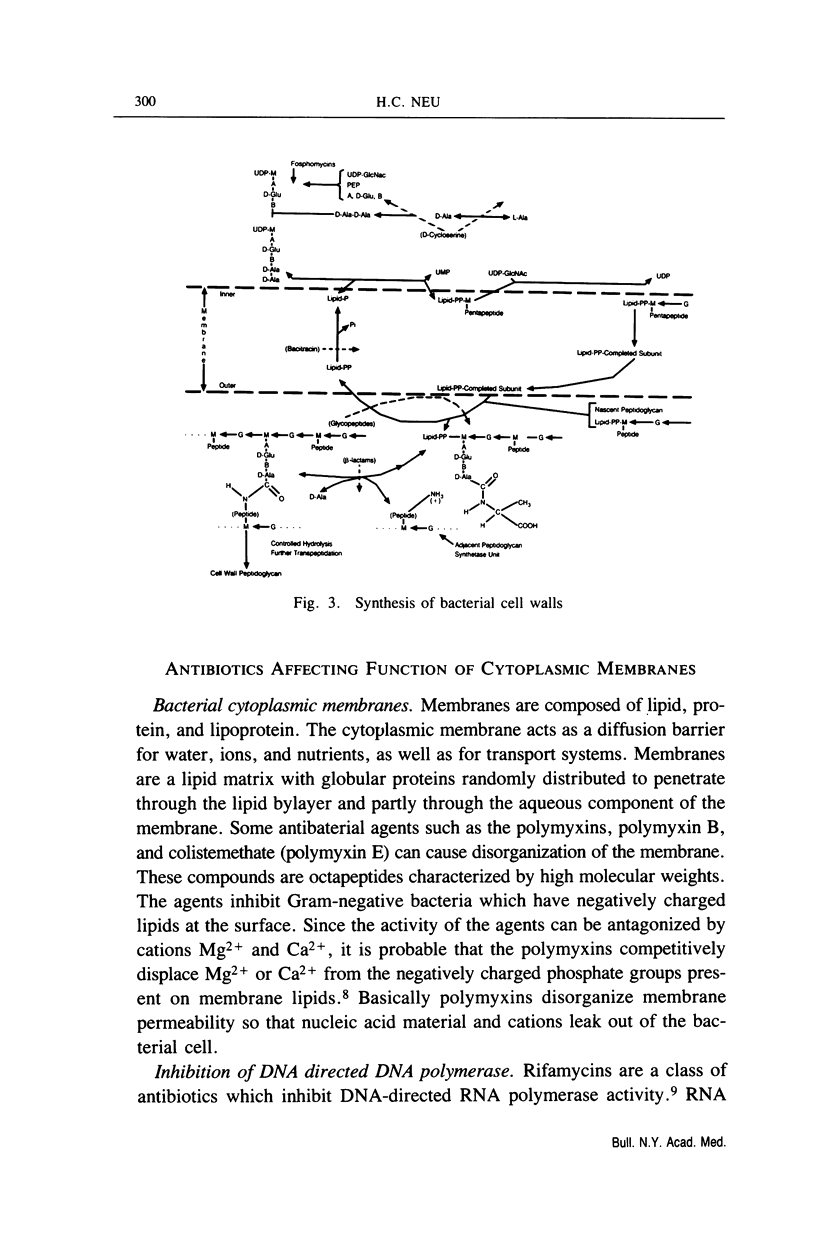


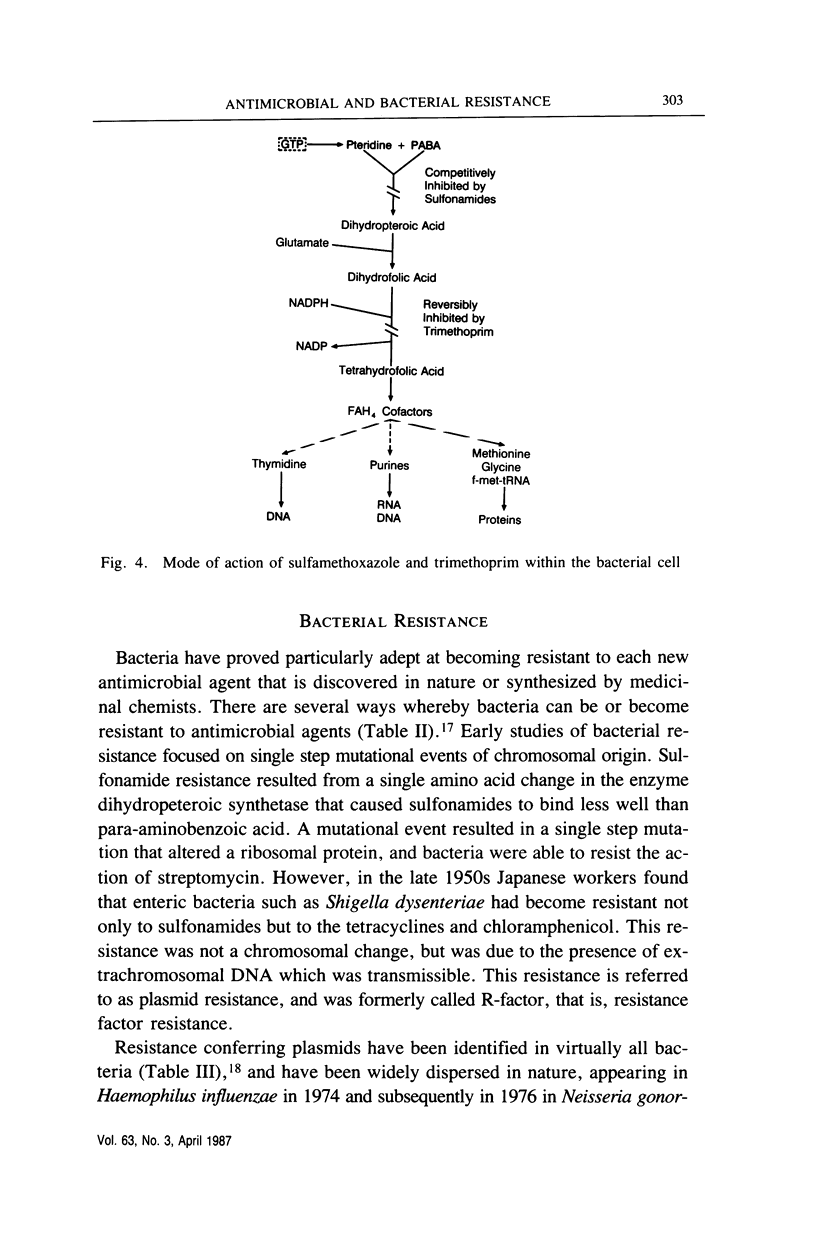






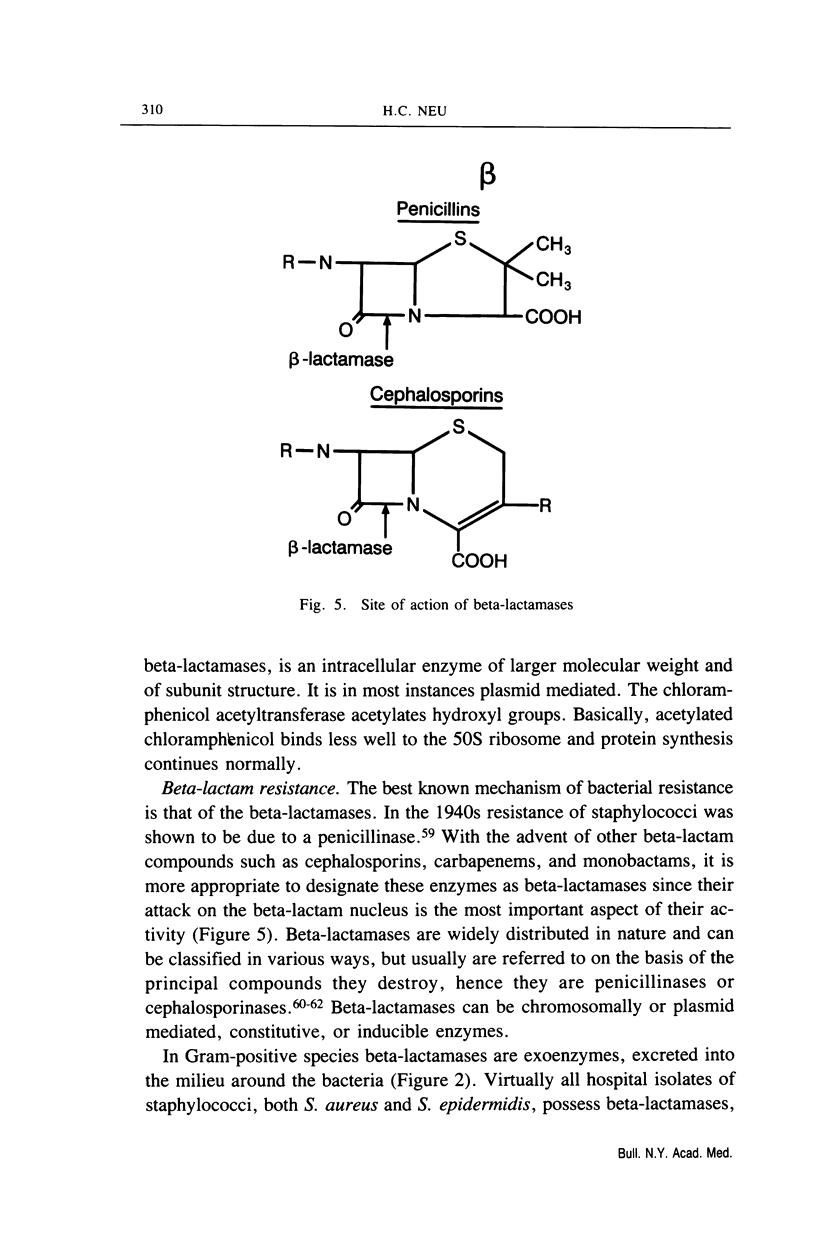






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen N. E. Macrolide resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: inducers of macrolide resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):669–674. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amyes S. G., Smith J. T. R-factor trimethoprim resistance mechanism: an insusceptible target site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 May 20;58(2):412–418. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball P. R., Shales S. W., Chopra I. Plasmid-mediated tetracycline resistance in Escherichia coli involves increased efflux of the antibiotic. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Mar 13;93(1):74–81. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R., Stöffler G., Wittmann H. G. Ribosome structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:217–249. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Haraphongse R., Van den Elzen H. M. Gentamicin resistance in clinical-isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with diminished gentamicin accumulation and no detectable enzymatic modification. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Jul;29(7):743–753. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Kowand S. K., Van Den Elzen H. M. Mechanism of aminoglycoside antibiotic resistance in anaerobic bacteria: Clostridium perfringens and Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jan;15(1):7–13. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van Den Elzen H. M. Effects of membrane-energy mutations and cations on streptomycin and gentamicin accumulation by bacteria: a model for entry of streptomycin and gentamicin in susceptible and resistant bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Aug;12(2):163–177. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Hartman B. J., Tomasz A. Increased amounts of a novel penicillin-binding protein in a strain of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus exposed to nafcillin. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):325–331. doi: 10.1172/JCI111965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I., Eccles S. J. Diffusion of tetracycline across the outer membrane of Escherichia coli K-12: involvement of protein Ia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jul 28;83(2):550–557. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Plasmids, drug resistance, and gene transfer in the genus Streptococcus. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Sep;45(3):409–436. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.3.409-436.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Kontomichalou P. Penicillinase synthesis controlled by infectious R factors in Enterobacteriaceae. Nature. 1965 Oct 16;208(5007):239–241. doi: 10.1038/208239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Nugent M., Richards H. Transposons encoding trimethoprim or gentamicin resistance in medically important bacteria. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):45–51. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Koller A. E., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins of penicillin-susceptible and intrinsically resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):730–737. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel H. W., Soedirman N., Rost J. A., van Leeuwen W. J., van Embden J. D. Transferability of macrolide, lincomycin, and streptogramin resistances between group A, B, and D streptococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):407–413. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.407-413.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Cerini R., Longoni P., Grossato A., Canepari P. Identification of a streptococcal penicillin-binding protein that reacts very slowly with penicillin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1343–1350. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1343-1350.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey A. J., Bryan L. E., Rabin H. R. beta-Lactam-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa with modified penicillin-binding proteins emerging during cystic fibrosis treatment. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):705–711. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakenbeck R., Tarpay M., Tomasz A. Multiple changes of penicillin-binding proteins in penicillin-resistant clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):364–371. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M. beta-Lactamases and their clinical significance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Feb;9 (Suppl B):11–19. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.suppl_b.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. Aminoglycoside uptake and mode of action--with special reference to streptomycin and gentamicin. I. Antagonists and mutants. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Oct;8(4):249–276. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.4.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Byeon W. H., Weisblum B. A complex attenuator regulates inducible resistance to macrolides, lincosamides, and streptogramin type B antibiotics in Streptococcus sanguis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1252–1262. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1252-1262.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. R., Koornhof H. J., Robins-Browne R. M., Stevenson C. M., Vermaak Z. A., Freiman I., Miller G. B., Witcomb M. A., Isaäcson M., Ward J. I. Emergence of multiply resistant pneumococci. N Engl J Med. 1978 Oct 5;299(14):735–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197810052991402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan F. M., Kahan J. S., Cassidy P. J., Kropp H. The mechanism of action of fosfomycin (phosphonomycin). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):364–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby W. M. EXTRACTION OF A HIGHLY POTENT PENICILLIN INACTIVATOR FROM PENICILLIN RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCI. Science. 1944 Jun 2;99(2579):452–453. doi: 10.1126/science.99.2579.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Weisblum B. Altered methylation of ribosomal RNA in an erythromycin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):856–860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Weisblum B., Fahnestock S. R., Nomura M. Alteration of 23 S ribosomal RNA and erythromycin-induced resistance to lincomycin and spiramycin in Staphylococcus aureus. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 15;74(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S. B. Microbial resistance to antibiotics. An evolving and persistent problem. Lancet. 1982 Jul 10;2(8289):83–88. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91701-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M. Plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases of Gram-negative bacteria: properties and distribution. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Jul;5(4):349–358. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.4.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurry L., Levy S. B. Two transport systems for tetracycline in sensitive Escherichia coli: critical role for an initial rapid uptake system insensitive to energy inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Aug;14(2):201–209. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.2.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza C., Garcia J. M., Llaneza J., Mendez F. J., Hardisson C., Ortiz J. M. Plasmid-determined resistance to fosfomycin in Serratia marcescens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Aug;18(2):215–219. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. H., Edberg S. C., Mandel L. J., Behar C. F., Steigbigel N. H. Gentamicin uptake in wild-type and aminoglycoside-resistant small-colony mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):722–729. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi M., Nishimura T., Komai T., Tanaka N. Interaction of kanamycin and related antibiotics with the large subunit of ribosomes and the inhibition of translocation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Sep 29;84(2):358–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Rensimer E. R., DuPont H. L. Emergence of high-level trimethoprim resistance in fecal Escherichia coli during oral administration of trimethoprim or trimethoprim--sulfamethoxazole. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jan 21;306(3):130–135. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198201213060302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Changing patterns of hospital infections: implications for therapy. Changing mechanisms of bacterial resistance. Am J Med. 1984 Jul 31;77(1B):11–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATO M. L., BROWN G. M. MECHANISMS OF RESISTANCE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI TO SULFONAMIDES. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Dec;103:443–448. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90435-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percheson P. B., Bryan L. E. Penicillin-binding components of penicillin-susceptible and -resistant strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Sep;18(3):390–396. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.3.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins H. R., Nieto M. The chemical basis for the action of the vancomycin group of antibiotics. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):348–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Antibiotics as probes of ribosome structure: binding of chloramphenicol and erythromycin to polyribosomes; effect of other antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):255–267. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi L., Tonin E., Cheng Y. R., Fontana R. Regulation of penicillin-binding protein activity: description of a methicillin-inducible penicillin-binding protein in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):828–831. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito T., Hashimoto H., Mitsuhashi S. Drug resistance of staphylococci. Foation of erythromycin-ribosome complex. Decrease in the formation of erythromycin-ribosome complex in erythromycin resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Jpn J Microbiol. 1969 Mar;13(1):119–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1969.tb00441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon K., Phillips I. Mechanisms of resistance to aminoglycosides in clinical isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Feb;9(2):91–102. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.2.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siewert G., Strominger J. L. Bacitracin: an inhibitor of the dephosphorylation of lipid pyrophosphate, an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):767–773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sköld O. R-factor-mediated resistance to sulfonamides by a plasmid-borne, drug-resistant dihydropteroate synthase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):49–54. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
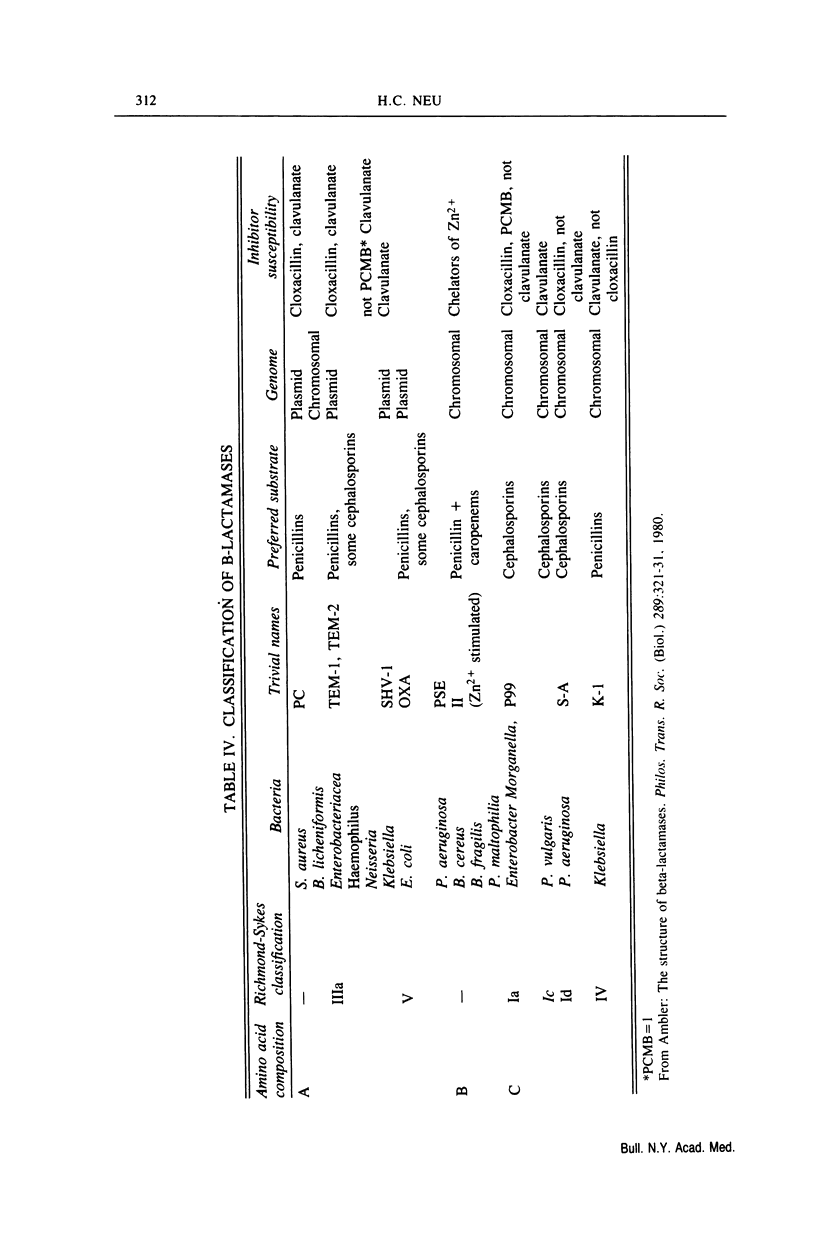
- Spratt B. G. Biochemical and genetical approaches to the mechanism of action of penicillin. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 May 16;289(1036):273–283. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1980.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm D. R., Rosenthal K. S., Swanson P. E. Polymyxin and related peptide antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:723–763. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Matthew M. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their role in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):115–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towner K. J., Venning B. M., Pinn P. A. Occurrence of transposable trimethoprim resistance in clinical isolates of Escherichia coli devoid of self-transmissible resistance plasmids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):336–338. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tritton T. R. Ribosome-tetracycline interactions. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 6;16(18):4133–4138. doi: 10.1021/bi00637a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata K., Yamashita N., Konno M. Occurrence of a beta-lactam-inducible penicillin-binding protein in methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):851–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Hakenbeck R., Tomasz A. In vivo interaction of beta-lactam antibiotics with the penicillin-binding proteins of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Oct;18(4):629–637. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. The fluoroquinolones: structures, mechanisms of action and resistance, and spectra of activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):581–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


