Abstract
MicroRNAs are an extensive family of ∼22-nucleotide-long noncoding RNAs expressed in a wide range of eukaryotes, including humans, and they are important in development and disease. We found that microRNA Mir-17-5p has extensive complementarity to the mRNA of AIB1 (named for “amplified in breast cancer 1”). Cell culture experiments showed that AIB1 expression was downregulated by Mir-17-5p, primarily through translational inhibition. Expression of Mir-17-5p was low in breast cancer cell lines. We also found that downregulation of AIB1 by Mir-17-5p resulted in decreased estrogen receptor-mediated, as well as estrogen receptor-independent, gene expression and decreased proliferation of breast cancer cells. Mir-17-5p also completely abrogated the insulin-like growth factor 1-mediated, anchorage-independent growth of breast cancer cells. Our results reveal that Mir-17-5p has a role as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer cells.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are genomically encoded, ∼22-nucleotide-long noncoding RNAs found in many organisms. miRNAs are produced from primary RNA polymerase II transcripts by sequential processing in the nucleus and cytoplasm (26, 27). Nuclear precursor RNAs are cleaved by the endonuclease Drosha in a “microprocessor complex” to release pre-miRNAs, which are 60- to 70-nucleotide-long imperfect hairpin structures (10, 20, 25). After being transported to the cytoplasm by exportin-5, pre-miRNAs are processed by the endonuclease DICER, generating ∼22-nucleotide duplexes, one strand of which is the mature miRNA (34, 55, 56). miRNAs inhibit the translation of their respective RNA targets through imperfect base-pairing interactions, often with the 3′-untranslated regions (UTRs) of target mRNAs, or degrade their targets through perfect or near-perfect base pairing (1, 9). A single miRNA can regulate a number of genes, as shown by Lim et al. in an experimental model (29), and genetic studies in various organisms suggest that miRNAs have pivotal roles in development, cell death, proliferation, and disease (3, 8, 19, 45).
There is increasing evidence that miRNAs are mutated or differentially expressed in many types of cancer. The miRNAs Mir-15 and Mir-16 were found to be deleted in 68% of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (5). Downregulation of Mir-143 and Mir-145 has been observed in colorectal cancer (38), and let-7 expression is often reduced in lung cancers with a poor prognosis (23, 49). In addition, increased expression of the precursor of Mir-155 has been detected in pediatric Burkitt lymphoma (13). Based on cancer-associated alterations in miRNA expression and the location of miRNAs at genomic regions often involved in cancers, it has been suggested that miRNAs act as tumor suppressors or oncogenes (6, 33). For example, Mir-17-5p, also known as Mir-91, is located on chromosome 13q31; this gene is amplified in childhood lymphoma (42, 48). The genomic location of Mir-17-5p also undergoes loss of heterozygosity in different types of cancer, including breast cancer (12, 30, 47, 51).
The clinical and epidemiological evidence for the necessary role of estrogen in breast cancer is substantial (35). There are two receptors for estrogen: ERα and ERβ (24, 37, 53). Estrogen receptors (ERs) are members of the steroid/thyroid hormone nuclear receptor superfamily, and both of these receptors act as ligand-dependent nuclear transcription factors (36). Transcriptional activation of genes by nuclear receptors is accomplished through the recruitment of coactivators (36). The nuclear receptor coactivator amplified in breast cancer 1 (AIB1) is a member of the p160/SRC family of coactivators (also named ACTR, RAC3, TRAM1, SRC-3, and NCOA3). The AIB1 gene is amplified in several cancers, including breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and gastric cancers (2, 18, 46), and acts as an oncogene (50). AIB1 enhances the transcriptional activity of the ER, E2F1, and other transcription factors (2, 32). AIB1 is a rate-limiting factor for the estrogen- and E2F1-mediated growth of human breast cancer cells and is involved in growth hormone-signaling pathways (32, 41, 54, 58). We report here on the role of Mir-17-5p, a potential translational repressor of the AIB1 oncogene, in the control of breast cancer cell proliferation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell cultures, plasmids, stable transfectants, and reporter gene assays.
All cell lines were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection and maintained in the recommended media. For the generation of stable MCF-7 cells overexpressing Mir-17-5p or Mir-95, pSilencer-neo vectors (Ambion) expressing Mir-17-5p or Mir-95 were transfected into MCF-7 cells, and stable cells were selected in medium containing G418.
Reporter genes were constructed by PCR amplification of the AIB1 3′-UTR, gel purification, and restriction digestion. The products were inserted into the XbaI site immediately downstream of the stop codon in the pGL3 promoter vector (Promega). Site-directed mutagenesis was done by using a site-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene).
The AIB1 expression construct pcDNA3AIB1 was generated by PCR amplification of entire AIB1 coding sequences from normal breast tissue and cloned into pcDNA3 vector (Invitrogen). The expression constructs pcAIB3′-UTR and pcAIBm3′-UTR were generated by replacing the original 3′-UTR from pcDNA3AIB1 with wild-type or mutated 3′-UTR of AIB1 cDNA.
Reporter assays were performed by cotransfection of various cell lines with vectors or synthetic 2′-O-methyl oligoribonucleotides by using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen). At 48 h after transfection, cells were collected for use in luciferase assay kits (Tropix). A β-galactosidase expression vector driven by the simian virus 40 promoter was used for transfection control. All reporter gene assays were performed in triplicate, with the entire experiment repeated several times.
Northern blotting and solution hybridization.
Northern blots were performed according to standard procedures. Briefly, for conventional Northern blotting, 20 μg of total RNA was separated on formaldehyde-agarose gels, transferred to a nylon membrane, and hybridized with randomly primed, labeled AIB1-complementary probes using NorthernMax hybridization buffer (Ambion). The blots were stripped and reanalyzed with a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) probe.
For miRNA analysis, miRNA was purified from cells by using a mirVANA miRNA isolation kit (Ambion). Total RNA (20 μg) was separated on 15% denaturing polyacrylamide gels, transferred to a nylon membrane, and hybridized with UltraHyb-Oligo buffer (Ambion). An oligonucleotide complementary to Mir-17-5p (5′-ACTACCTGCACTGTAAGCACTTTG-3′) was end labeled with T4 polynucleotide kinase (New England Biolabs) and used as a probe. A U6 snRNA probe was used as an internal control. The blots were analyzed with a PhosphorImager.
Breast tumor samples were obtained from the M. D. Anderson Cancer Center tissue repository, and miRNA was isolated as described above. Total RNA (100 ng) was used for the detection of Mir-17-5p and Mir-15a using an mirVANA miRNA detection kit (Ambion, TX) according to the manufacturer's instruction.
Western blotting.
Whole-cell extracts were prepared in modified radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer. Western blots were developed by using SuperSignal West Femto chemiluminescent substrate (Pierce). We used primary antibodies against AIB1 (BD Transduction Laboratories) and β-actin (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and a peroxidase-conjugated anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G secondary antibody (Amersham).
Cell proliferation and soft agar colony formation assays.
For the estrogen-dependent cell proliferation assay, equal numbers of stable MCF-7 cells expressing Mir-17-5p, Mir-95, or control vector were plated in a 96-well plate and treated with improved minimum essential medium (Invitrogen) and 1% charcoal-stripped calf serum containing 10 nM E2 or vehicle only. Cell growth was determined by using a standard tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay and verified by counting with trypan blue and a hemacytometer.
For the estrogen-independent cell proliferation assay, ER-negative BT-20 cells were plated in a six-well plate at 50% confluence 24 h before transfection. The next day, cells were transfected with 2′-O-methyl Mir-17-5p or 2′-O-methyl Mir-95 by using Oligofectamine (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. After 24 h, transfected cells were treated with trypsin, and equal numbers of viable cells were plated into 96-well plates. The cells were then incubated for another 96 h, with one change of medium after 48 h. Cell growth was determined by using a standard MTT assay and verified by counting and trypan blue exclusion.
For the soft agar assay, stably transformed MCF-7 cells were resuspended in 0.35% soft agar and layered onto 0.6% solidified agar in a 5-cm dish in 10% charcoal-stripped calf serum with or without 100 ng of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1)/ml. The soft agar colonies were allowed to grow for 12 days at 37°C. Colonies with a diameter of >80 μm were scored as positive. Experiments were carried out in triplicate.
RESULTS
AIB1 is a target of Mir-17-5p.
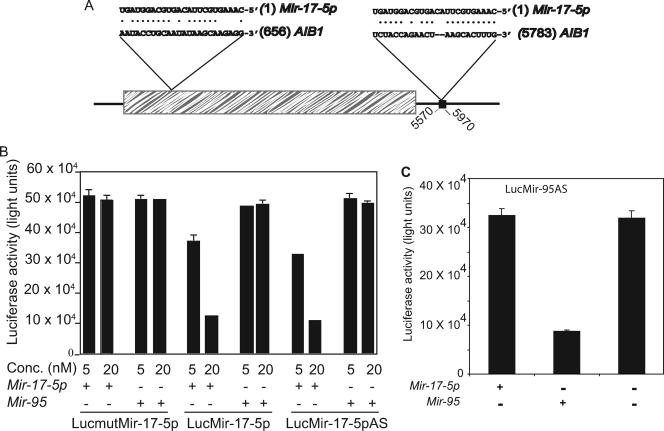
To identify the mRNA targets of Mir-17-5p, we performed a computational screen for genes with Mir-17-5p complementary sites in their sequences. One of the high-scoring candidates was the human oncogene AIB1. We identified two Mir-17-5p complementary sites within the 3′-UTR and coding region of AIB1 (Fig. 1A). The most important criteria for target recognition is the 5′-eight-nucleotide core sequences of miRNA. However, some mismatches and gaps are allowed between the 3′ end of miRNA and its target mRNA, as this is the case for many proven miRNA targets (14, 15, 23). The degree of similarity at the 3′ end increases the specificity of target recognition by miRNAs (4, 11, 28). The first ten nucleotides of Mir-17-5p were perfectly matched with their AIB1 mRNA targets, and the two-nucleotide gap at positions 11 and 12 decreased the free energy of the duplex and is predicted to favor the formation of a Mir-17-5p-AIB1 duplex. mFold analysis of the local mRNA secondary structure also revealed no noticeable complex secondary structure surrounding the Mir-17-5p binding site in the 3′-UTR of AIB1. A duplex between AIB1 and Mir-17-5p was also observed upon using mFold analysis, with a ΔG value of −13.0 kcal mol−1, which is well within the range of a true miRNA target site (11). By fulfilling the above-mentioned criteria AIB1 became a good candidate target of Mir-17-5p and merited further experimental analysis.
FIG. 1.
AIB1 is a target of Mir-17-5p. (A) Sequence alignment and diagram of Mir-17-5p and its complementary sites in the AIB1 cDNA. The hatched area indicates the coding region; the black square indicates the region cloned at the end of the luciferase reporter gene. (B) Activity of luciferase reporters containing the Mir-17-5p complementary site from human AIB1 (LucMir-17-5p), a mutant Mir-17-5p complementary site from human AIB1 (mutLucMir-17-5p), or the perfect antisense sequence of Mir-17-5p (LucMir-17-5pAS). The reporters were cotransfected with the indicated amounts of 2′-O-methyl Mir-17-5p or Mir-95. Firefly luciferase activity was normalized to that of β-galactosidase. The data shown are the mean of three independent experiments, and error bars indicate the standard deviations. (C) Activity of luciferase reporters containing the perfect antisense sequence of Mir-95 (LucMir-95AS). The reporters were cotransfected with the indicated amounts of 2′-O-methyl Mir-17-5p or Mir-95. Firefly luciferase activity was normalized to that of β-galactosidase. The data shown are means of three independent experiments, and error bars indicate standard deviations.
To examine whether AIB1 is repressed by Mir-17-5p, segments of the AIB1 3′UTR containing wild-type or mutated Mir-17-5p complementary sites were inserted into the 3′-UTR of a luciferase reporter gene. The resulting reporter plasmids were transfected into HeLa cells together with a transfection control and 2′-O-methyloligoribonucleotides of Mir-17-5p (2′-O-methyl Mir-17-5p) or a noncognate miRNA (2′-O-methyl Mir-95). As expected, Mir-17-5p inhibited luciferase activity from the construct with the wild-type complementary site but not the construct with the mutated complementary site (Fig. 1B). There was no change in luciferase reporter activity when Mir-95 was cotransfected with either reporter construct, indicating that the observed inhibition is specific to Mir-17-5p. The inhibition was essentially the same as that of a reporter with perfect complementarity to Mir-17-5p (Fig. 1B). These results suggest that the complementary site in AIB1 mRNA is a target of Mir-17-5p-mediated posttranscriptional silencing of gene expression. To eliminate the possibility that the Mir-95 used here was nonfunctional, we fused Mir-95 antisense sequences downstream of the luciferase gene and used these sequences for a Mir-95 functional assay. Mir-95 significantly reduced the luciferase activity, but Mir-17-5p could not do so (Fig. 1C), indicating that the Mir-95 used here was indeed functional.
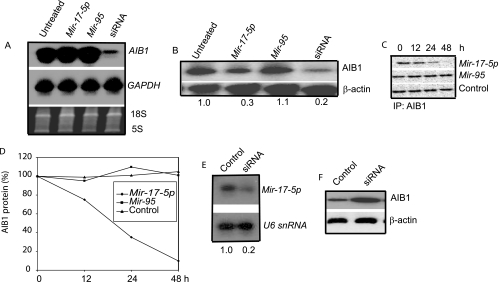
Translation of endogenous AIB1 is suppressed by Mir-17-5p.
To gain insight into the mechanism by which Mir-17-5p inhibits luciferase expression (Fig. 1B), we transfected 2′-O-methyl Mir-17-5p or 2′-O-methyl Mir-95 into MCF-7 cells. We chose MCF-7 cells because AIB1 is highly expressed in these cells, and AIB1 activity is essential for their growth in vitro and in vivo (31, 41). As expected, AIB1 mRNA levels were unaffected by Mir-17-5p (Fig. 2A), although Northern blotting (Fig. 2A) and real-time PCR (data not shown) revealed that AIB1 mRNA was sharply reduced by cotransfection of an AIB1-specific short interfering RNA (siRNA) molecule. In contrast, AIB1 protein levels decreased substantially after treatment with Mir-17-5p, as shown by Western blotting (Fig. 2B) and by pulse-labeling (Fig. 2C); the reduction level was comparable to that using AIB1-specific siRNA, which occasionally decreased AIB1 protein to almost undetectable levels (data not shown). In contrast, in the presence of Mir-95, the AIB1 mRNA and protein levels remained unchanged and were similar to those in untreated MCF-7 cells, indicating that Mir-17-5p regulation is specific to AIB1 (Fig. 2A and B).
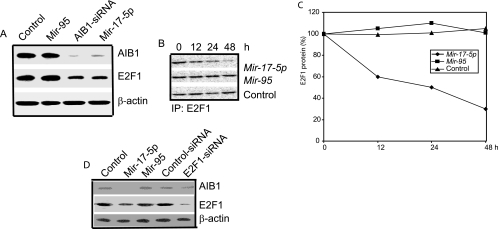
FIG. 2.
Mir-17-5p regulates translation of endogenous AIB1. (A) Northern blot of RNA from untreated MCF-7 cells and cells treated with Mir-17-5p, Mir-95, or anti-AIB1 siRNA. The RNA transcript levels were equal in all experimental samples, as shown by GAPDH and ethidium bromide staining (bottom two panels). (B) Western blot of AIB1 protein in untreated MCF-7 cells and cells treated with Mir-17-5p, Mir-95, anti-AIB1 siRNA, or scrambled siRNA. Anti-β-actin antibody was used as a loading control (bottom panel). (C and D) MCF-7 cells were transfected with Mir-17-5p, Mir-95, or vehicle only. Cells were starved in methionine-free medium and then pulse-labeled with [35S]methionine. The cells were then harvested and immunoprecipitated with anti-AIB1 antibody. Precipitated proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and visualized by using a phosphorimager. (E and F) Level of Mir-17-5p mature transcript (E) and AIB1 protein (F) in HeLa cells treated with siRNA targeted to the loop region of pre-Mir-17p transcript or a scrambled siRNA (control). U6 snRNA (snU6) and β-actin were used as internal controls.
To further examine the function of Mir-17-5p, we tested whether the levels of endogenous Mir-17-5p in HeLa cells could be reduced by using synthetic siRNA targeted to the Mir-17-5p precursor. We selected HeLa cells for their high expression of endogenous mature Mir-17-5p. The intracellular levels of Mir-17-5p decreased significantly after treatment with Mir-17-5p-specific siRNA (Fig. 2D). As expected, the levels of endogenous AIB1 protein increased in the presence of Mir-17-5p-specific siRNA, whereas mutant siRNA did not affect the expression of Mir-17-5p or AIB1 protein (Fig. 2E). These results suggest that synthetic Mir-17-5p suppresses the expression of AIB1, primarily at the level of translation.
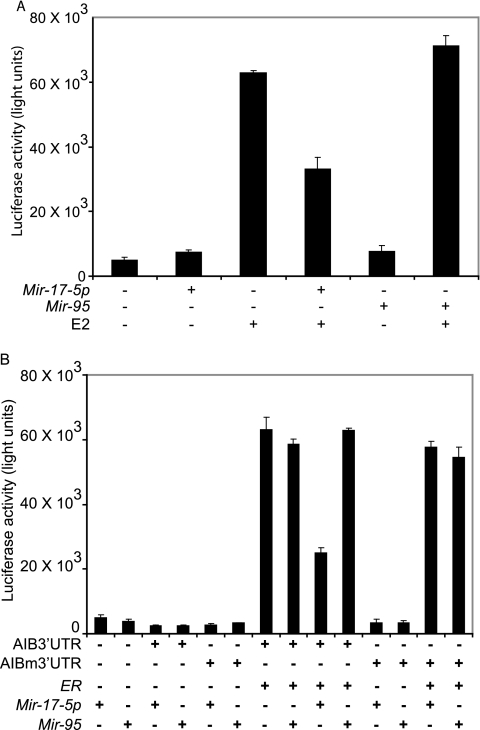
Mir-17-5p modulates ER-mediated signaling.
Because AIB1 enhances the transcriptional activity of ER (2), we tested the effects of Mir-17-5p by using ER-mediated transactivation or estrogen-responsive elements (EREs) containing a luciferase reporter gene (ERE-Luc). Transfection of ERE-Luc with Mir-17-5p in CHO-K1 cells reduced ER-dependent transcriptional activity by ca. 50% in the presence of estrogen (Fig. 3A). As expected, noncognate Mir-95 had no effect on ER-dependent transcriptional activity (Fig. 3A).
FIG. 3.
Mir-17-5p suppresses ER-mediated signaling. (A) Luciferase activity in CHO-K1 cells transiently transfected with an ER expression vector, a luciferase reporter plasmid, and 2′-O-methyl Mir17p or Mir-95, in the absence or presence of 10 nM E2. The data shown are means of triplicate experiments, and error bars indicate the standard deviations. (B) Luciferase activity in cells cotransfected with AIB1-expressing reporter plasmids containing wild-type (AIB3′UTR) or mutant (AIBm3′UTR) AIB1 3′UTRs, ER, ERE-Luc, and 2′-O-methyl Mir-17-5p or 2′-O-methyl Mir-95. The data shown are means of triplicate experiments, and error bars indicate the standard deviations.
To confirm the negative effect of Mir-17-5p on estrogen signaling, we fused wild-type (pcAIB3′-UTR) and mutated (pcAIBm3′-UTR) AIB1 3′-UTR to the AIB1 expression vector, pcDNA3AIB1, by replacing the original 3′-UTR sequences present in the pcDNA3 vector. These constructs were used for transcription assays by transient transfection into CHO-K1 cells, along with reporter plasmids containing the ERE-Luc and ER expression vectors. Cotransfection of the pcAIB3′-UTR and ERE-Luc in the presence of 2′-O-methyl Mir-17-5p substantially reduced ER-mediated transactivation (Fig. 3B). In contrast, cotransfection of pcAIBm3′-UTR and ERE-Luc resulted in potent transcriptional activity in the presence of Mir-17-5p (Fig. 3B). No significant differences were observed upon treatment with 2′-O-methyl Mir-95. These results clearly demonstrate that Mir-17-5p-mediated reduction of AIB1 protein requires the presence of AIB1 3′-UTR target sites and can effectively block ER-mediated signaling.
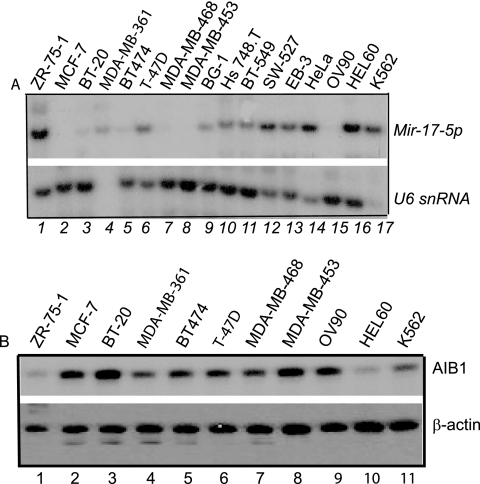
Expression of Mir-17-5p in cancer cell lines and breast tumors.
Upregulation of AIB1 by gene amplification or other means is a key event in breast cancer cell proliferation (32, 41, 54, 58). Because Mir-17-5p clearly affects estrogen signaling and because AIB1 is a rate-limiting factor for estrogen-mediated growth of breast cancer cells (31), it is possible that loss of Mir-17-5p control over AIB1 translational regulation can lead to unregulated breast cancer cell growth. To test this, we used Northern blotting to examine the expression of Mir-17-5p in several breast cancer cell lines: ZR-75-1, MCF-7, BT-20, MDA-MB-361, BT-474, T-47D, MDA-MB-468, MDA-MB-453, Hs 748.T, BT-549, SW527 and in non-breast cancer cell lines: BG-1, EB-3, HeLa, OV90, HEL60, and K562. Mir-17-5p expression was low to barely detectable in the breast cancer cell lines compared to the non-breast-tumor cell lines (Fig. 4A). To detect any existing correlation between Mir-17-5p and AIB1 protein expression, we used Western blotting with cell extracts from selected cell lines. We found that AIB1 was highly expressed when Mir-17-5p expression was low (Fig. 4B). These data indicate that the downregulation of Mir-17-5p may be important for breast cancer cell growth.
FIG. 4.
Expression of Mir-17-5p is reduced or silent in some cancer cell lines. (A) Northern blot sequentially assayed with radiolabeled probes specific for Mir-17-5p, with U6 snRNA used as a control. Lanes 1 to 17 show RNA from the cell lines ZR-75-1, MCF-7, BT-20, MDA-MB-361, BT-474, T-47D, MDA-MB-468, MDA-MB-453, BG-1, Hs 748.T, BT-549, SW527, EB-3, HeLa, OV90, HEL60, and K562. Lanes 1 to 12 show breast cancer cell lines, and lanes 13 to 17 show other types of cancer cells. (B) Western blot of AIB1 protein in different cell lines. Cell lysates (50 μg) of the different cell lines were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane, and probed with anti-AIB1 antibody. The same blot was stripped and reprobed with anti-β-actin antibody and was used as a loading control (bottom panel).
Translation of endogenous E2F1 is regulated by Mir-17-5p.
A recent report suggests that E2F1 is a target of Mir-17-5p at the translational level (40). By careful examination of E2F1 coding and noncoding 3′-UTR, we found only one Mir-17-5p recognition site. It is also known that AIB1 is involved in E2F1 transcriptional regulation (32). Therefore, there is a possibility that Mir-17-5p may not directly regulate the expression of E2F1 but rather have an indirect effect on E2F1 activity. To resolve at which level Mir-17-5p may affect E2F1, we treated MCF-7 cells with Mir-17-5p and Mir-95, and cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting with E2F1 specific antibody. E2F1 protein level was significantly downregulated by the treatment of Mir-17-5p (Fig. 5A and B). However, this does not mean that E2F1 is a direct target of Mir-17-5p, since AIB1 expression was also completely abrogated by Mir-17-5p. We therefore tested the effects of Mir-17-5p in ZR-75-1 cells, which express a very low level of AIB1 (Fig. 4B). Residual expression of AIB1 was completely abrogated by the treatment of Mir-17-5p (Fig. 5C). In contrast, we did not observe a large reduction of E2F1 levels by the treatment of Mir-17-5p compared to its effects on E2F1 protein levels in MCF-7 cells that express high levels of AIB1. However, we also observed a measurable reduction of E2F1 protein level by the treatment of Mir-17-5p in this cell line. This observation further established that Mir-17-5p could directly inhibit the translation of E2F1, albeit less effectively than the reduction of AIB1. We included E2F1-specific siRNA to avoid any doubt concerning the transfection efficiency in this cell line. These results suggest that the negative influence of Mir-17-5p on E2F1 was both directly and indirectly due to AIB1 downregulation at least in breast cancer cells.
FIG. 5.
Mir-17-5p regulates translation of endogenous E2F1. Cell lysates (50 μg) from MCF-7 (A) and ZR-75-1 (D) were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane, and probed with anti-AIB1 and anti-E2F1 antibody. The same blot was stripped and reprobed with anti-β-actin antibody and used as a loading control (bottom panel). (B and C) MCF-7 cells were transfected with Mir-17-5p, Mir-95, or vehicle only. Cells were starved in methionine-free medium and then pulse-labeled with [35S]methionine. The cells were then harvested and immunoprecipitated with anti-E2F1 antibody. Precipitated proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by using a phosphorimager.
Mir-17-5p represses ER and E2F1 target genes.
To understand better the role of Mir-17-5p on estrogen-mediated signal transduction, we tested the effects of Mir-17-5p on ER-regulated genes. The cyclin D1 gene is a known target of ER (43, 44). Transfection of Mir-17-5p in MCF-7 cells reduced the ER-dependent upregulation of cyclin D1 significantly in the presence of estrogen (Fig. 6). As expected, noncognate Mir-95 had no effect on the ER-dependent upregulation of cyclin D1 (Fig. 6).
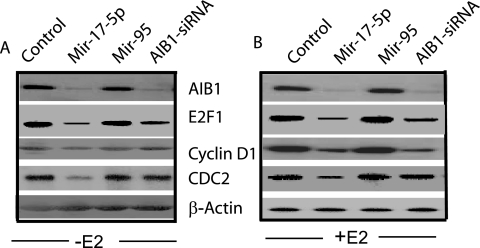
FIG. 6.
Mir-17-5p represses the expression of some ER and E2F1 target genes. Cells were treated with the indicated 2′-O-methyl RNA, and cell lysates (50 μg) were prepared and separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane, and probed with the indicated antibodies. Cells were treated with (B) or without (A) E2 to check target gene expression. The control reflects cells treated with phosphate-buffered saline only. The same blot was stripped and reprobed with anti-β-actin antibody and used as a loading control (bottom panel).
We also tested the regulation of known E2F1 target gene CDC2 by the treatment of Mir-17-5p (17). The Cdc2 protein level was reduced significantly by the treatment of Mir-17-5p in MCF-7 cells (Fig. 6). These results suggest that Mir-17-5p has an important role on both ER- and E2F1-mediated signal transduction pathways.
Mir-17-5p suppresses estrogen-stimulated breast cancer cell proliferation.
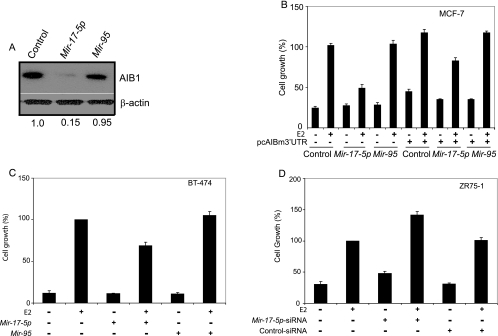
Our findings that Mir-17-5p is involved in regulating AIB1 translation and that Mir-17-5p expression is low in breast cancer cells prompted us to examine the role of Mir-17-5p in the proliferation of estrogen-responsive breast cancer cells. To this end, we established stable transformants containing vectors overexpressing Mir-17-5p or Mir-95. We used pooled transformants instead of selective clones to avoid clonal bias. AIB1 protein levels were markedly reduced in MCF7 cells expressing Mir-17-5p, whereas no significant effect was observed in cells expressing Mir-95 (Fig. 7A).
FIG. 7.
Mir-17-5p suppresses both estrogen-stimulated and estrogen/ER-independent breast cancer cell proliferation. (A) Reduction of AIB1 protein in stably transfected MCF-7 cells expressing Mir-17-5p but not Mir-95 compared to pSilencer vector only (control). Anti-β-actin antibody was used as a loading control. (B) Estrogen (E2)-stimulated cell proliferation assay. MCF-7 cells were stably transformed with pSilencer empty vector (control), pSilencerMir-17-5p (Mir-17-5p), or pSilencerMir-95 (Mir-95) and treated with 10 nM E2 or vehicle only. pcAIBm3′UTR was reintroduced by transient transfection in the stably transformed MCF-7 cells described above, which were treated with 10 nM E2. Cell proliferation was measured by the MTT assay. The data shown are means of triplicate experiments, and error bars indicate the standard deviations. (C) 2′-O-methyl Mir-17-5p or 2′-O-methyl Mir-95 was transiently transfected into BT-474 cells and treated with 10 nM E2 or vehicle only. Cell growth was measured by the MTT assay after 96 h. The data shown are means of triplicate experiments, and error bars indicate the standard deviations. (D) ZR75-1cells were treated with siRNA targeted to the loop region of pre-Mir-17p transcript or a scrambled siRNA (control) and treated with 10 nM E2 or vehicle only. Cell growth was measured by MTT assay after 96 h. The data shown are means of triplicate experiments, and error bars indicate the standard deviations.
To examine the effect of Mir-17-5p-mediated AIB1 depletion on estrogen-stimulated cell proliferation, we treated AIB1-depleted MCF-7 cells with the estrogen 17β-estradiol (E2). Depletion of AIB1 by Mir-17-5p markedly inhibited E2-stimulated cell proliferation (Fig. 7B). Reintroduction of AIB1-containing mutated 3′-UTRs, which are capable of escaping Mir-17-5p-mediated translational control, rescued the cells from the proliferation defects caused by the overexpression of Mir-17-5p in MCF-7 cells (Fig. 5B). These results were confirmed in another ER-positive breast cancer cell line. Depletion of AIB1 by Mir-17-5p by transient transfection also reduced E2-stimulated growth of BT-474 cell line (Fig. 7C).
To further address the role of Mir-17-5p in E2-stimulated growth, we introduced Mir-17-5p-specific siRNA into another ER-positive cancer cell line, ZR-75-1, that expresses high levels of endogenous Mir-17-5p (Fig. 5A). Depletion of endogenous Mir-17-5p by anti-Mir-17-5p siRNA increased E2-stimulated growth of ZR-75-1 cells (Fig. 7D). Taken together, these results suggested that Mir-17-5p plays an important role in estrogen-dependent breast cancer cell proliferation by regulating AIB1 translation.
Mir-17-5p represses estrogen/ER-independent breast cancer cell proliferation by targeting AIB1.
AIB1 is also involved in the estrogen-independent proliferation of breast cancer cells (32). To examine whether Mir-17-5p can inhibit estrogen-independent breast cancer cell proliferation, we transiently transfected ER-negative BT-20 cells with 2′-O-methyl Mir17-5p or Mir-95. Mir-17-5p repressed the hormone-independent proliferation of BT-20 cells (Fig. 8A and B), and the reintroduction of pcAIBm3′-UTR partially restored Mir-17-5p-mediated growth of the BT-20 cells (Fig. 8B). Thus, in addition to regulating breast cancer cell proliferation, Mir-17-5p has an important role in breast cancer cell proliferation that is independent of estrogen and ER.
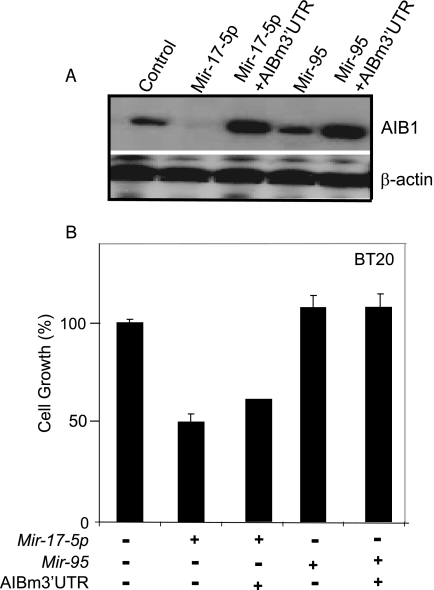
FIG. 8.
Mir-17-5p suppresses estrogen/ER-independent breast cancer cell proliferation. 2′-O-Methyl Mir-17-5p or 2′-O-methyl Mir-95 with or without pcAIBm3′UTR was transiently transfected into BT-20 cells, and cells were maintained in hormone-deprived medium. (A) Western blot of AIB1 protein. Cell lysates (50 μg) of transfected cells were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane, and probed with anti-AIB1 antibody. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (B) Cell proliferation assay. Cell growth was measured by the MTT assay after 96 h. The data shown are means of triplicate experiments, and error bars indicate the standard deviations.
Mir-17-5p-mediated AIB1 depletion impairs the anchorage-independent growth of MCF-7 cells.
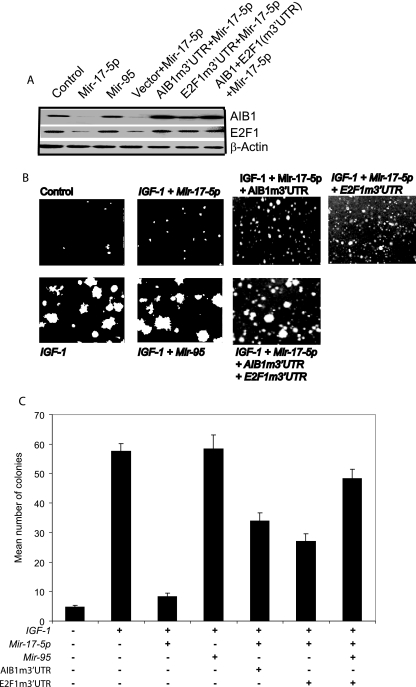
To further establish the role of Mir-17-5p in breast cancer cell proliferation, we investigated the anchorage-independent growth of breast cancer cells in the presence or absence of Mir-17-5p. AIB1 has an important role in the anchorage-independent growth of MCF-7 cells caused by IGF-1 by regulating E2F1 function (41). Since E2F1 is a direct target of Mir-17-5p, we used a Mir-17-5p-insensitive E2F1 expression construct, i.e., E2F1 coding sequences without their own 3′-UTRs. First, we checked the expression of E2F1 and AIB1 after the transient transfection of Mir-17-5p and control Mir-95. As expected, the levels of both AIB1 and E2F1 expression were reduced by the treatment of Mir-17-5p. We were able to rescue the expression of AIB1 and E2F1 by overexpressing the Mir-17-5p-insensitive forms of AIB1 and E2F1 (Fig. 9A) in these cells. We then checked the effect of Mir-17-5p on the IGF-1-induced anchorage-independent growth of MCF-7 cells. IGF-1 induced severalfold increases in the numbers of colonies larger than 80 μm formed by control MCF-7 cells; this increase was completely abrogated in cells treated with Mir-17-5p (Fig. 9B and C). We attempted to rescue the growth inhibition of MCF-7 cells by Mir-17-5p using previously characterized Mir-17-5p insensitive forms of AIB1 and E2F1. Overexpression of either alone did not significantly rescue the anchorage-independent growth of these cells. However, the coexpression of both AIB1 and E2F1 significantly improved the anchorage-independent growth of these cells in the presence of IGF-1 and Mir-17-5p (Fig. 9B and C). Therefore, the inhibitory effects of Mir-17-5p on estrogen-independent breast cancer cell growth appears to be due to translational regulation of two important players in this pathway: AIB1 and E2F1.
FIG. 9.
Reduction of endogenous AIB1 by Mir-17-5p inhibits the anchorage-independent growth of MCF-7 Cells. (A) Mir-17-5p and Mir-95 overexpressing stably transfected MCF-7 cells were grown in improved minimal essential medium and 1% charcoal-stripped calf serum in 0.35% soft agar dishes in the absence or presence of 100 ng of IGF-1/ml. (B) Mean numbers of colonies with a diameter >80 μm. The data shown are means of triplicate experiments, and error bars indicate the standard deviations.
DISCUSSION
Increasing evidence has implicated several miRNAs in tumorigenesis (7). Many miRNA genes are located within regions associated with amplification, deletion, and translocation in cancer (6, 33). The lack of knowledge about genuine miRNA gene targets impedes a full understanding of the true role of miRNAs in tuomorigenesis.
In the present study, we identified Mir-17-5p as a genuine regulator of oncogene AIB1 translation. AIB1 is overexpressed in primary breast cancer and is involved in hormone-dependent and hormone-independent breast cancer cell proliferation. We also observed that Mir-17-5p represses E2F1-mediated pathways. We clearly demonstrated an important role of Mir-17-5p in breast cancer cell proliferation and anchorage-independent growth by both overexpression and knockdown experiments. We also showed that Mir-17-5p expression was reduced in breast cancer lines.
AIB1 is a coactivator for nuclear receptors, including ER, and AIB1 accelerates breast cancer cell proliferation by amplifying the mitogenic effect of estrogen through an increase in the transactivation functions of ER (2, 16, 58). The growth of MCF-7 cells in response to estrogen depends on ER and AIB1 (31). The treatment of MCF-7 cells with Mir-17-5p substantially reduced their ability to proliferate in response to estrogen. However, reintroduction of Mir-17-5p recognition-defective AIB1 in these cells restored their growth. This finding indicates that AIB1 is the target of Mir-17-5p and that Mir-17-5p-mediated growth reduction of estrogen-sensitive breast cancer cells is caused by the regulation of AIB1 translation by Mir-17-5p. Hormone-independent growth of BT-20 cells was also inhibited by Mir-17-5p. However, reintroduction of the Mir-17-5p recognition-defective AIB1 in these cells only partially restored cell proliferation. A recent report suggests that E2F1 is also a target of Mir-17-5p-mediated translational regulation (40). Louie et al. reported that AIB1 and E2F1 cooperate in the proliferation of ER-negative BT-20 breast cancer cells (32). This is most likely the reason why we could not restore maximum proliferation activity of Mir-17-5p-treated BT-20 cells by reintroducing AIB1 only. AIB1 amplification and/or overexpression are commonly observed in primary breast cancer (2). Analogously, the loss of heterozygosity at chromosome region 13q31 has been documented in breast carcinomas (12). A genetically amplified AIB1 gene is likely to bypass the Mir-17-5p-mediated translational regulation of growth hormone signaling, resulting in uncontrolled growth of tumor cells. Our results suggest a scenario in which Mir-17-5p functions as a key regulator of hormone-mediated enhancement of breast cancer cell growth.
IGF-1-mediated and estrogen-independent growth of breast cancer cells are dependent on functional AIB1 and E2F1 (32). We observed that the anchorage-independent growth of MCF-7 cells in response to IGF-1 was abrogated by Mir-17-5p. Growth retardation of these cells was directly related to the downregulation of AIB1 and E2F1 translation, since we were able to rescue substantial growth of MCF-7 cells by the reintroduction of Mir-17-5p-insensitive forms of AIB1 and E2F1. These results further established the role of Mir-17-5p in the hormone-dependent and hormone-independent growth of breast cancer cells.
During the preparation of the present report, two independent groups described the regulation and possible function of the c13orf25 locus that contains the Mir-17*92 cluster of seven miRNAs (Mir-17-5p, Mir-17-3p, Mir-18, Mir-19a, Mir-20, Mir-19b-1, and Mir-92-1) (22, 40). The c13orf25 locus is overexpressed in human B-cell lymphomas, and forced expression of c13orf25 and c-myc accelerates tumor development in a mouse B-cell lymphoma model (22, 42); however, it was not clear from these studies (22, 42) which individual miRNA is crucial for B-cell lymphoma development. It is also important to mention that in lung cancer, all members of Mir-17*92 are overexpressed, except for Mir-17-5p (21). This indicates that although miRNAs are expressed as a cluster in many cases, individual miRNA biogenesis is under differential control by a still unknown mechanism. In agreement with the present study, O'Donnell et al. showed that translation of the oncogene E2F1 is negatively regulated by Mir-17-5p and suggested that Mir-17-5p acts as a tumor suppressor (40).
Because expression of Mir-17-5p is very low in some breast tumors and cell lines (32), it is plausible that the transcriptional regulation of Mir17-5p is somewhat different in breast tissue than in B cells. For example, expression of the Mir-17*92 cluster in breast cancer cells may be downregulated by an epigenetic mechanism, since a loss of heterozygosity at the 13q31 region has been reported in some cases (12). During the preparation of the present report, Volinia et al. reported that Mir-17-5p is upregulated in breast cancer (52). Their observation directly contradicts an earlier report by Lu et al. (33). These two groups used different techniques, and this may explain the discrepancy between these two reports. It is important to mention that Mir-106a is a homolog of Mir-17-5p and was downregulated in the study by Volina et al. (39, 52). Structural differences between these two miRNAs (Mir-17-5p and Mir-106a) are insignificant and should give similar results with the solid base hybridization technique. The small size of miRNAs made it complicated to detect by conventional hybridization techniques. A comprehensive assay with large number of samples using both solid- and liquid-based hybridization techniques are required to uncover the true status of Mir-17-5p in breast cancer. During the final preparation of the present study, Zhang et al. (57) reported that the region containing this Mir-17-92 polycistron was deleted in 16.5% of ovarian cancers, 21.9% of breast cancers, and 20.0% of melanomas.
Deregulation of Mir-17-5p function could represent an important alternative mechanism to derail the control of cell proliferation in breast cancer. Our observations in the present study and from others suggest that Mir-17-5p acts as both as a tumor suppressor and as an oncogene by influencing cell proliferation in a cell-type-specific manner, depending on the cellular environment and target mRNAs that are expressed.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Institutes of Health grants CA34936 and CA16672 to G.F.S.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 28 August 2006.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ambros, V. 2004. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Anzick, S. L., J. Kononen, R. L. Walker, D. O. Azorsa, M. M. Tanner, X. Y. Guan, G. Sauter, O. P. Kallioniemi, J. M. Trent, and P. S. Meltzer. 1997. AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science 277:965-968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Brennecke, J., D. R. Hipfner, A. Stark, R. B. Russell, and S. M. Cohen. 2003. bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell 113:25-36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Brennecke, J., A. Stark, R. B. Russell, and S. M. Cohen. 2005. Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol. 3:e85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Calin, G. A., C. D. Dumitru, M. Shimizu, R. Bichi, S. Zupo, E. Noch, H. Aldler, S. Rattan, M. Keating, K. Rai, L. Rassenti, T. Kipps, M. Negrini, F. Bullrich, and C. M. Croce. 2002. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:15524-15529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Calin, G. A., C. Sevignani, C. D. Dumitru, T. Hyslop, E. Noch, S. Yendamuri, M. Shimizu, S. Rattan, F. Bullrich, M. Negrini, and C. M. Croce. 2004. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:2999-3004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chen, C. Z. 2005. MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. N. Engl. J. Med. 353:1768-1771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chen, C. Z., L. Li, H. F. Lodish, and D. P. Bartel. 2004. MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 303:83-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cullen, B. R. 2004. Transcription and processing of human microRNA precursors. Mol. Cell 16:861-865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Denli, A. M., B. B. Tops, R. H. Plasterk, R. F. Ketting, and G. J. Hannon. 2004. Processing of primary microRNAs by the microprocessor complex. Nature 432:231-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Doench, J. G., and P. A. Sharp. 2004. Specificity of microRNA target selection in translational repression. Genes Dev. 18:504-511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Eiriksdottir, G., G. Johannesdottir, S. Ingvarsson, I. B. Bjornsdottir, J. G. Jonasson, B. A. Agnarsson, J. Hallgrimsson, J. Gudmundsson, V. Egilsson, H. Sigurdsson, and R. B. Barkardottir. 1998. Mapping loss of heterozygosity at chromosome 13q: loss at 13q12-q13 is associated with breast tumour progression and poor prognosis. Eur. J. Cancer 34:2076-2081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Eis, P. S., W. Tam, L. Sun, A. Chadburn, Z. Li, M. F. Gomez, E. Lund, and J. E. Dahlberg. 2005. Accumulation of miR-155 and BIC RNA in human B-cell lymphomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102:3627-3632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fazi, F., A. Rosa, A. Fatica, V. Gelmetti, M. L. De Marchis, C. Nervi, and I. Bozzoni. 2005. A minicircuitry comprised of microRNA-223 and transcription factors NFI-A and C/EBPα regulates human granulopoiesis. Cell 123:819-831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Felli, N., L. Fontana, E. Pelosi, R. Botta, D. Bonci, F. Facchiano, F. Liuzzi, V. Lulli, O. Morsilli, S. Santoro, M. Valtieri, G. A. Calin, C. G. Liu, A. Sorrentino, C. M. Croce, and C. Peschle. 2005. MicroRNAs 221 and 222 inhibit normal erythropoiesis and erythroleukemic cell growth via kit receptor down-modulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102:18081-18086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Font de Mora, J., and M. Brown. 2000. AIB1 is a conduit for kinase-mediated growth factor signaling to the estrogen receptor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:5041-5047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Furukawa, Y., Y. Terui, K. Sakoe, M. Ohta, and M. Saito. 1994. The role of cellular transcription factor E2F in the regulation of cdc2 mRNA expression and cell cycle control of human hematopoietic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 269:26249-26258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ghadimi, B. M., E. Schrock, R. L. Walker, D. Wangsa, A. Jauho, P. S. Meltzer, and T. Ried. 1999. Specific chromosomal aberrations and amplification of the AIB1 nuclear receptor coactivator gene in pancreatic carcinomas. Am. J. Pathol. 154:525-536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Giraldez, A. J., R. M. Cinalli, M. E. Glasner, A. J. Enright, J. M. Thomson, S. Baskerville, S. M. Hammond, D. P. Bartel, and A. F. Schier. 2005. MicroRNAs regulate brain morphogenesis in zebra fish. Science 308:833-838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gregory, R. I., K. P. Yan, G. Amuthan, T. Chendrimada, B. Doratotaj, N. Cooch, and R. Shiekhattar. 2004. The microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature 432:235-240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hayashita, Y., H. Osada, Y. Tatematsu, H. Yamada, K. Yanagisawa, S. Tomida, Y. Yatabe, K. Kawahara, Y. Sekido, and T. Takahashi. 2005. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 65:9628-9632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.He, L., J. M. Thomson, M. T. Hemann, E. Hernando-Monge, D. Mu, S. Goodson, S. Powers, C. Cordon-Cardo, S. W. Lowe, G. J. Hannon, and S. M. Hammond. 2005. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 435:828-833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Johnson, S. M., H. Grosshans, J. Shingara, M. Byrom, R. Jarvis, A. Cheng, E. Labourier, K. L. Reinert, D. Brown, and F. J. Slack. 2005. RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 120:635-647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kuiper, G. G. J. M., E. Enmark, M. Pelto-Huikko, S. Nilsson, and J.-A. Gustafsson. 1996. Cloning of a novel estrogen receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93:5925-5930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lee, Y., C. Ahn, J. Han, H. Choi, J. Kim, J. Yim, J. Lee, P. Provost, O. Radmark, S. Kim, and V. N. Kim. 2003. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature 425:415-419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lee, Y., K. Jeon, J. T. Lee, S. Kim, and V. N. Kim. 2002. MicroRNA maturation: stepwise processing and subcellular localization. EMBO J. 21:4663-4670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lee, Y., M. Kim, J. Han, K. H. Yeom, S. Lee, S. H. Baek, and V. N. Kim. 2004. MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J. 23:4051-4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lewis, B. P., I. H. Shih, M. W. Jones-Rhoades, D. P. Bartel, and C. B. Burge. 2003. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115:787-798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lim, L. P., N. C. Lau, P. Garrett-Engele, A. Grimson, J. M. Schelter, J. Castle, D. P. Bartel, P. S. Linsley, and J. M. Johnson. 2005. Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature 433:769-773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lin, Y. W., J. C. Sheu, L. Y. Liu, C. H. Chen, H. S. Lee, G. T. Huang, J. T. Wang, P. H. Lee, and F. J. Lu. 1999. Loss of heterozygosity at chromosome 13q in hepatocellular carcinoma: identification of three independent regions. Eur. J. Cancer 35:1730-1734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.List, H. J., K. J. Lauritsen, R. Reiter, C. Powers, A. Wellstein, and A. T. Riegel. 2001. Ribozyme targeting demonstrates that the nuclear receptor coactivator AIB1 is a rate-limiting factor for estrogen-dependent growth of human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 276:23763-23768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Louie, M. C., J. X. Zou, A. Rabinovich, and H. W. Chen. 2004. ACTR/AIB1 functions as an E2F1 coactivator to promote breast cancer cell proliferation and antiestrogen resistance. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24:5157-5171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lu, J., G. Getz, E. A. Miska, E. Alvarez-Saavedra, J. Lamb, D. Peck, A. Sweet-Cordero, B. L. Ebert, R. H. Mak, A. A. Ferrando, J. R. Downing, T. Jacks, H. R. Horvitz, and T. R. Golub. 2005. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435:834-838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lund, E., S. Guttinger, A. Calado, J. E. Dahlberg, and U. Kutay. 2004. Nuclear export of microRNA precursors. Science 303:95-98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.MacGregor, J. I., and V. C. Jordan. 1998. Basic guide to the mechanisms of antiestrogen action. Pharmacol. Rev. 50:151-196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.McDonnell, D. P., and J. D. Norris. 2002. Connections and regulation of the human estrogen receptor. Science 296:1642-1644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Means, A. R., J. P. Comstock, G. C. Rosenfeld, and B. W. O'Malley. 1972. Ovalbumin messenger RNA of chick oviduct: partial characterization, estrogen dependence, and translation in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 69:1146-1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Michael, M. Z., S. M. O'Connor, N. G. van Holst Pellekaan, G. P. Young, and R. J. James. 2003. Reduced accumulation of specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol. Cancer Res. 1:882-891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mourelatos, Z., J. Dostie, S. Paushkin, A. Sharma, B. Charroux, L. Abel, J. Rappsilber, M. Mann, and G. Dreyfuss. 2002. miRNPs: a novel class of ribonucleoproteins containing numerous microRNAs. Genes Dev. 16:720-728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.O'Donnell, K. A., E. A. Wentzel, K. I. Zeller, C. V. Dang, and J. T. Mendell. 2005. c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature 435:839-843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Oh, A., H. J. List, R. Reiter, A. Mani, Y. Zhang, E. Gehan, A. Wellstein, and A. T. Riegel. 2004. The nuclear receptor coactivator AIB1 mediates insulin-like growth factor I-induced phenotypic changes in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 64:8299-8308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ota, A., H. Tagawa, S. Karnan, S. Tsuzuki, A. Karpas, S. Kira, Y. Yoshida, and M. Seto. 2004. Identification and characterization of a novel gene, C13orf25, as a target for 13q31-q32 amplification in malignant lymphoma. Cancer Res. 64:3087-3095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Planas-Silva, M. D., J. L. Donaher, and R. A. Weinberg. 1999. Functional activity of ectopically expressed estrogen receptor is not sufficient for estrogen-mediated cyclin D1 expression. Cancer Res. 59:4788-4792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Planas-Silva, M. D., Y. Shang, J. L. Donaher, M. Brown, and R. A. Weinberg. 2001. AIB1 enhances estrogen-dependent induction of cyclin D1 expression. Cancer Res. 61:3858-3862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Poy, M. N., L. Eliasson, J. Krutzfeldt, S. Kuwajima, X. Ma, P. E. Macdonald, S. Pfeffer, T. Tuschl, N. Rajewsky, P. Rorsman, and M. Stoffel. 2004. A pancreatic islet-specific microRNA regulates insulin secretion. Nature 432:226-230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sakakura, C., A. Hagiwara, R. Yasuoka, Y. Fujita, M. Nakanishi, K. Masuda, A. Kimura, Y. Nakamura, J. Inazawa, T. Abe, and H. Yamagishi. 2000. Amplification and overexpression of the AIB1 nuclear receptor coactivator gene in primary gastric cancers. Int. J. Cancer 89:217-223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Shao, J., Y. Li, Q. Wu, X. Liang, X. Yu, L. Huang, J. Hou, X. Huang, I. Ernberg, L. F. Hu, and Y. Zeng. 2002. High frequency loss of heterozygosity on the long arms of chromosomes 13 and 14 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Southern China. Chin. Med. J. 115:571-575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sioud, M., and O. Rosok. 2004. Profiling microRNA expression using sensitive cDNA probes and filter arrays. BioTechniques 37:574-580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Takamizawa, J., H. Konishi, K. Yanagisawa, S. Tomida, H. Osada, H. Endoh, T. Harano, Y. Yatabe, M. Nagino, Y. Nimura, T. Mitsudomi, and T. Takahashi. 2004. Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res. 64:3753-3756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Torres-Arzayus, M. I., J. F. De Mora, J. Yuan, F. Vazquez, R. Bronson, M. Rue, W. R. Sellers, and M. Brown. 2004. High tumor incidence and activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway in transgenic mice define AIB1 as an oncogene. Cancer Cell 6:263-274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tsang, Y. S., K. W. Lo, S. F. Leung, P. H. Choi, Y. Fong, J. C. Lee, and D. P. Huang. 1999. Two distinct regions of deletion on chromosome 13q in primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 83:305-308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Volinia, S., G. A. Calin, C. G. Liu, S. Ambs, A. Cimmino, F. Petrocca, R. Visone, M. Iorio, C. Roldo, M. Ferracin, R. L. Prueitt, N. Yanaihara, G. Lanza, A. Scarpa, A. Vecchione, M. Negrini, C. C. Harris, and C. M. Croce. 2006. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:2257-2261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Walter, P., S. Green, G. Greene, A. Krust, J.-M. Bornert, J.-M. Jeltsch, A. Staub, E. Jensen, G. Scrace, M. Waterfield, and P. Chambon. 1985. Cloning of the human estrogen receptor cDNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:7889-7893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Wang, Z., D. W. Rose, O. Hermanson, F. Liu, T. Herman, W. Wu, D. Szeto, A. Gleiberman, A. Krones, K. Pratt, R. Rosenfeld, C. K. Glass, and M. G. Rosenfeld. 2000. Regulation of somatic growth by the p160 coactivator p/CIP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:13549-13554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Yi, R., Y. Qin, I. G. Macara, and B. R. Cullen. 2003. Exportin-5 mediates the nuclear export of pre-microRNAs and short hairpin RNAs. Genes Dev. 17:3011-3016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Zhang, H., F. A. Kolb, L. Jaskiewicz, E. Westhof, and W. Filipowicz. 2004. Single processing center models for human Dicer and bacterial RNase III. Cell 118:57-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zhang, L., J. Huang, N. Yang, J. Greshock, M. S. Megraw, A. Giannakakis, S. Liang, T. L. Naylor, A. Barchetti, M. R. Ward, G. Yao, A. Medina, A. O'Brien-Jenkins, D. Katsaros, A. Hatzigeorgiou, P. A. Gimotty, B. L. Weber, and G. Coukos. 2006. microRNAs exhibit high frequency genomic alterations in human cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:9136-9141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zhou, G., Y. Hashimoto, I. Kwak, S. Y. Tsai, and M. J. Tsai. 2003. Role of the steroid receptor coactivator SRC-3 in cell growth. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23:7742-7755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]