Abstract
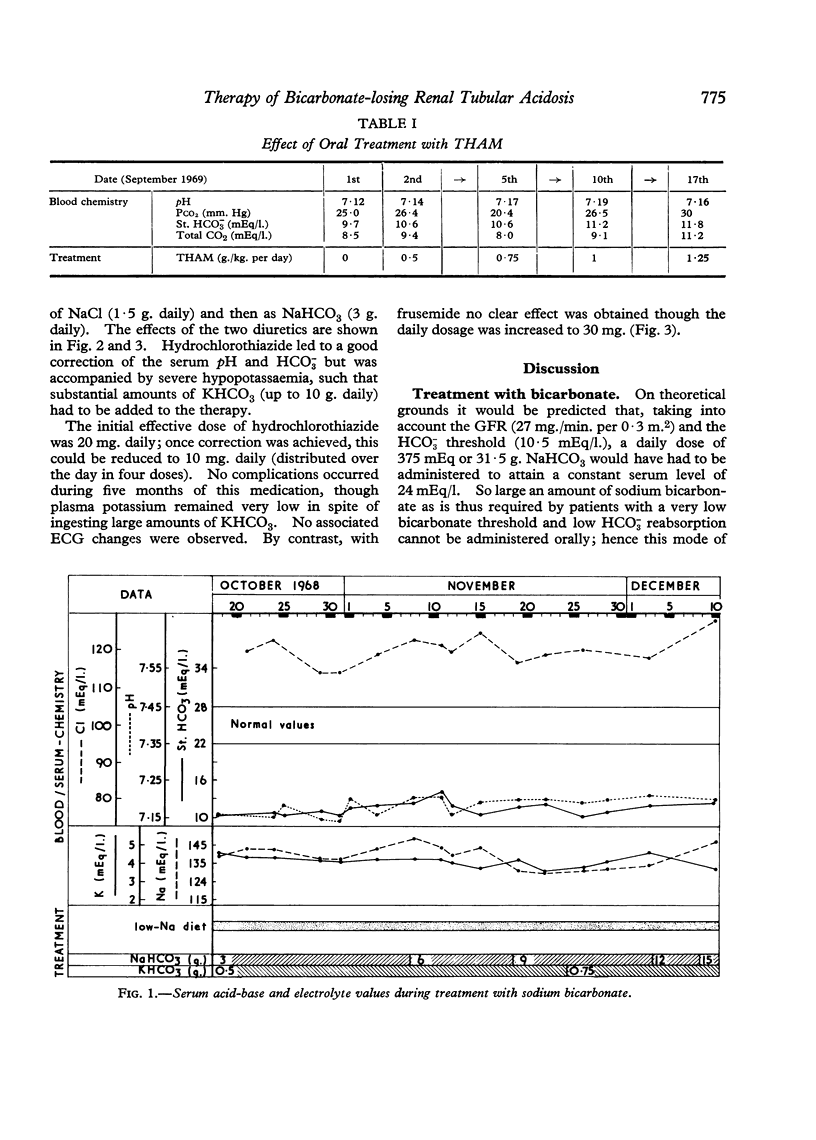
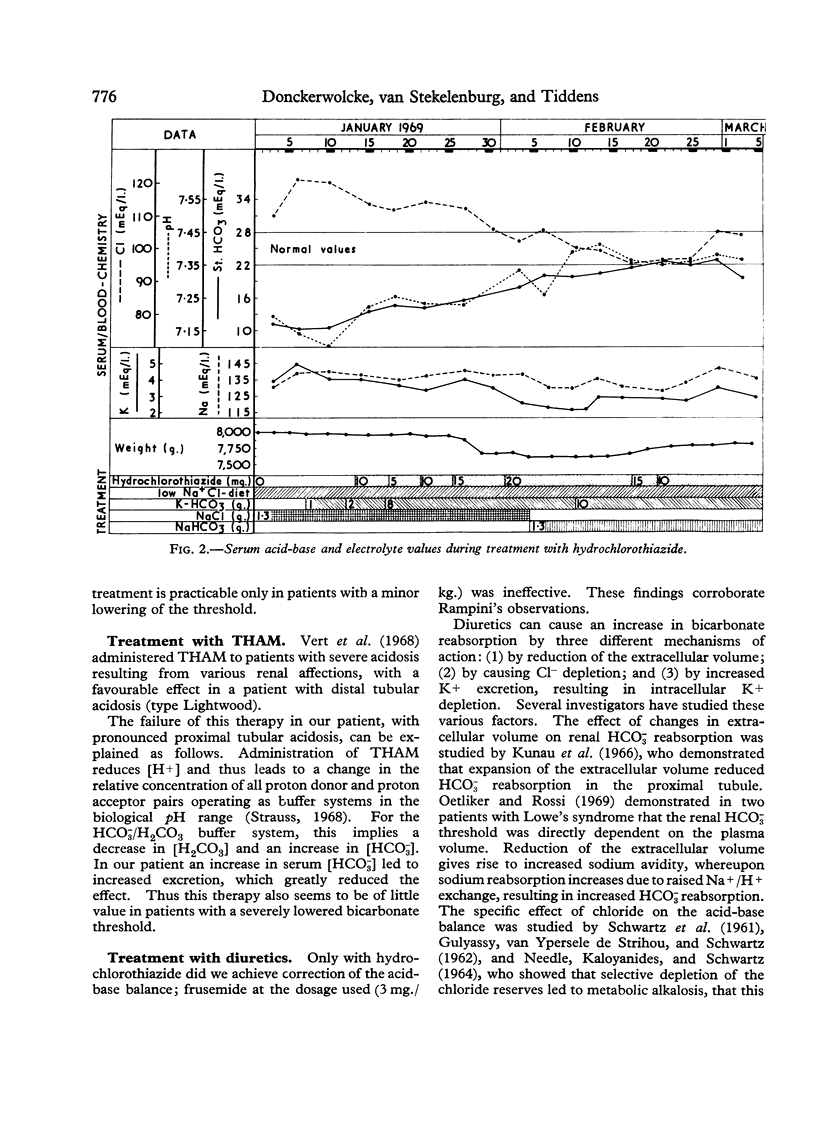
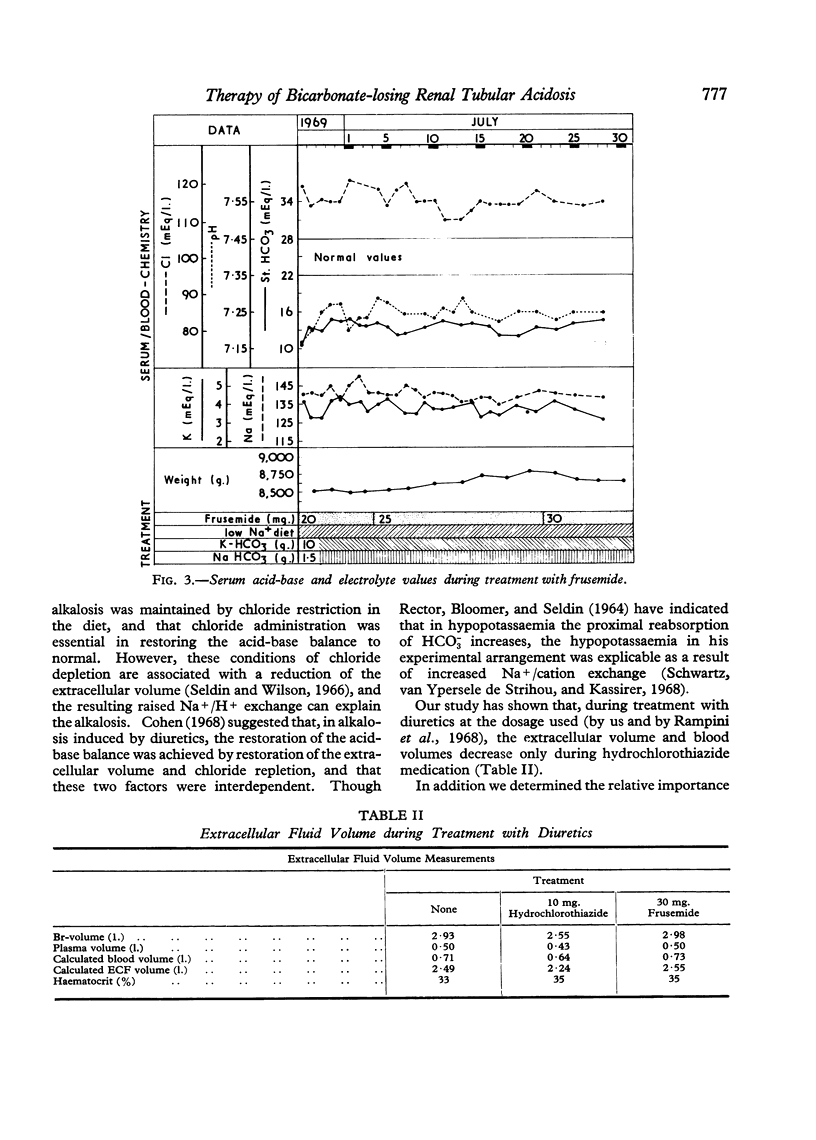
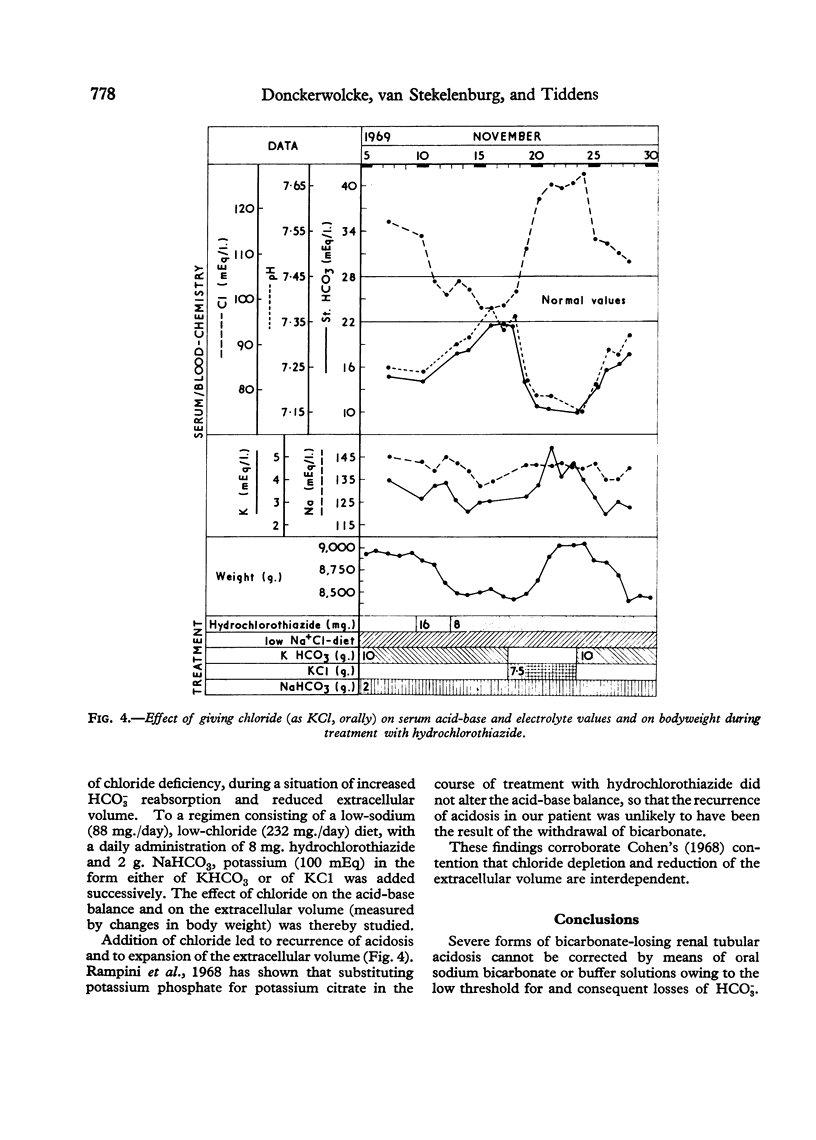
A 2-year-old-girl with severe bicarbonate-losing renal tubular acidosis was treated successively with bicarbonate, THAM, and two diuretics, hydrochlorothiazide and frusemide. Only with hydrochlorothiazide was adequate correction of the acid-base balance achieved. The relative importance of changes induced by this treatment in the extracellular fluid volume and in chloride depletion was assessed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen J. J. Correction of metabolic alkalosis by the kidney after isomertric expansion of extracellular fluid. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1181–1192. doi: 10.1172/JCI105807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donckerwolcke R. A., van Stekelenburg G. J., Tiddens H. A. A case of bicarbonate-losing renal tubular acidosis with defective carboanhydrase activity. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Dec;45(244):769–773. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.244.769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GULYASSY P. F., VAN YPERSELE DE STRIHOU C., SCHWARTZ W. B. On the mechanism of nitrate-induced alkalosis. The possible role of selective chloride depletion in acid-base regulation. J Clin Invest. 1962 Oct;41:1850–1862. doi: 10.1172/JCI104642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEDLE M. A., KALOYANIDES G. J., SCHWARTZ W. B. THE EFFECTS OF SELECTIVE DEPLETION OF HYDROCHLORIC ACID ON ACID-BASE AND ELECTROLYTE EQUILIBRIUM. J Clin Invest. 1964 Sep;43:1836–1846. doi: 10.1172/JCI105057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oetliker O., Rossi E. The influence of extracellular fluid volume on the renal bicarbonate threshold. A study of two children with Lowe's syndrome. Pediatr Res. 1969 Mar;3(2):140–148. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196903000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECTOR F. C., Jr, BLOOMER H. A., SELDIN D. W. EFFECT OF POTASSIUM DEFICIENCY ON THE REABSORPTION OF BICARBONATE IN THE PROXIMAL TUBULE OF THE RAT KIDNEY. J Clin Invest. 1964 Oct;43:1976–1982. doi: 10.1172/JCI105071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ W. B., HAYS R. M., POLAK A., HAYNIE G. D. Effects of chronic hypercapnia on electrolyte and acid-base equilibrium. II. Recovery, with special reference to the influence of chloride intake. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jul;40:1238–1249. doi: 10.1172/JCI104354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz W. B., Van Ypersele de Strihou, Kassirer J. P. Role of anions in metabolic alkalosis and potassium deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1968 Sep 19;279(12):630–639. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196809192791204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano J. R., Boichis H., Edelmann C. M., Jr Bicarbonate reabsorption and hydrogen ion excretion in children with renal tubular acidosis. J Pediatr. 1967 Dec;71(6):802–813. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss J. Tris (hydroxymethyl) amino-methane (Tham): a pediatric evaluation. Pediatrics. 1968 Mar;41(3):667–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. M., Whitehouse R. H., Takaishi M. Standards from birth to maturity for height, weight, height velocity, and weight velocity: British children, 1965. I. Arch Dis Child. 1966 Oct;41(219):454–471. doi: 10.1136/adc.41.219.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vert P., Marchal C., Neimann N., Pierson M. Traitement symptomatique des acidoses renales par administration orale de citrate de THAM. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1968 Jan;25(1):91–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


