Abstract
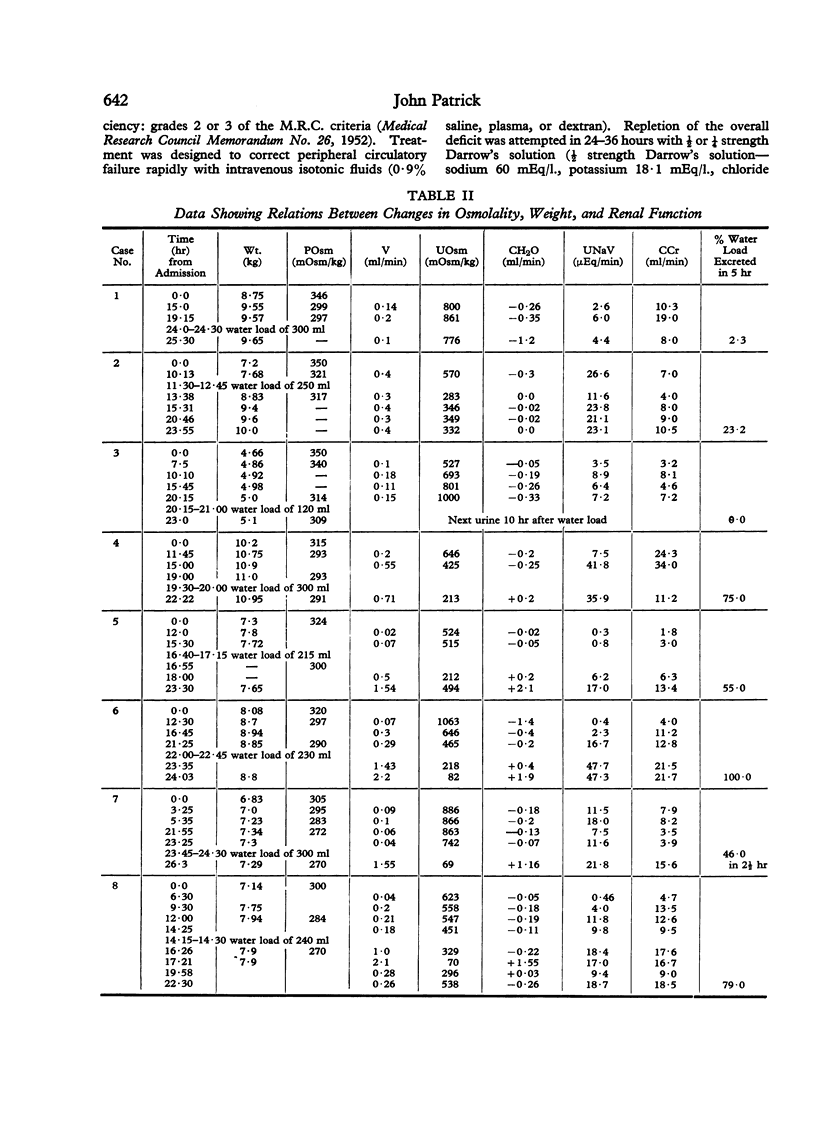
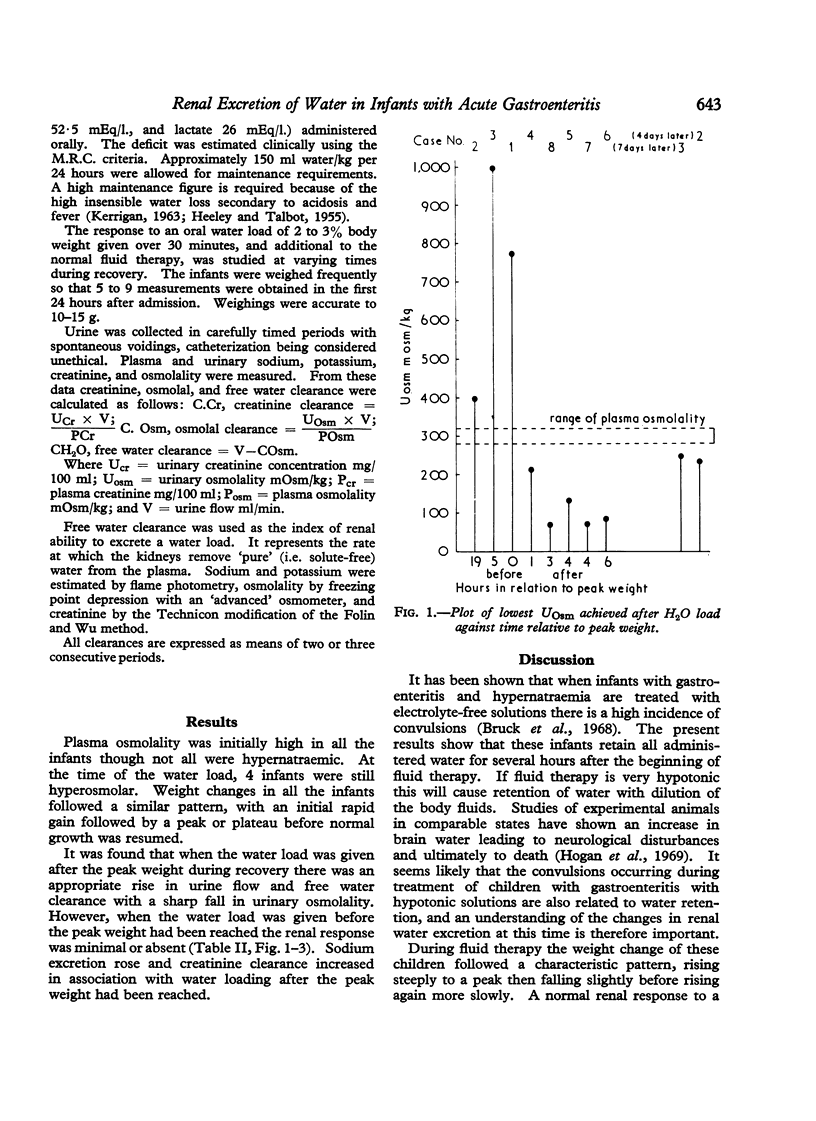
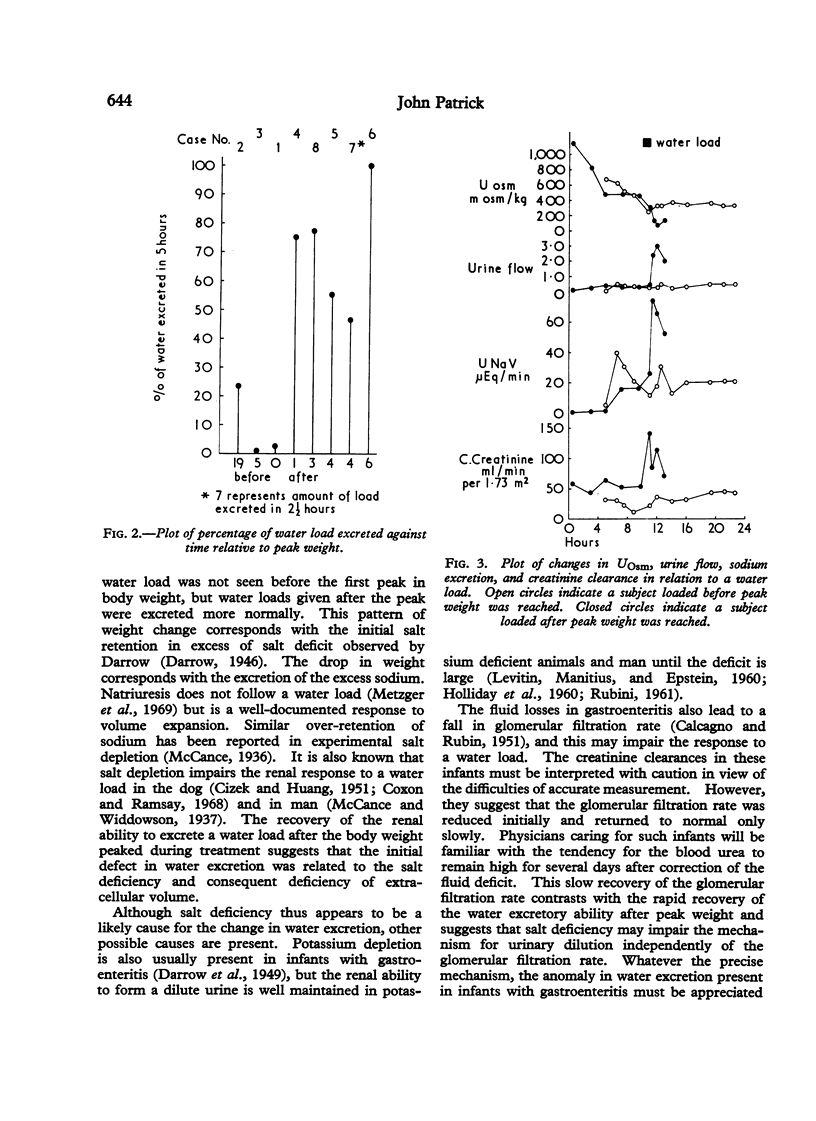
Infants with severe gastroenteritis were given water loads of 20 ml/kg body weight during their recovery. The renal responses were correlated with changes in body weight and osmolality. A water load was not excreted until the body weight had reached a peak. It is concluded that while volume depletion persists administration of hypotonic fluids leads to a fall in osmolality which will not be corrected by renal excretion of water. The relevance of this observation to the high incidence of neurological disturbances during the treatment of hyperosmolar states is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruck E., Abal G., Aceto T., Jr Therapy of infants with hypertonic dehydration due to diarrhea. A controlled study of clinical, chemical, and pathophysiological response to two types of therapeutic fluid regimen, with evaluation of late sequelae. Am J Dis Child. 1968 Mar;115(3):281–301. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1968.02100010283001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALCAGNO P. L., RUBIN M. I. Effect of dehydration produced by water deprivation, diarrhea and vomiting on renal function in infants. Pediatrics. 1951 Mar;7(3):328–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CIZEK L. J., HUANG K. C. Water diuresis in the salt-depleted dog. Am J Physiol. 1951 Nov;167(2):473–484. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.167.2.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coxon R. V., Ramsay D. J. The effect of sodium depletion of the renal response to water-loading in dogs. J Physiol. 1968 Aug;197(3):617–630. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINBERG L., CHEUNG C. S., FLEISHMAN E. The significance of the concentrations of electrolytes in stool water during infantile diarrhea. Am J Dis Child. 1960 Dec;100:809–813. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1960.04020040811002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINBERG L., KILEY J., LUTTRELL C. N. Mass accidental salt poisoning in infancy. A study of a hospital disaster. JAMA. 1963 Apr 20;184:187–190. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.03700160063009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINBERG L., RUSH B. F., Jr, CHEUNG C. S. RENAL EXCRETION OF SODIUM DURING HYPERNATREMIA. EXPERIMENTAL OBSERVATIONS. Am J Dis Child. 1964 May;107:483–488. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1964.02080060485008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEELEY A. M., TALBOT N. B. Insensible water losses per day by hospitalized infants and children. AMA Am J Dis Child. 1955 Sep;90(3):251–255. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1955.04030010253001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLIDAY M. A., SEGAR W. E., BRIGHT N. H., EGAN T. The effect of potassium deficiency on the kidney. Pediatrics. 1960 Dec;26:950–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan G. R., Dodge P. R., Gill S. R., Master S., Sotos J. F. Pathogenesis of seizures occurring during restoration of plasma tonicity to normal in animals previously chronically hypernatremic. Pediatrics. 1969 Jan;43(1):54–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVITIN H., MANITIUS A., EPSTEIN F. H. Urinary dilution in potassium deficiency. Yale J Biol Med. 1960 Apr;32:390–399. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaulay D., Watson M. Hypernatraemia in infants as a cause of brain damage. Arch Dis Child. 1967 Oct;42(225):485–491. doi: 10.1136/adc.42.225.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance R. A., Widdowson E. M. The secretion of urine in man during experimental salt deficiency. J Physiol. 1937 Nov 26;91(2):222–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1937.sp003554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger R. A., Vaamonde L. S., Vaamonde C. A., Papper S. Renal excretion of sodium during oral water loading in man. Nephron. 1969;6(1):11–27. doi: 10.1159/000179709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris-Jones P. H., Houston I. B., Evans R. C. Prognosis of the neurological complications of acute hypernatraemia. Lancet. 1967 Dec 30;2(7531):1385–1389. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)93022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBINI M. E. Water excrtion in potassium-deficient man. J Clin Invest. 1961 Dec;40:2215–2224. doi: 10.1172/JCI104448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIL W. B., WALLACE W. M. Hypertonic dehydration in infancy. Pediatrics. 1956 Feb;17(2):171–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


