Abstract
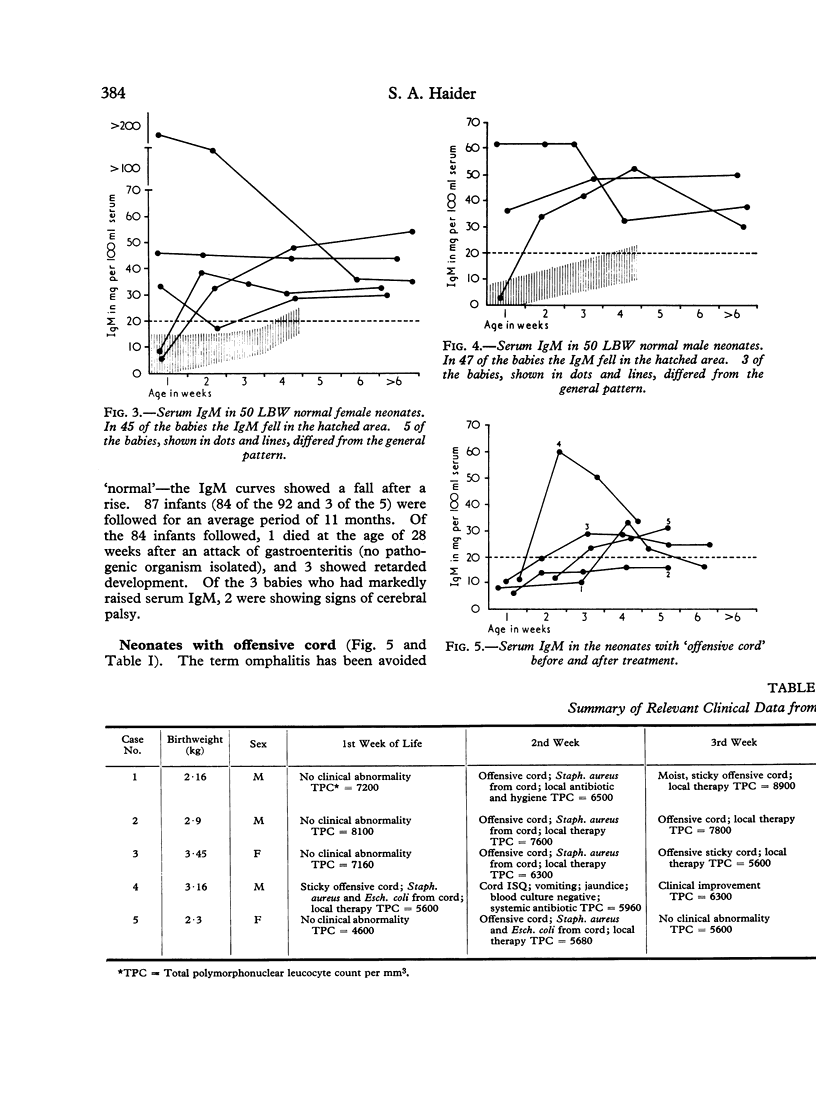
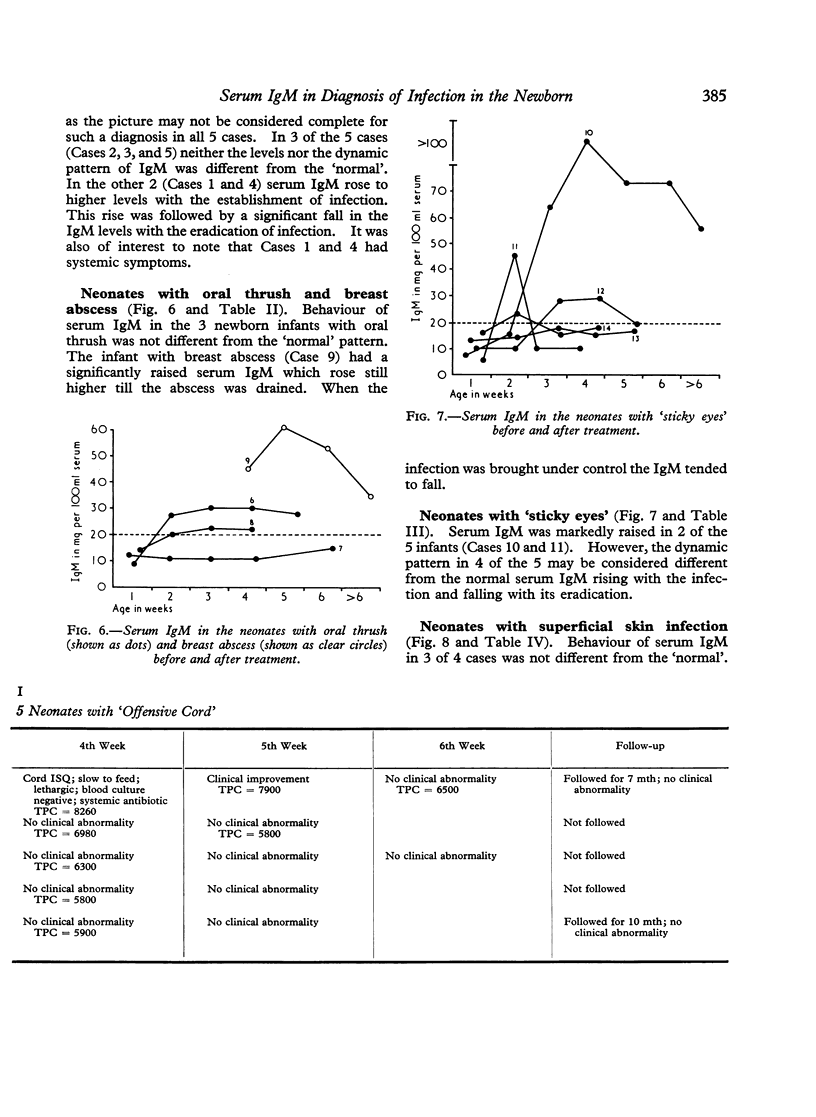
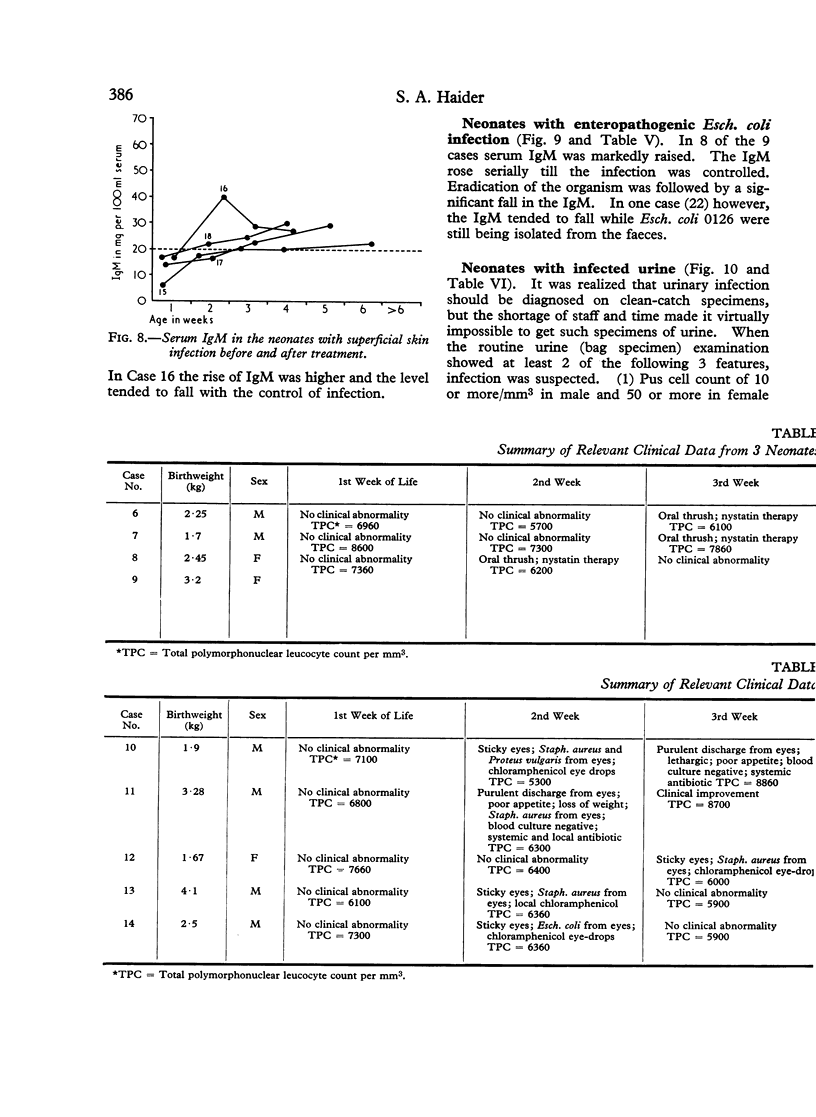
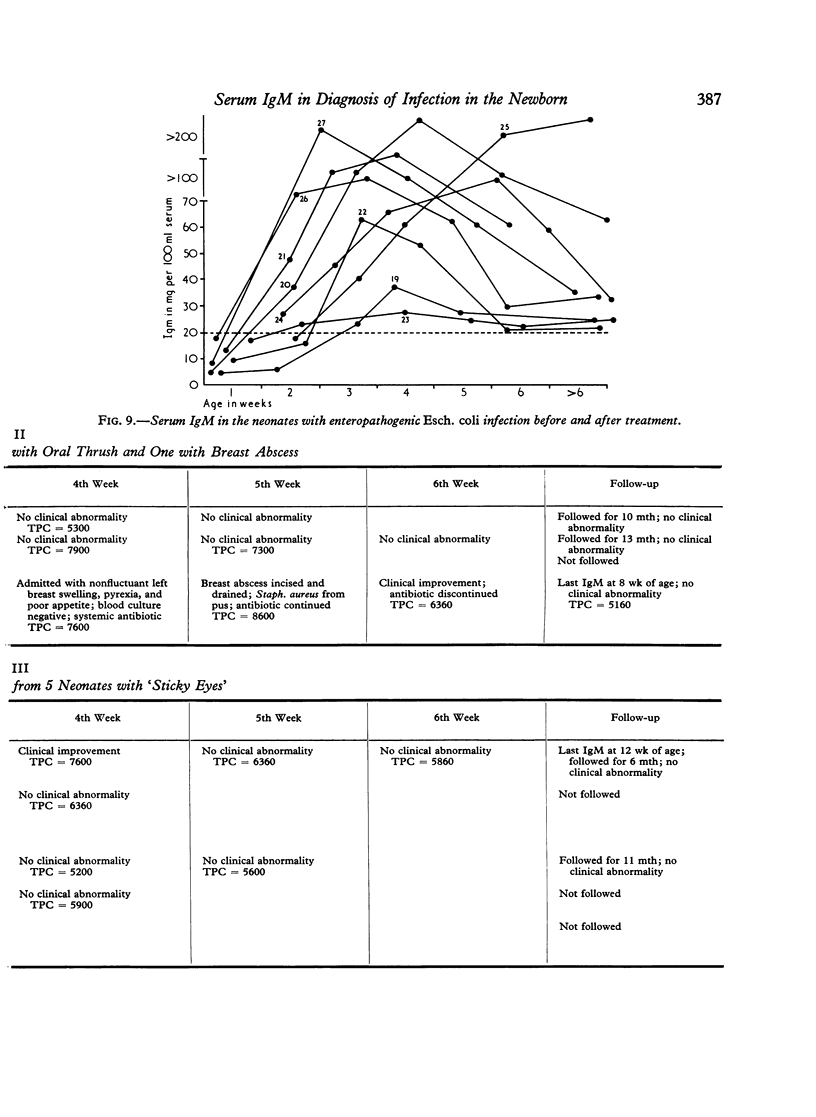
Serum IgM levels were determined at weekly intervals from birth in 100 normal low birthweight and 100 normal birthweight infants during the first 4 weeks of life. The dynamics of serum IgM was also studied in 36 newborn infants with different types of infection and in 19 infants with probable infection. The behaviour of serum IgM in the infants with systemic infection and also in those suffering from superficial infection with systemic symptoms was significantly different from the normal. Serum IgM rose within two days of appearance of symptoms and the rise persisted as long as the infection was `active'. With the eradication of infection the IgM level tended to fall. This characteristic dynamic pattern of serum IgM may be of considerable help in the diagnosis of neonatal infection, especially the clinically inapparent and atypical varieties that may have serious sequelae later in life.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alford C. A., Schaefer J., Blankenship W. J., Straumfjord J. V., Cassady G. A correlative immunologic, microbiologic and clinical approach to the diagnosis of acute and chronic infections in newborn infants. N Engl J Med. 1967 Aug 31;277(9):437–449. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196708312770901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg T. Immunoglobulin levels in infants with low birth weights. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1968 Sep;57(5):369–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1968.tb07307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S. G., Berg T. Immunoglobulin levels in healthy children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1967 Nov;56(6):572–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1967.tb15982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Tobin B. M. Umbilical-cord IgM and amniotic infection. Lancet. 1969 Feb 15;1(7590):372–372. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORTON P. M., KUNZ H., PRATT E. L. Electrophoretic analysis of serum proteins in premature infants. Pediatrics. 1952 Nov;10(5):527–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes K., Markham R. L., Maxwell P. M., Monk-Jones M. E. Immunoglobulins and the X-chromosome. Br Med J. 1969 Aug 23;3(5668):439–441. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5668.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Ammann A. J., Cherry J. D. Elevated cord macroglobulins in the diagnosis of intrauterine infections. N Engl J Med. 1966 Nov 3;275(18):971–977. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196611032751801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Fudenberg H. H. Serum levels of immune globulins in health and disease: a survey. Pediatrics. 1966 May;37(5):715–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


