Abstract
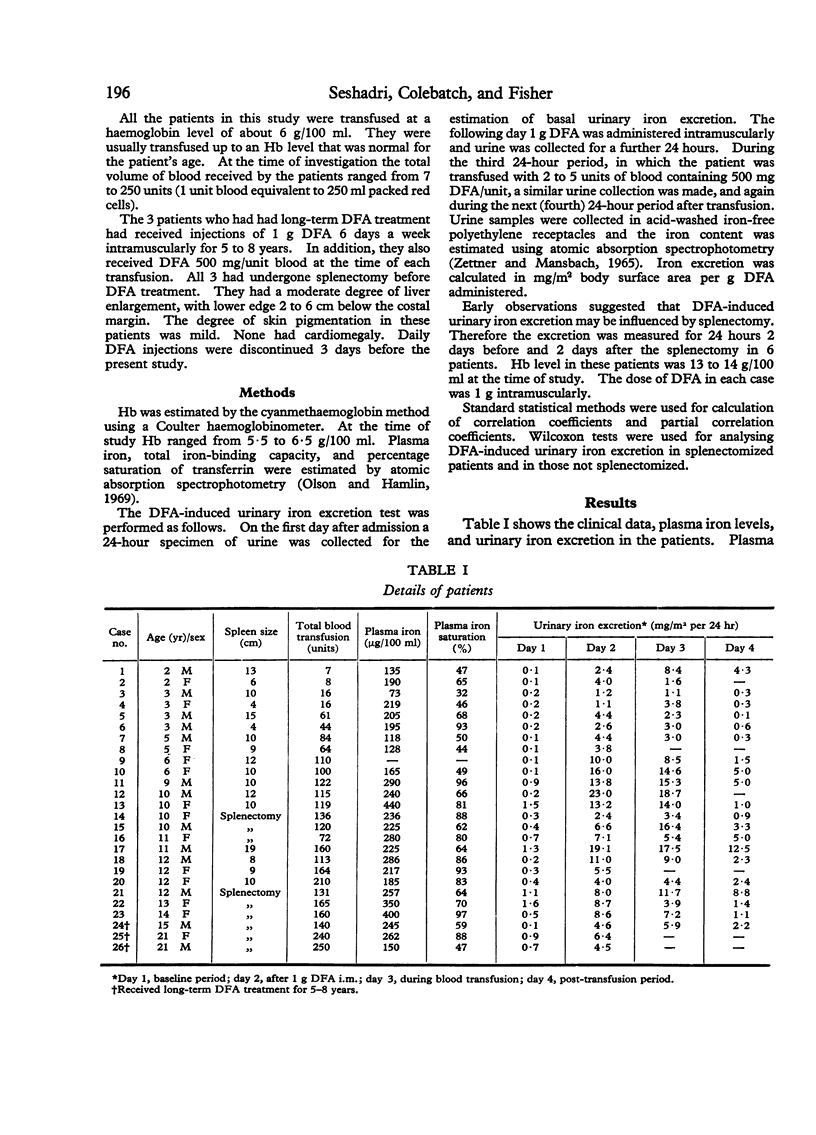
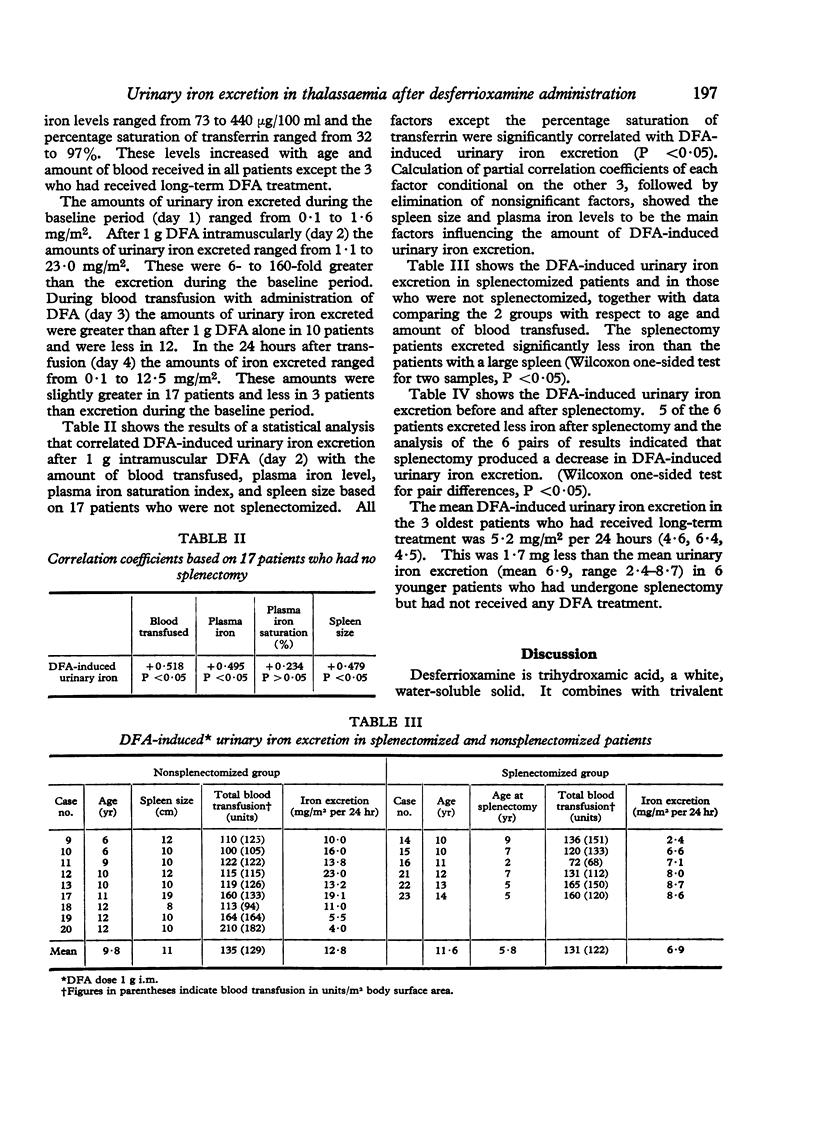
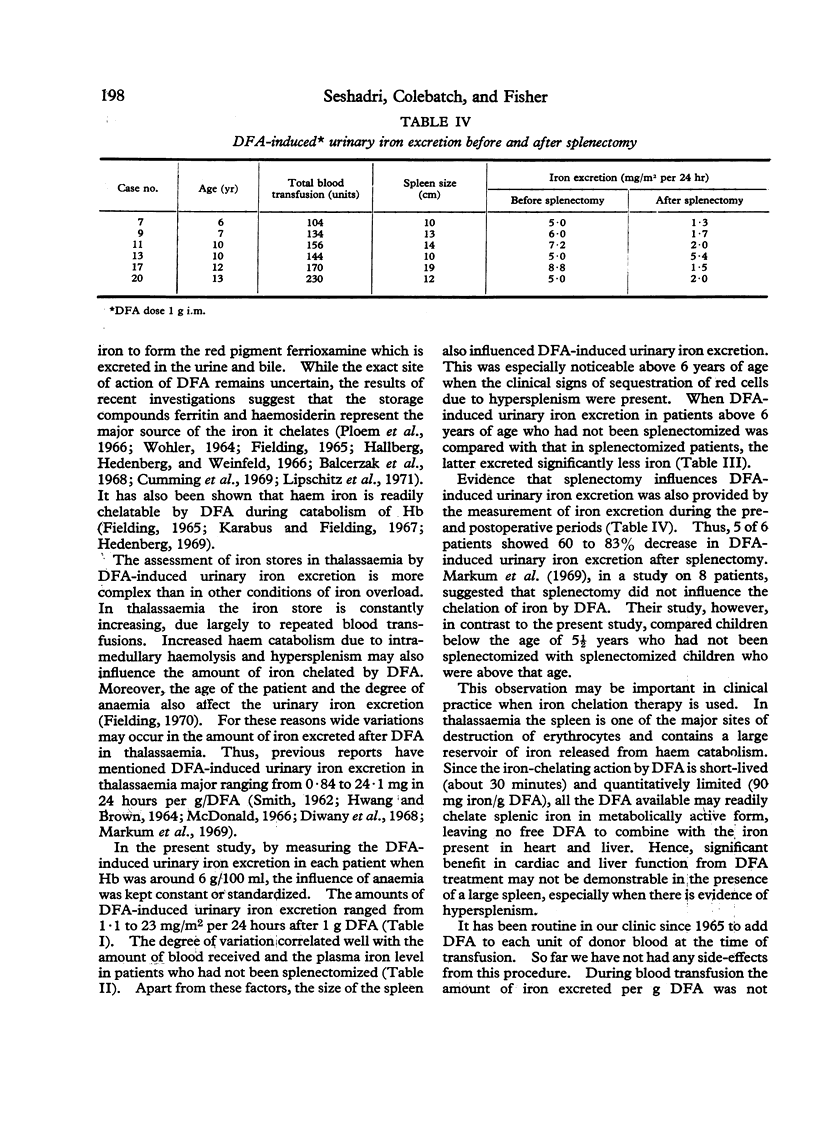
Urinary iron excretion induced with desferrioxamine (DFA) was estimated in 26 children with thalassaemia major. Four separate 24-hour urine collections were made—during a baseline period, after intramuscular injection of DFA 1 g, during blood transfusion with DFA 0·5 g/unit transfused blood, and during the post-transfusion period. Urinary iron, plasma iron, and total iron-binding capacity were estimated by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Urinary iron excretion in the 24 hours after 1 g DFA ranged from 1·1 to 23 mg/m2 surface area compared with 0·1 to 1·6 mg/m2 during the baseline period. A positive correlation was obtained between DFA-induced urinary iron excretion and the amount of blood transfused, plasma iron level, and size of the spleen. Splenectomized patients excreted less iron after DFA than those who were not splenectomized. DFA-induced urinary iron was measured before and after splenectomy in 6 patients. In 5 of the 6 patients a drop in iron excretion was observed and the analysis of the 6 pairs of results indicated that splenectomy produced a decrease in DFA-induced urinary iron excretion.
These findings indicate that the enlarged spleen in thalassaemia is a major source of iron chelated by DFA. It is suggested that treatment with DFA in the presence of a large spleen may be ineffective in removing excess iron from the myocardium and liver.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balcerzak S. P., Westerman M. P., Heinle E. W., Taylor F. H. Measurement of iron stores using deferoxamine. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Mar;68(3):518–525. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-3-518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumming R. L., Millar J. A., Smith J. A., Goldberg A. Clinical and laboratory studies on the action of desferrioxamine. Br J Haematol. 1969 Sep;17(3):257–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb01371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diwany M., Gabr M., el Hefni A., Mokhtar N. Desferrioxamine in thalassaemia. Arch Dis Child. 1968 Jun;43(229):340–343. doi: 10.1136/adc.43.229.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIELDING J. DIFFERENTIAL FERRIOXAMINE TEST FOR MEASURING CHELATABLE BODY IRON. J Clin Pathol. 1965 Jan;18:88–97. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding J. Storage iron and desferrioxamine. Proc R Soc Med. 1970 Dec;63(12):1218–1221. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HWANG Y. F., BROWN E. B. EVALUATION OF DEFEROXAMINE IN IRON OVERLOAD. Arch Intern Med. 1964 Dec;114:741–753. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1964.03860120053003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karabus C. D., Fielding J. Desferrioxamine chelatable iron in haemolytic, megaloblastic and sideroblastic anaemias. Br J Haematol. 1967 Nov;13(6):924–933. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb08862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipschitz D. A., Dugard J., Simon M. O., Bothwell T. H., Charlton R. W. The site of action of desferrioxamine. Br J Haematol. 1971 Apr;20(4):395–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb07051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markum A. H., Iskandar W., Keng K. L., Odang O. Iron excretion in thalassemia after the administration of chelating agents. Paediatr Indones. 1969 May-Jun;9(3):89–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald R. Deferoxamine and diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) in thalassemia. J Pediatr. 1966 Oct;69(4):563–571. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(66)80041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson A. D., Hamlin W. B. A new method for serum iron and total iron-binding capacity by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Clin Chem. 1969 Jun;15(6):438–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploem J. E., de Wael J., Verloop M. C., Punt K. Sideruria following a single dose of desferrioxamine-B as a diagnostic test in iron overload. Br J Haematol. 1966 Jul;12(4):396–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1966.tb05649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH R. S. Iron excretion in thalassaemia major after administration of chelating agents. Br Med J. 1962 Dec 15;2(5319):1577–1580. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5319.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wöhler F. Diagnosis of iron storage disease with desferrioxamine (Desferal test). Acta Haematol. 1964 Dec;32(6):321–337. doi: 10.1159/000209579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zettner A., Mansbach L. Application of atomic absorption spectrophotometry in the determination of iron in urine. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Nov;44(5):517–519. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/44.5.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


