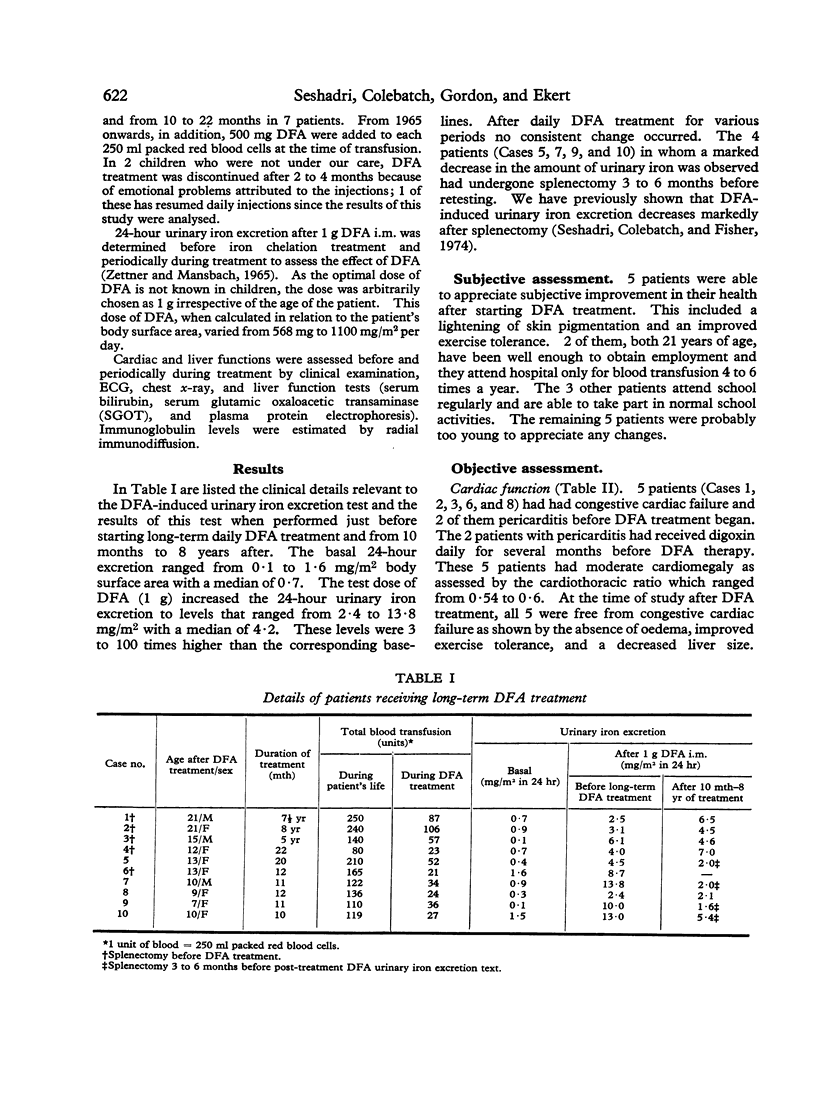
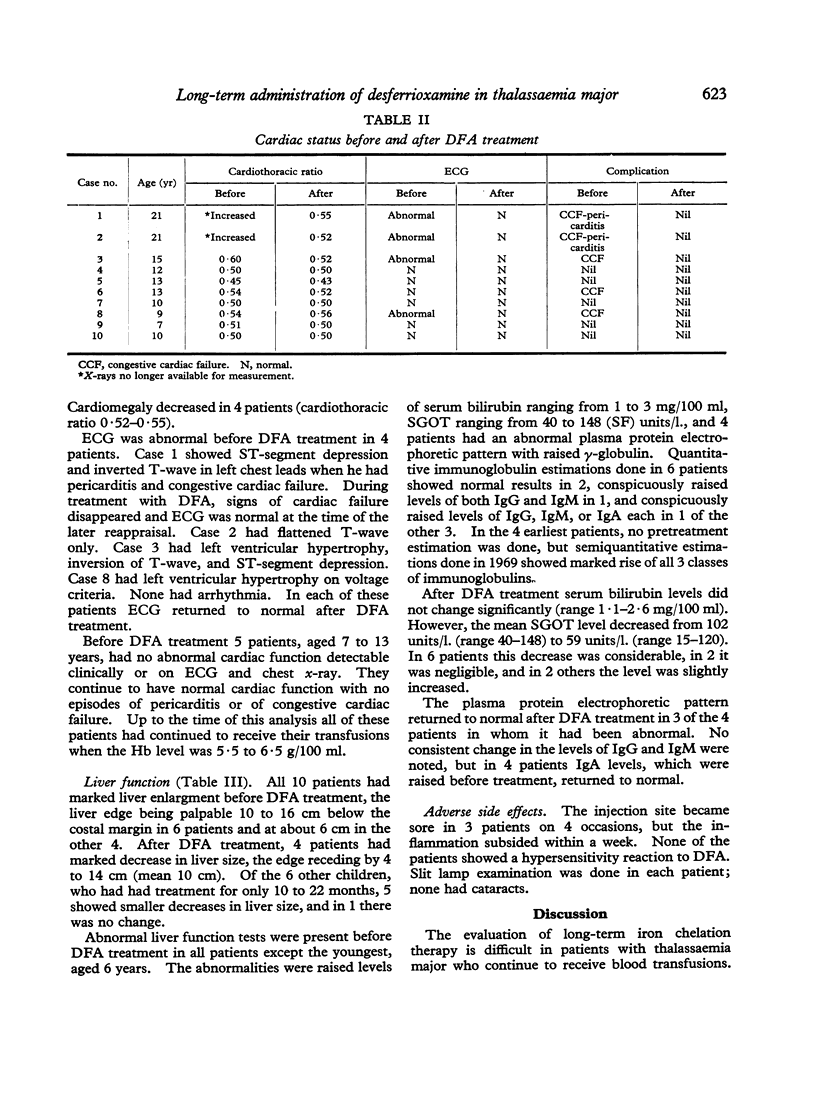
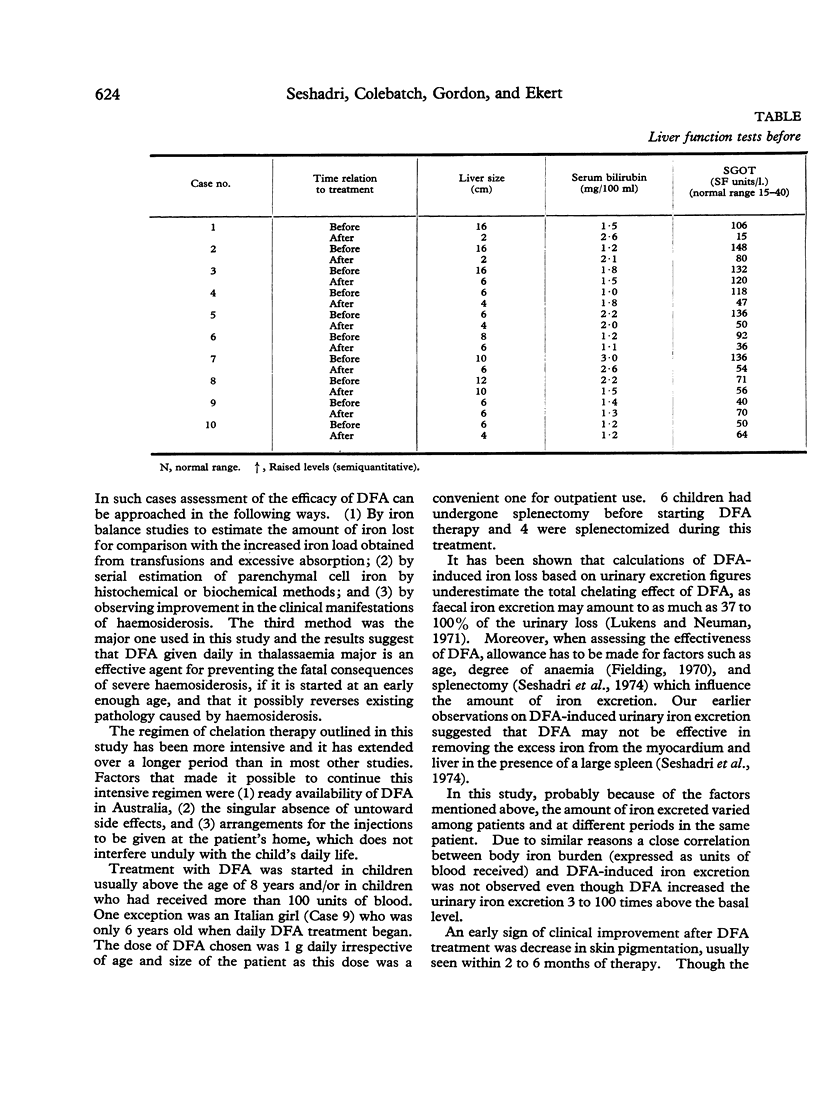
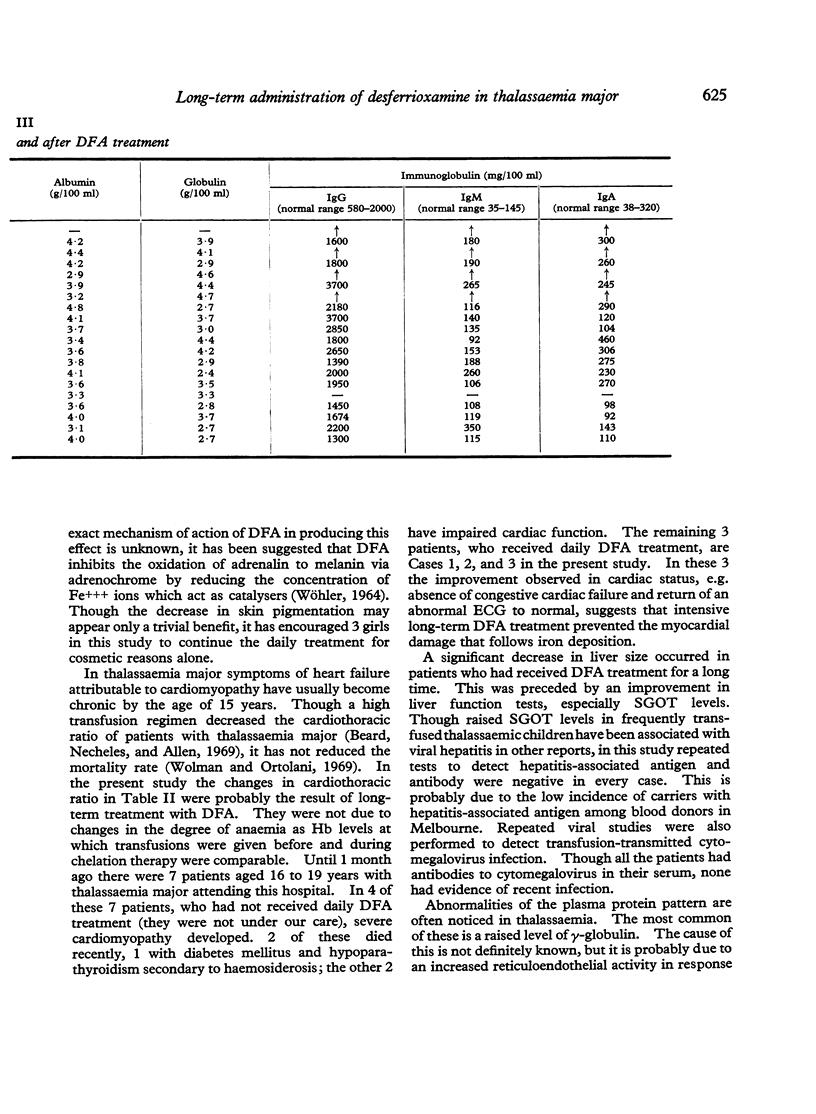
Abstract
Studies of desferrioxamine (DFA) as a specific iron-chelating agent in the treatment of haemosiderosis have been reported in various conditions, but there has been only limited evaluation of its long-term use in thalassaemia major. In the present study 1 g DFA was given intramuscularly daily 6 days per week in 3 patients for 5 to 8 years, and in another 7 patients for 10 to 22 months. In addition, 500 mg DFA was added to each unit of donor blood at the time of transfusions. Urinary iron excretion after DFA was estimated using atomic absorption spectrophotometry both before and periodically during DFA treatment. During follow-up, cardiac and liver functions were assessed by ECG, chest x-ray, and liver function tests.
The results show that DFA therapy increased urinary iron excretion, and that this was associated with a significant improvement in the clinical symptoms and signs of haemosiderosis and with return towards normal in the ECG and liver function tests.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beard M. E., Necheles T. F., Allen D. M. Clinical experience with intensive transfusion therapy in Cooley's anemia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Nov 20;165(1):415–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb27812.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diwany M., Gabr M., el Hefni A., Mokhtar N. Desferrioxamine in thalassaemia. Arch Dis Child. 1968 Jun;43(229):340–343. doi: 10.1136/adc.43.229.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIS J. T., SCHULMAN I., SMITH C. H. Generalized siderosis with fibrosis of liver and pancreas in Cooley's (Mediterranean) anemia; with observations on the pathogenesis of the siderosis and fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 1954 Mar-Apr;30(2):287–309. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLE M. A., ERLANDSON M., SMITH C. H. LATE CARDIAC COMPLICATIONS OF CHRONIC, SEVERE, REFRACTORY ANEMIA WITH HEMOCHROMATOSIS. Circulation. 1964 Nov;30:698–705. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.30.5.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINK H. TRANSFUSION HEMOCHROMATOSIS IN COOLEY'S ANEMIA. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Oct 7;119:680–685. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb54068.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding J. Storage iron and desferrioxamine. Proc R Soc Med. 1970 Dec;63(12):1218–1221. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn D. M. Proceedings: 5-year controlled trial of chelating agents in treatment of thalassaemia major. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Oct;48(10):829–829. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.10.829-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HWANG Y. F., BROWN E. B. EVALUATION OF DEFEROXAMINE IN IRON OVERLOAD. Arch Intern Med. 1964 Dec;114:741–753. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1964.03860120053003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukens J. N., Neuman L. A. EXcretion and distribution of iron during chronic deferoxamine therapy. Blood. 1971 Nov;38(5):614–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markum A. H., Iskandar W., Keng K. L., Odang O. Iron excretion in thalassemia after the administration of chelating agents. Paediatr Indones. 1969 May-Jun;9(3):89–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald R. Deferoxamine and diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) in thalassemia. J Pediatr. 1966 Oct;69(4):563–571. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(66)80041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seshadri R., Colebatch J. H., Fisher R. Urinary iron excretion in thalassaemia after desferrioxamine administration. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Mar;49(3):195–199. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.3.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasi C., Wasi P., Thongcharoen P. Serum-immunoglobulin levels in thalassaemia and the effects of splenectomy. Lancet. 1971 Jul 31;2(7718):237–239. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92573-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman H. S., Brown E. B. Clinical usefulness of iron chelating agents. Prog Hematol. 1969;6:338–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolman I. J., Ortolani M. Some clinical features of Cooley's anemia patients as related to transfusion schedules. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Nov 20;165(1):407–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb27811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wöhler F. Diagnosis of iron storage disease with desferrioxamine (Desferal test). Acta Haematol. 1964 Dec;32(6):321–337. doi: 10.1159/000209579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zettner A., Mansbach L. Application of atomic absorption spectrophotometry in the determination of iron in urine. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Nov;44(5):517–519. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/44.5.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


