Abstract
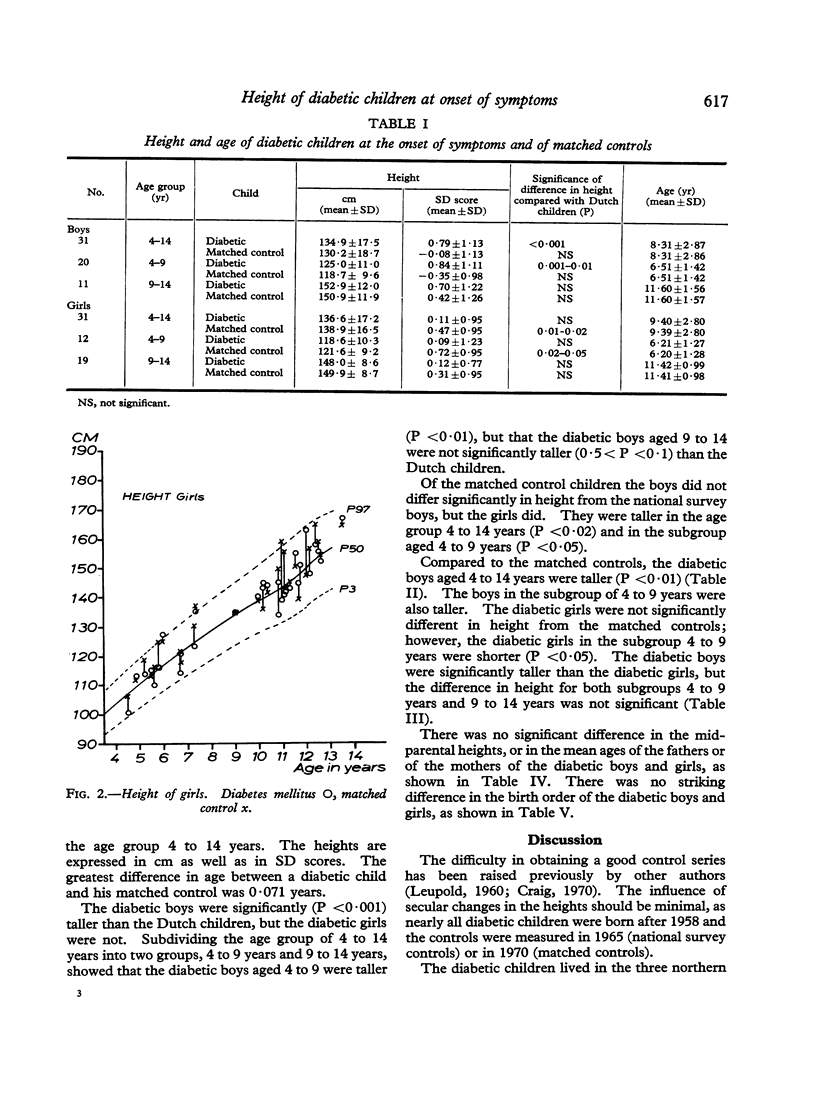
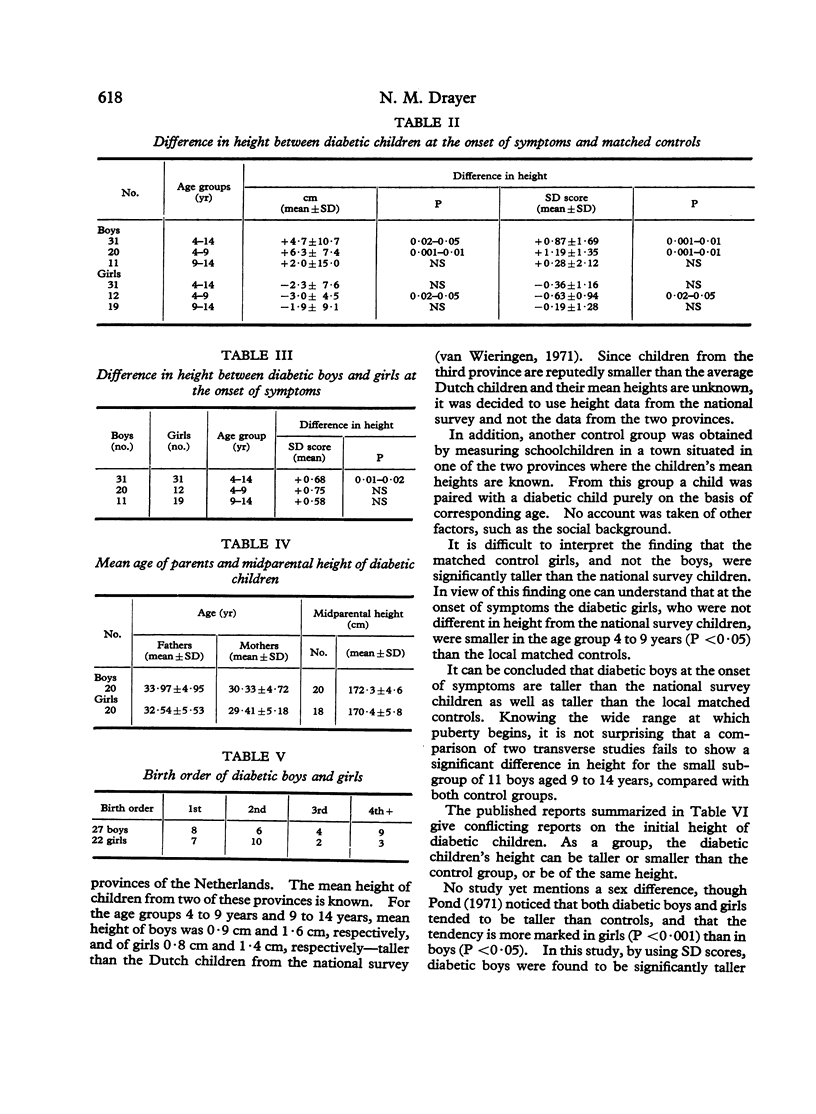
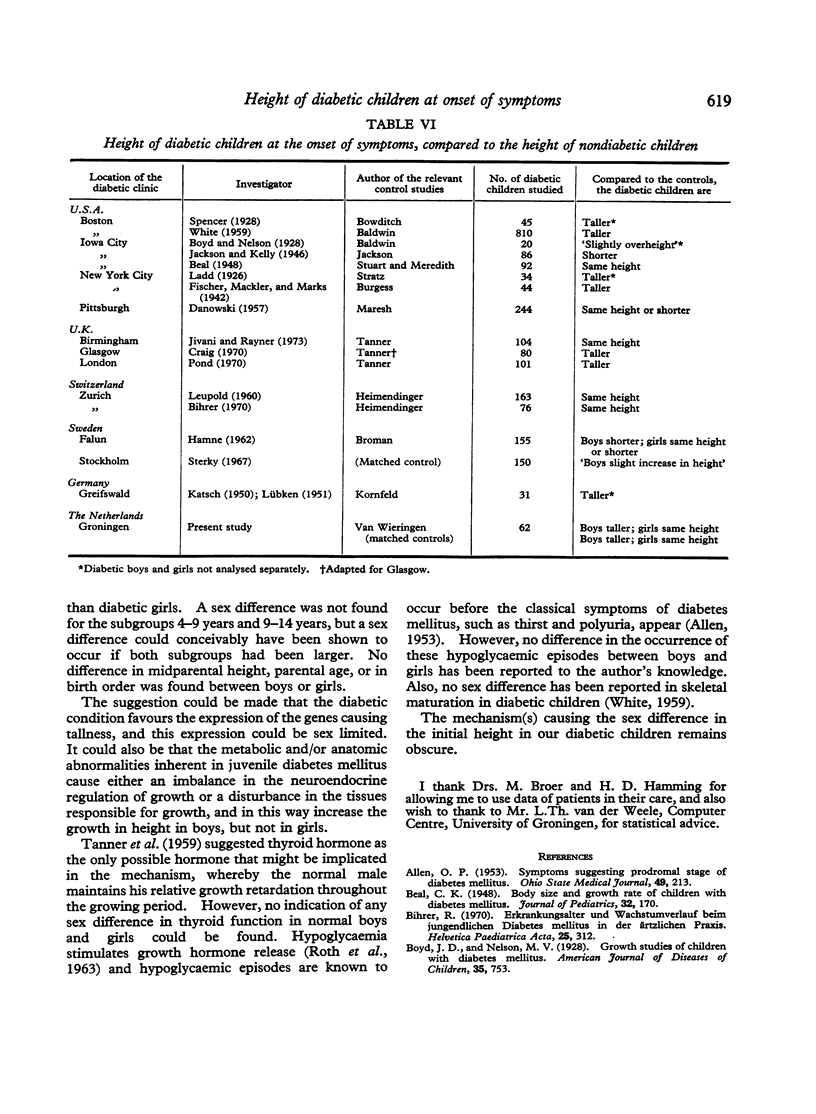
At the onset of classical symptoms of diabetes mellitus, the height of the boys (expressed as SD score) was greater than the height of the girls. Also, diabetic boys were significantly taller than healthy (control) boys, but diabetic girls were not significantly taller than control girls. There was no significant difference in the midparental height, or in the age of the parents of the diabetic boys and girls.
Full text
PDF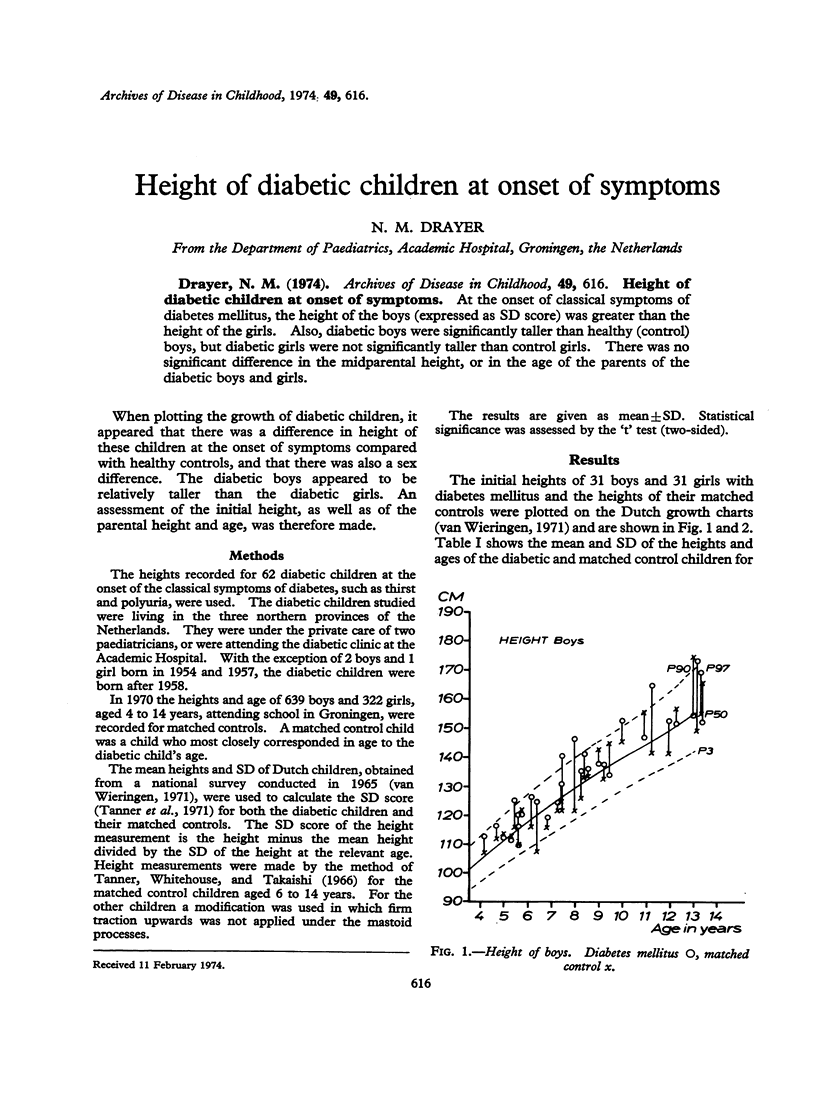

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN O. P. Symptoms suggesting prodromal stage of diabetes mellitus. Ohio State Med J. 1953 Mar;49(3):213–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bihrer R. Erkrankungsalter und Wachstumsverlauf beim jugendlichen Diabetes mellitus in der ärztlichen Praxis. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1970 Jul;25(3):312–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. O. Growth as a measurement of control in the management of diabetic children. Postgrad Med J. 1970 Sep;46(Suppl):607–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jivani S. K., Rayner P. H. Does control influence the growth of diabetic children? Arch Dis Child. 1973 Feb;48(2):109–115. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.2.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATSCH G. Uber die prädiabetische Phase der Zuckerkrankheit. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1950 Oct 6;75(40):1331–1332. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1117669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEUPOLD R. [Age of onset of the disease and course of growth in juvenile diabetes mellitus]. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1960 Sep;15:336–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pond H. Some aspects of growth in diabetic children. Postgrad Med J. 1970 Sep;46(Suppl):616–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH J., GLICK S. M., YALOW R. S., BERSONSA Hypoglycemia: a potent stimulus to secretion of growth hormone. Science. 1963 May 31;140(3570):987–988. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3570.987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterky G. Growth pattern in juvenile diabetes. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1967;(Suppl):80–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1967.tb05231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANNER J. M., PRADER A., HABICH H., FERGUSON-SMITH M. A. Genes on the Y chromosome influencing rate of maturation in man: skeletal age studies in children with Klinefelter's (XXY) and Turner's (XO) syndromes. Lancet. 1959 Aug 22;2(7095):141–144. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)90558-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. M., Whitehouse R. H., Hughes P. C., Vince F. P. Effect of human growth hormone treatment for 1 to 7 years on growth of 100 children, with growth hormone deficiency, low birthweight, inherited smallness, Turner's syndrome, and other complaints. Arch Dis Child. 1971 Dec;46(250):745–782. doi: 10.1136/adc.46.250.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. M., Whitehouse R. H., Takaishi M. Standards from birth to maturity for height, weight, height velocity, and weight velocity: British children, 1965. II. Arch Dis Child. 1966 Dec;41(220):613–635. doi: 10.1136/adc.41.220.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


