Abstract
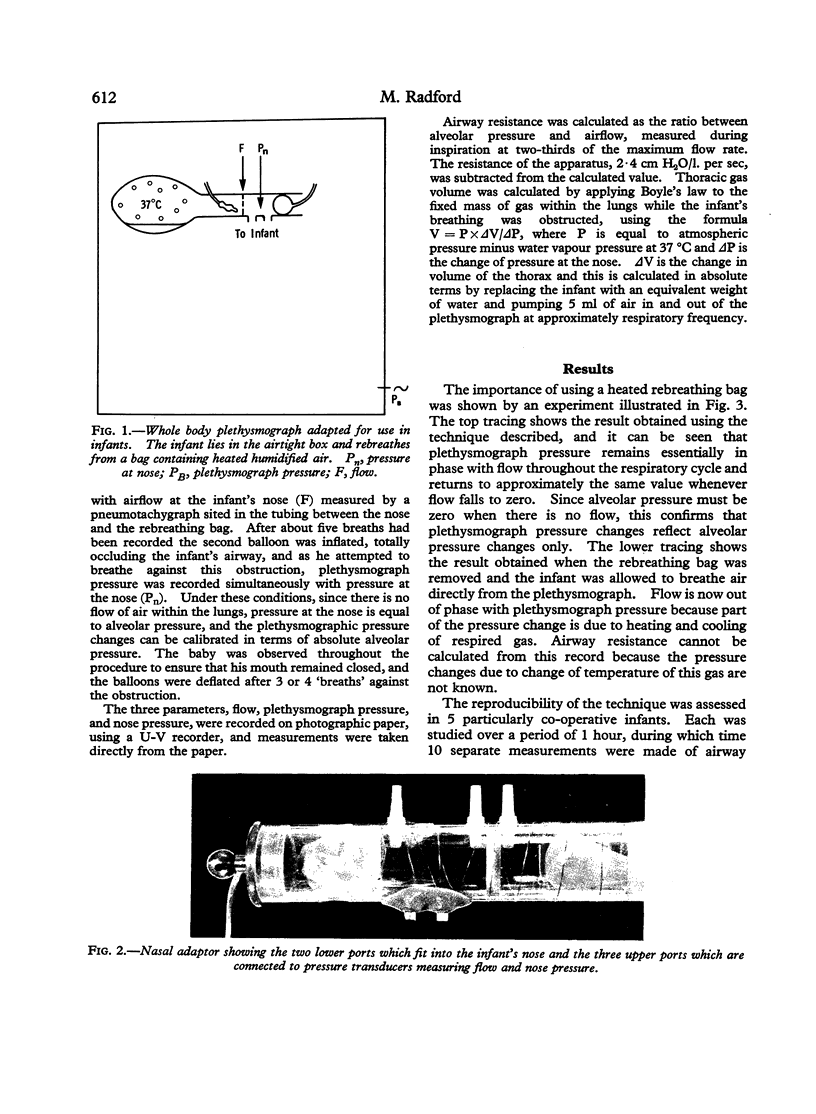
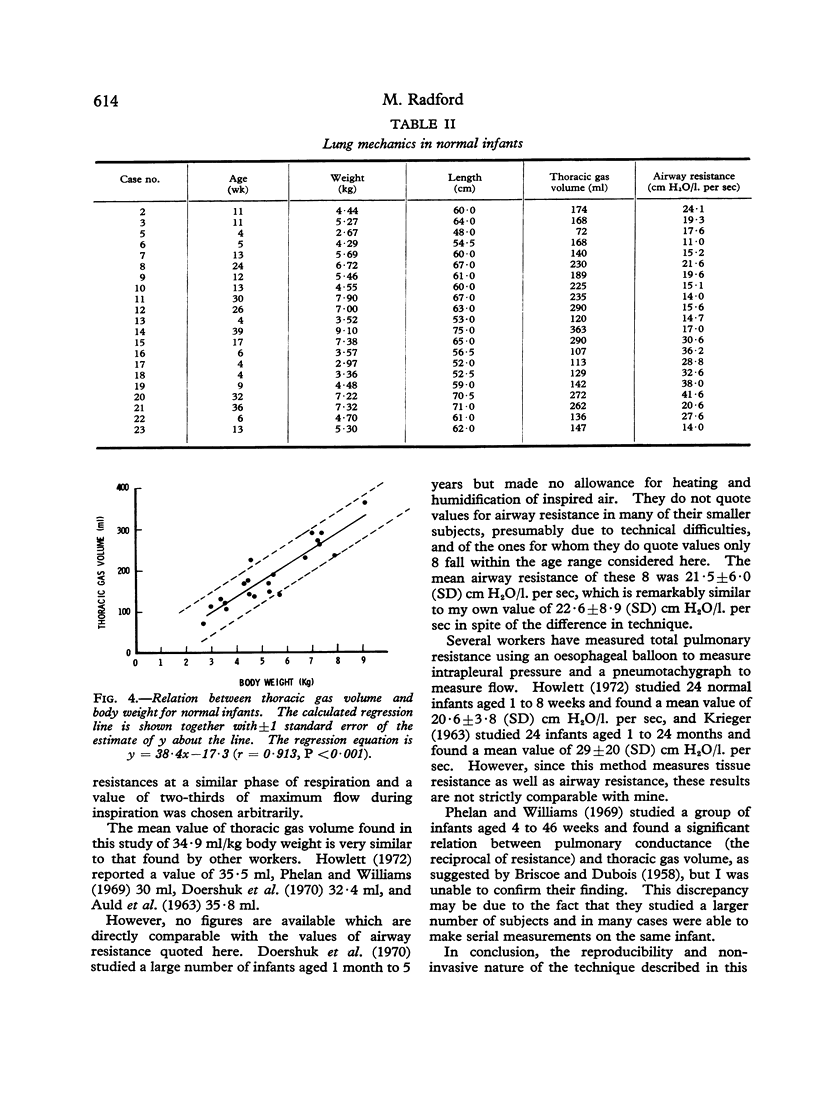
Airway resistance and thoracic gas volume were measured in 21 normal infants aged 1 to 10 months using a whole body plethysmograph. Precautions were taken to eliminate temperature changes of inspired and expired gas. The mean value of airway resistance was 22·6 ± 8·9 (SD) cm H2O/l. per sec, and the mean thoracic gas volume in relation to body weight 34·9 ± 5·8 (SD) ml/kg. The reproducibility of the technique was assessed by making repeated measurements in 5 subjects, when the mean coefficient of variation of airway resistance was 11·8% and of thoracic gas volume 10·1%.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AULD P. A., NELSON N. M., CHERRY R. B., RUDOLPH A. J., SMITH C. A. Measurement of thoracic gas volume in the newborn infant. J Clin Invest. 1963 Apr;42:476–483. doi: 10.1172/JCI104736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRISCOE W. A., DUBOIS A. B. The relationship between airway resistance, airway conductance and lung volume in subjects of different age and body size. J Clin Invest. 1958 Sep;37(9):1279–1285. doi: 10.1172/JCI103715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., BEDELL G. N., MARSHALL R., COMROE J. H., Jr A rapid plethysmographic method for measuring thoracic gas volume: a comparison with a nitrogen washout method for measuring functional residual capacity in normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):322–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI103281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., COMROE J. H., Jr A new method for measuring airway resistance in man using a body plethysmograph: values in normal subjects and in patients with respiratory disease. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):327–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI103282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doershuk C. F., Downs T. D., Matthews L. W., Lough M. D. A method for ventilatory measurements in subjects 1 month--5 years of age: Normal results and observations in disease. Pediatr Res. 1970 Mar;4(2):165–174. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197003000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett G. Lung mechanics in normal infants and infants with congenital heart disease. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Oct;47(255):707–715. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.255.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAEGER M. J., OTIS A. B. MEASUREMENT OF AIRWAY RESISTANCE WITH A VOLUME DISPLACEMENT BODY PLETHYSMOGRAPH. J Appl Physiol. 1964 Jul;19:813–820. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.4.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRIEGER I. Studies on mechanics of respiration in infancy. Am J Dis Child. 1963 May;105:439–448. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1963.02080040441003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelan P. D., Williams H. E. Ventilatory studies in healthy infants. Pediatr Res. 1969 Sep;3(5):425–432. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196909000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



