Abstract
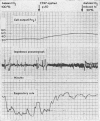
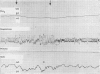
The use of a continuously recording intravascular Po2 electrode is described. The electrode, based on the Galvanic principle, is built into the tip of a French gauge (FG) 5 umbilical arterial catheter. Its use has considerably improved the management of oxygen therapy in the seriously ill premature newborn infant and has done so with at least a 50% reduction in the amount of blood needed to be removed for gas analysis.
Full text
PDF
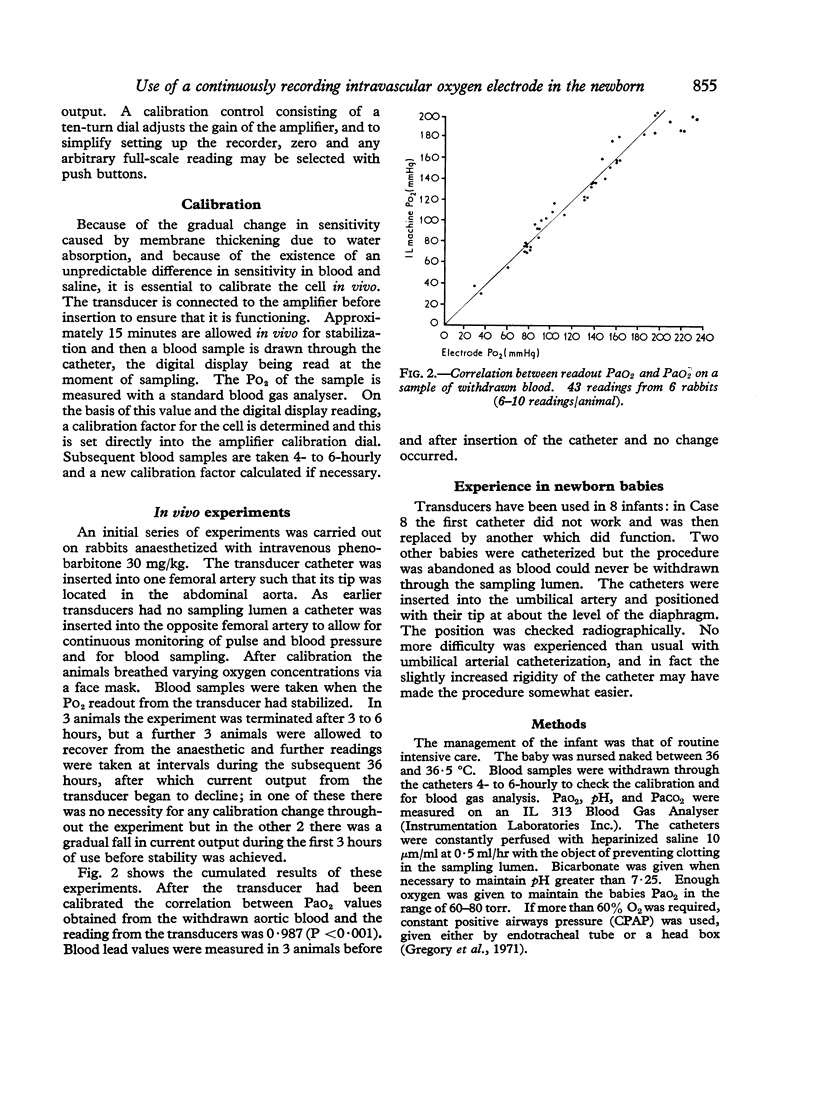
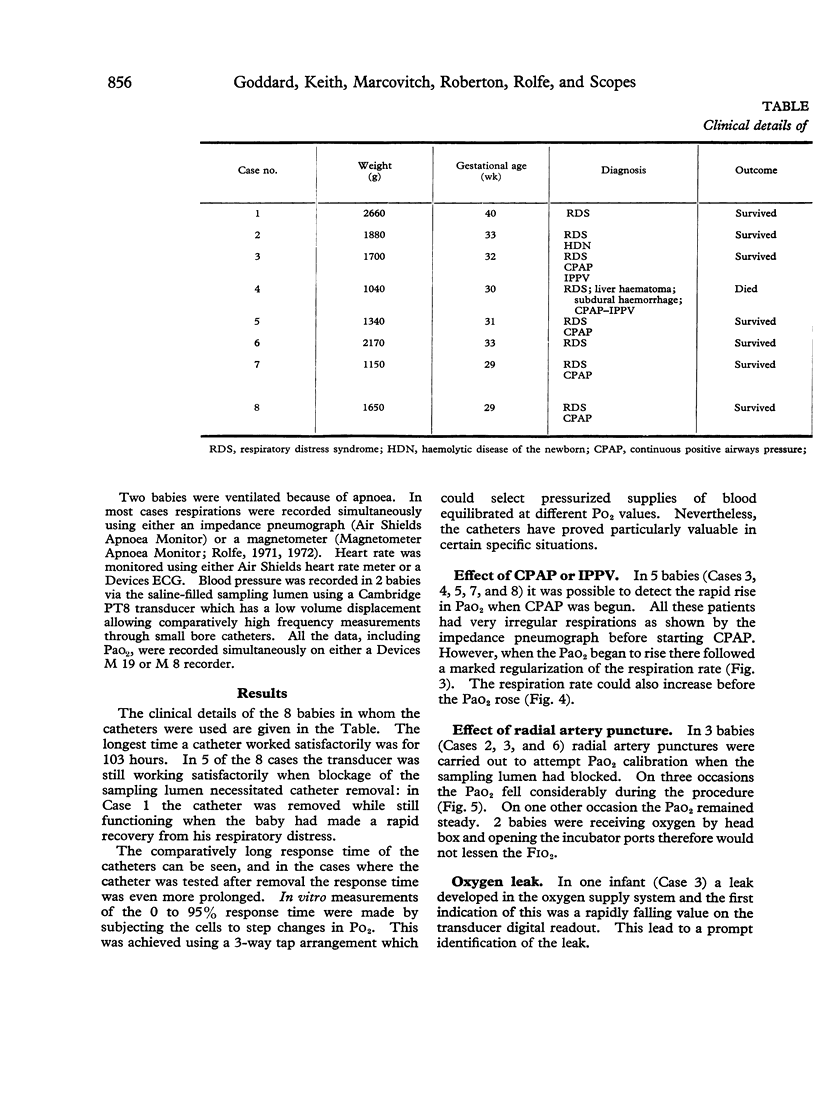
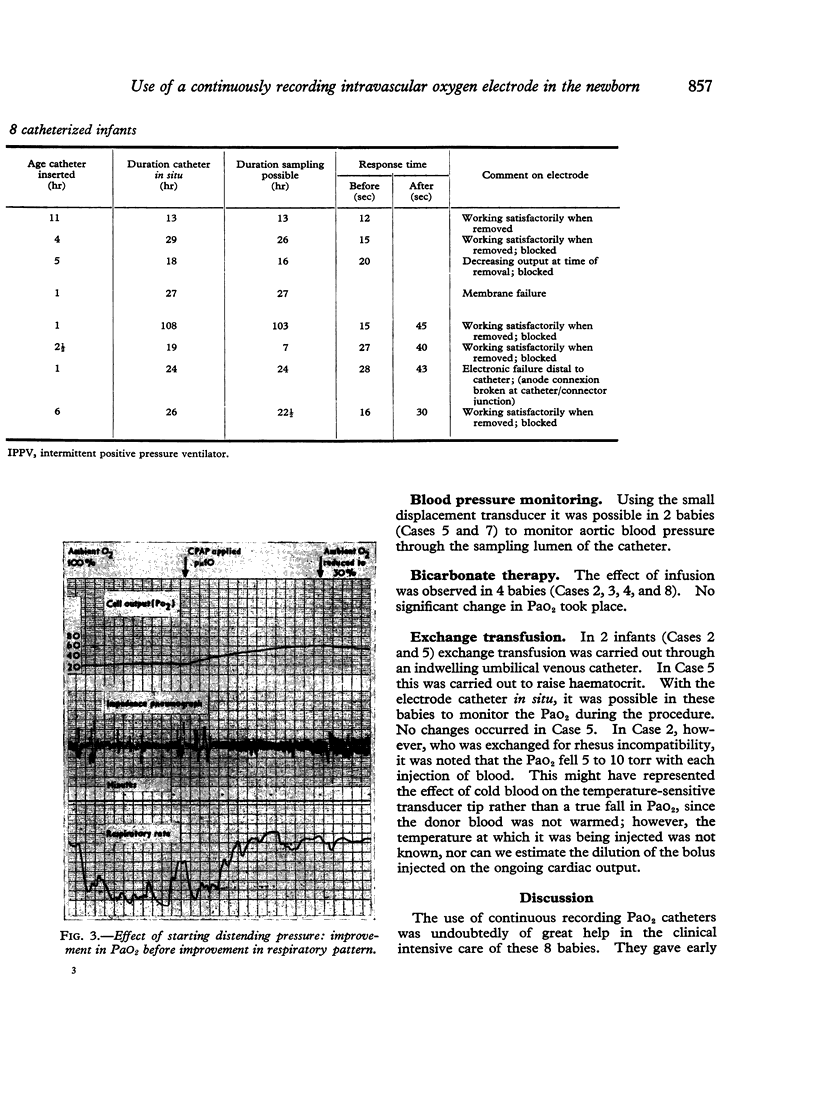
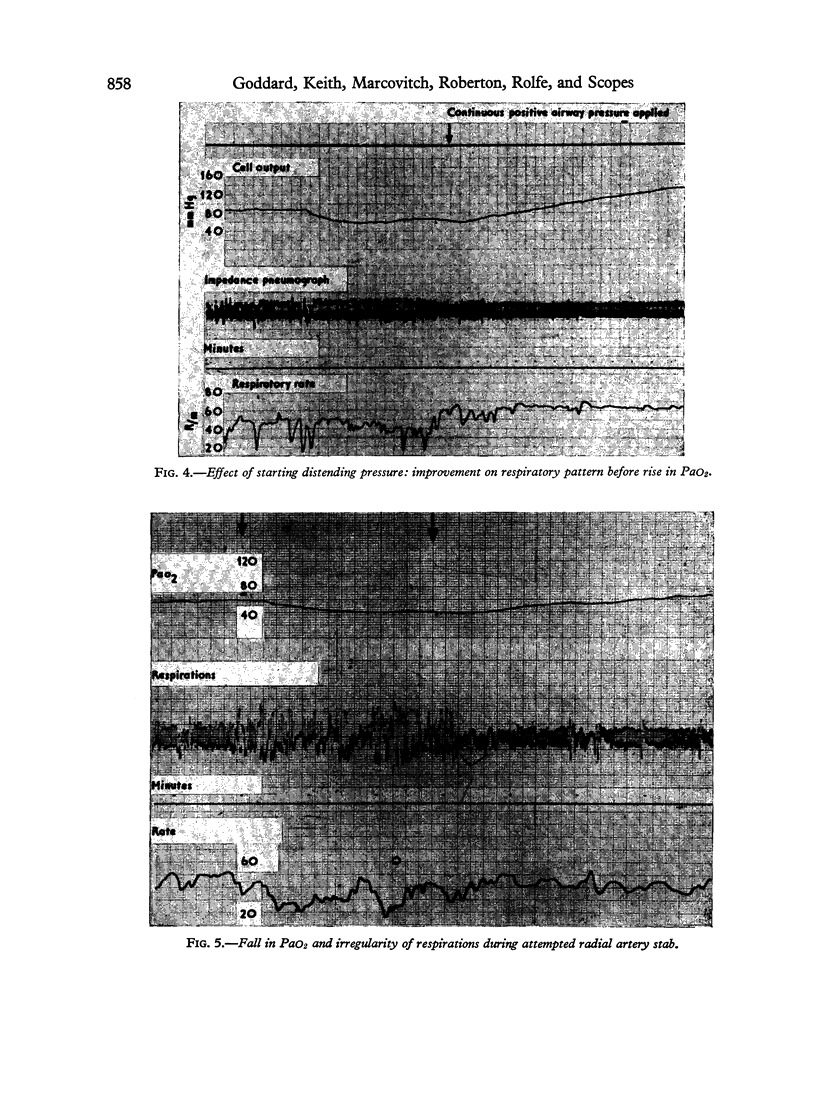


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee C. K., Girling D. J., Wigglesworth J. S. Pulmonary fibroplasia in newborn babies treated with oxygen and artificial ventilation. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Aug;47(254):509–518. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.254.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernick V., Vidyasagar D. Continuous negative chest wall pressure in hyaline membrane disease: one year experience. Pediatrics. 1972 May;49(5):753–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbie A. K. Electricity in hospitals. Biomed Eng. 1972 Jan-Feb;7(1):12–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M., Speidel B. D., Storrs C. N. Letter: In defence of the Gregory box (C.P.A.P.). Lancet. 1973 Oct 13;2(7833):853–854. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90907-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanaroff A. A., Cha C. C., Sosa R., Crumrine R. S., Klaus M. H. Controlled trial of continuous negative external pressure in the treatment of severe respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1973 Jun;82(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80418-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
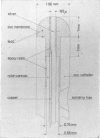
- Goddard P., Keith I., Marcovitch H., Rolfe P. J. Experience with a catheter-tip transducer for continuous measurement of blood oxygen tension, including evaluation in 4 newborn babies. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Aug;47(254):675–675. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.254.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory G. A., Kitterman J. A., Phibbs R. H., Tooley W. H., Hamilton W. K. Treatment of the idiopathic respiratory-distress syndrome with continuous positive airway pressure. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jun 17;284(24):1333–1340. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197106172842401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. R., Nugent M. Continuous arterial oxygen tension monitoring in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1973 Jun;82(6):929–939. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80419-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key A., Parker D., Davies R. Use of epoxy resin in oxygen electrodes. Phys Med Biol. 1970 Jul;15(3):569–572. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/15/3/422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D., Key A., Davies R., Scopes J. W., Marcovitch H. A disposable catheter-tip transducer for continuous measurement of blood oxygen tension in vivo. Biomed Eng. 1971 Jul;6(7):313–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocock S. N. Earth-free patient monitoring. I. Principles, practice and hazards. Biomed Eng. 1972 Jan-Feb;7(1):21–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberton N. R., Gupta J. M., Dahlenburg G. W., Tizard J. P. Oxygen therapy in the newborn. Lancet. 1968 Jun 22;1(7556):1323–1329. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfe P. A magnetometer respiration monitor for use with premature babies. Biomed Eng. 1971 Sep;6(9):402–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veasy L. G., Clark J. S., Jung A. L., Jenkins J. L. A system for computerized automated blood gas analysis. Its use in newborn infants with respiratory distress. Pediatrics. 1971 Jul;48(1):5–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]