Abstract
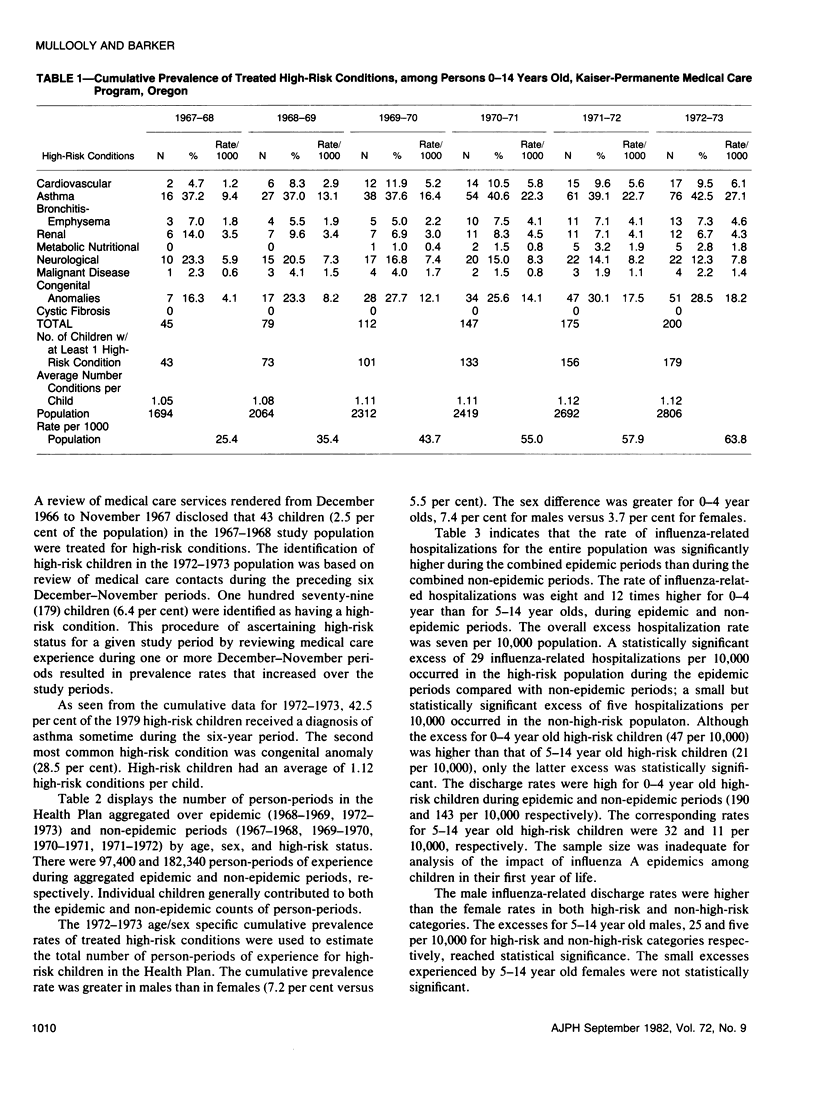
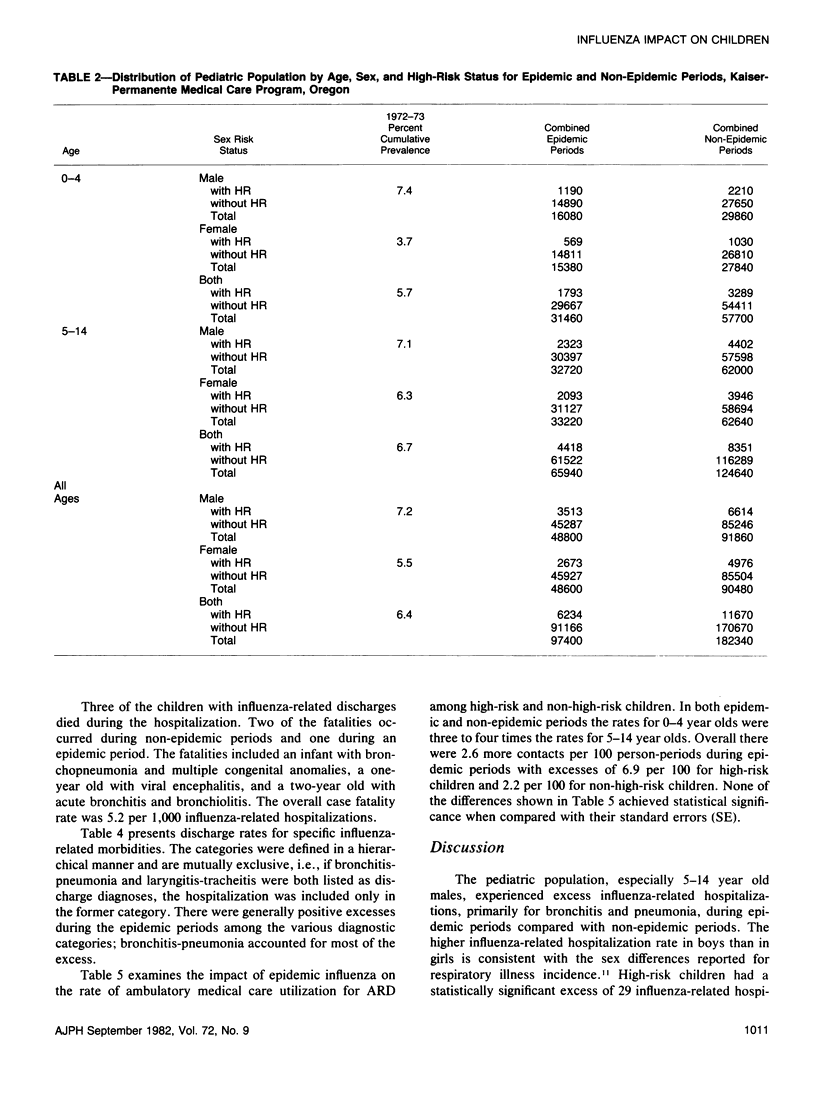
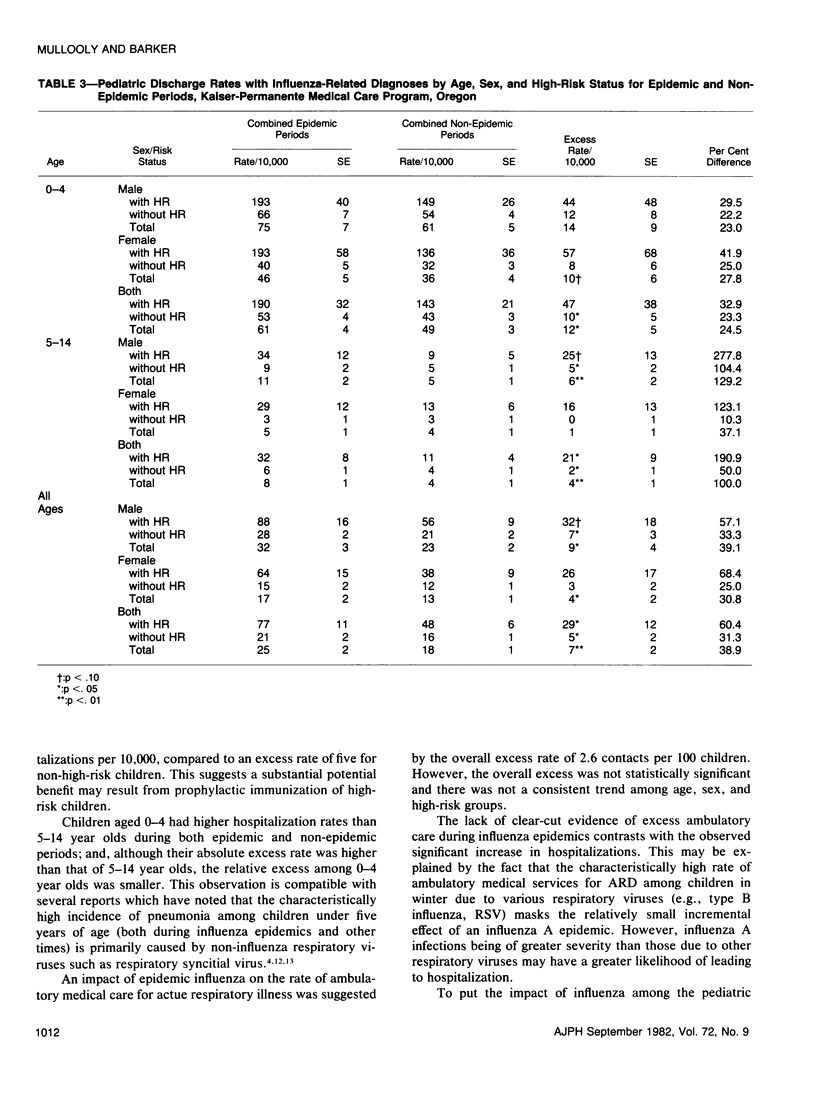
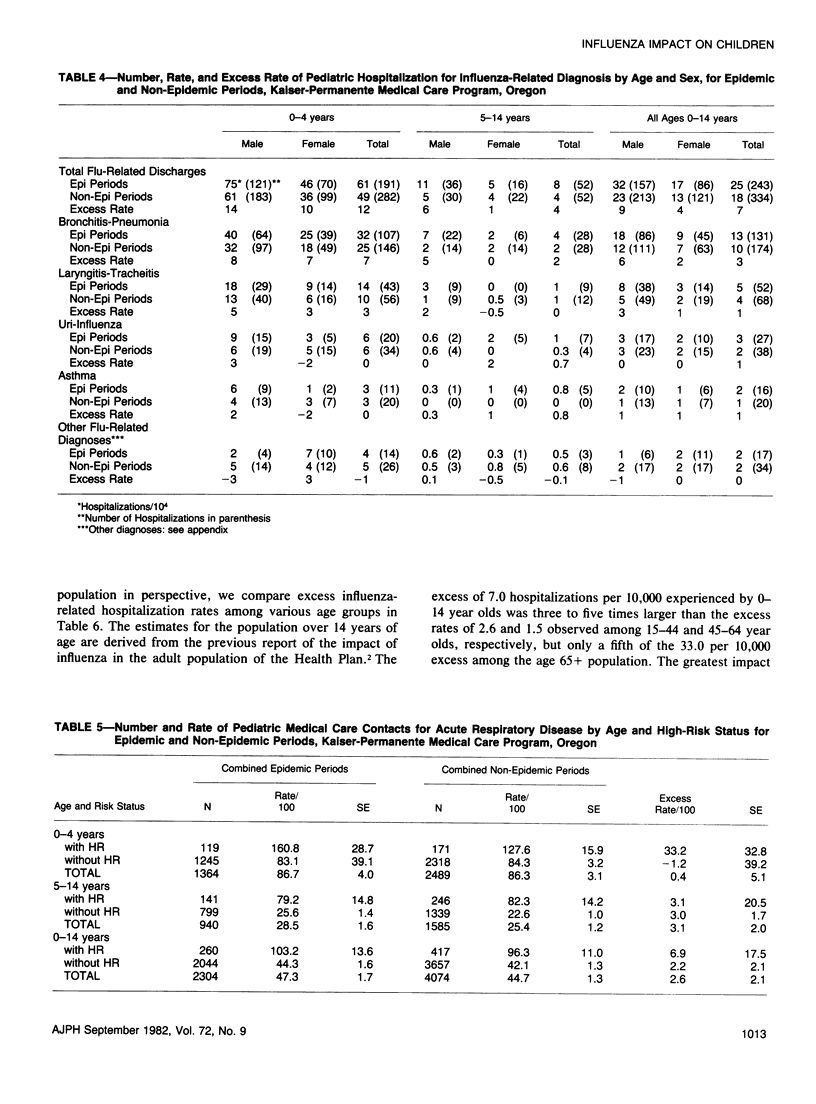
Excess morbidity was studied during influenza A epidemics (1968-69, 1972-73) among children in a large prepaid group practice program. Excess rates of hospitalization for influenza-related conditions, primarily pneumonia and bronchitis, ranged from 5 per 10,000 (95 per cent confidence limits (CL): 1 to 9) for non-high-risk children to 29 per 10,000 (95 per cent CL: 5 to 53) for children with high-risk conditions. The relative increases in hospitalization rates were greatest for 5-14 year old boys: 278 per cent and 104 per cent increases for high-risk and non-high-risk boys, respectively. The absolute increase was greatest for 0-4 year olds. The excess rate of ambulatory medical care contacts, 2.6 per 100 (95 per cent CL: -1.6 to 6.8 per 100) was not statistically significant. Excess hospitalization rates among 0-14 year olds during epidemics were three to five times larger than those for persons between 15 and 64 years of age but only one-fifth the rate of persons over age 65.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker W. H., Mullooly J. P. Impact of epidemic type A influenza in a defined adult population. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Dec;112(6):798–811. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EICKHOFF T. C., SHERMAN I. L., SERFLING R. E. Observations on excess mortality associated with epidemic influenza. JAMA. 1961 Jun 3;176:776–782. doi: 10.1001/jama.1961.03040220024005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Cooney M. K., Allan I., Kenny G. E. Rates of pneumonia during influenza epidemics in Seattle, 1964 to 1975. JAMA. 1979 Jan 19;241(3):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glezen W. P., Loda F. A., Clyde W. A., Jr, Senior R. J., Sheaffer C. I., Conley W. G., Denny F. W. Epidemiologic patterns of acute lower respiratory disease of children in a pediatric group practice. J Pediatr. 1971 Mar;78(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grist N. R., Ross C. A., Stott E. J. Influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, and pneumonia in Glasgow, 1962-5. Br Med J. 1967 Feb 25;1(5538):456–457. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5538.456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. B., Douglas R. G., Jr Respiratory syncytial virus and influenza. Practical community surveillance. Am J Dis Child. 1976 Jun;130(6):615–620. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1976.02120070041009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. E., Cooney M. K., Fox J. P. The Seattle virus watch. IV. Comparative epidemiologic observations of infections with influenza A and B viruses, 1965-1969, in families with young children. Am J Epidemiol. 1973 Nov;98(5):365–380. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORDAN W. S., Jr, DENNY F. W., Jr, BADGER G. F., CURTISS C., DINGLE J. H., OSEASOHN R., STEVENS D. A. A study of illness in a group of Cleveland families. XVII. The occurrence of Asian influenza. Am J Hyg. 1958 Sep;68(2):190–212. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. W., Brandt C. D., Arrobio J. O., Murphy B., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Influenza A and B virus infection in infants and young children during the years 1957-1976. Am J Epidemiol. 1979 Apr;109(4):464–479. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monto A. S., Kioumehr F. The Tecumseh Study of Respiratory Illness. IX. Occurence of influenza in the community, 1966--1971. Am J Epidemiol. 1975 Dec;102(6):553–563. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


