Abstract
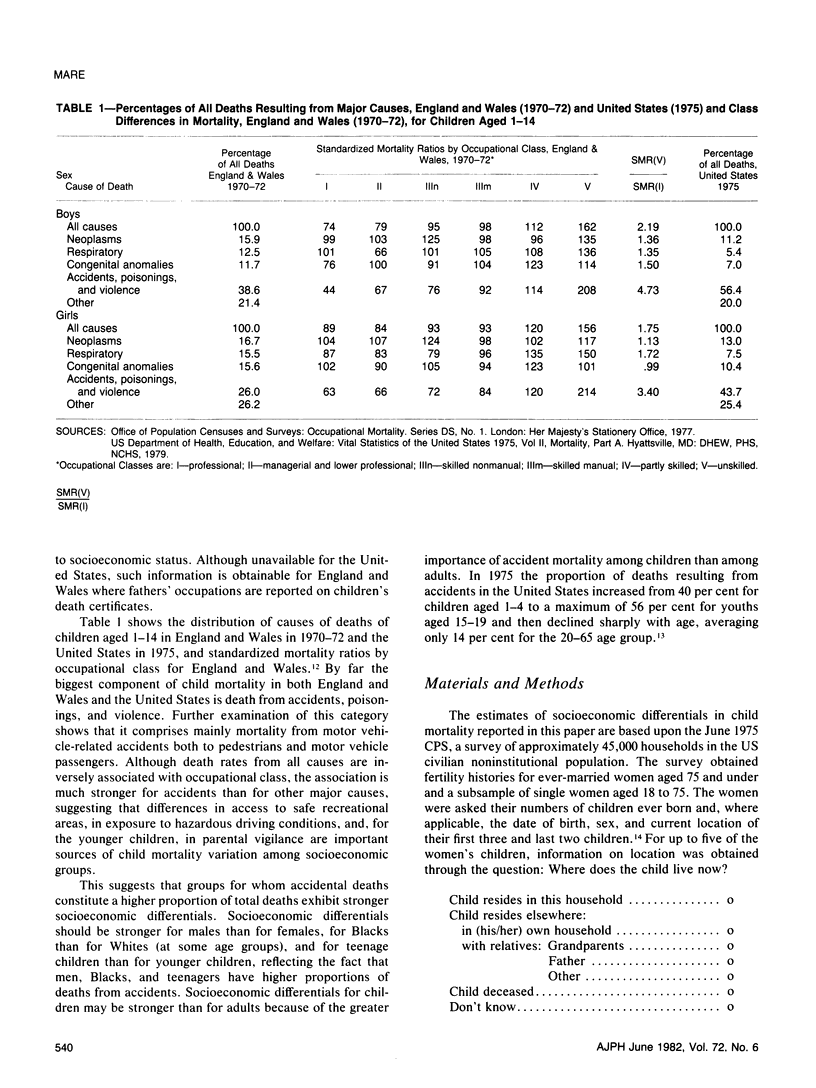
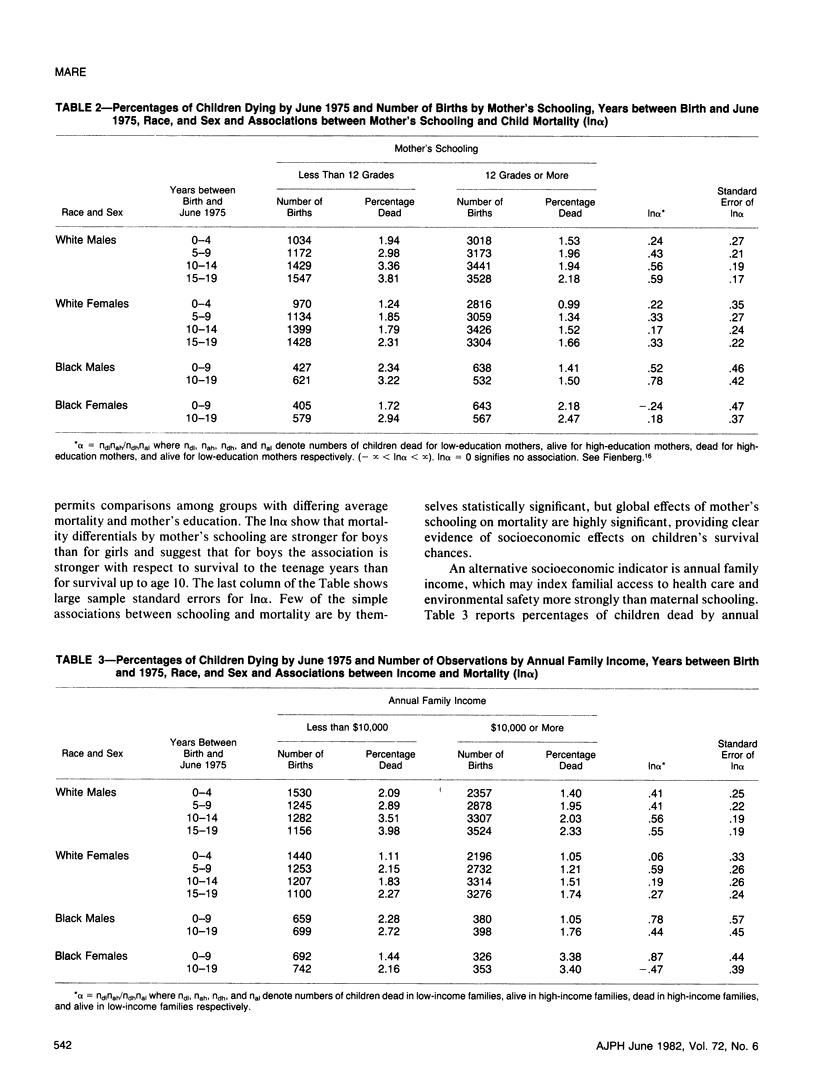
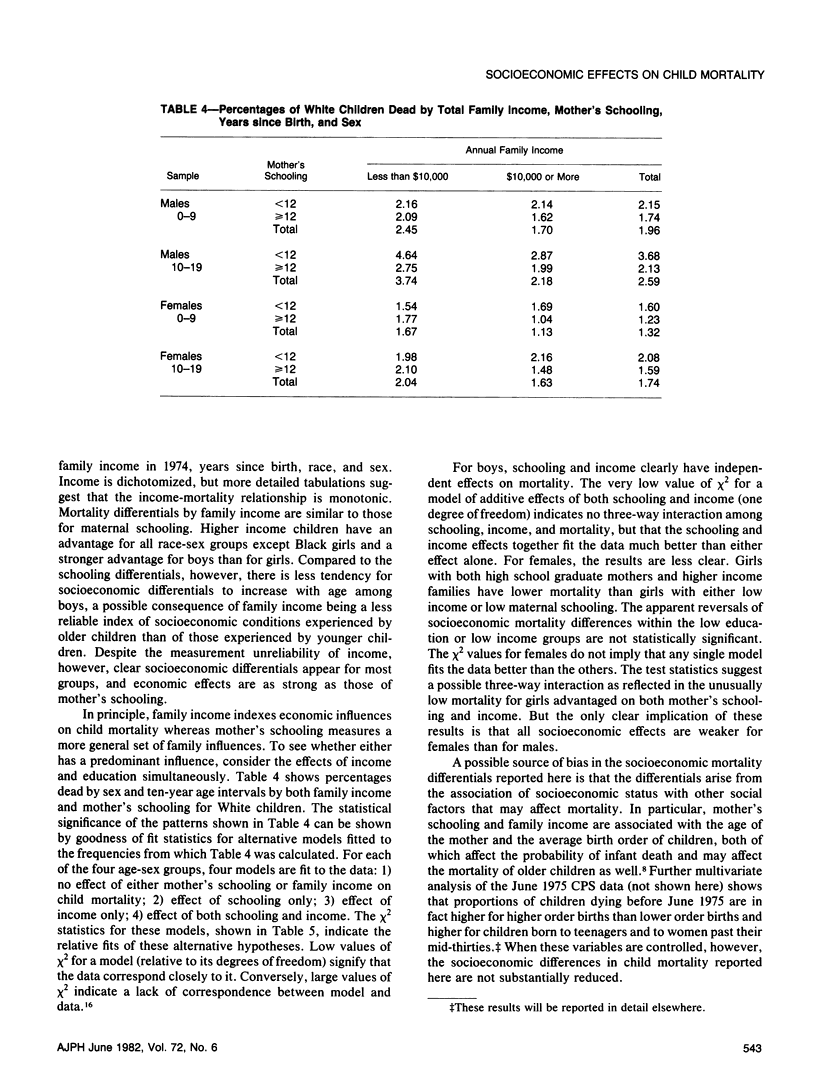
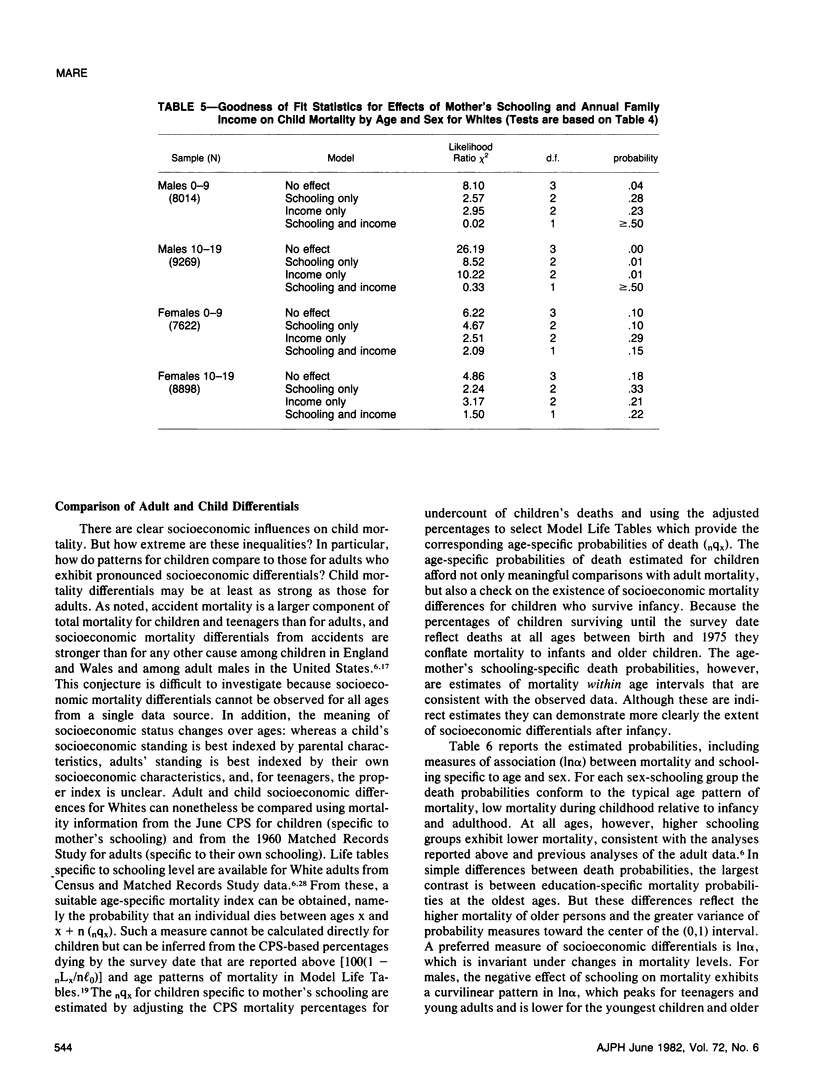
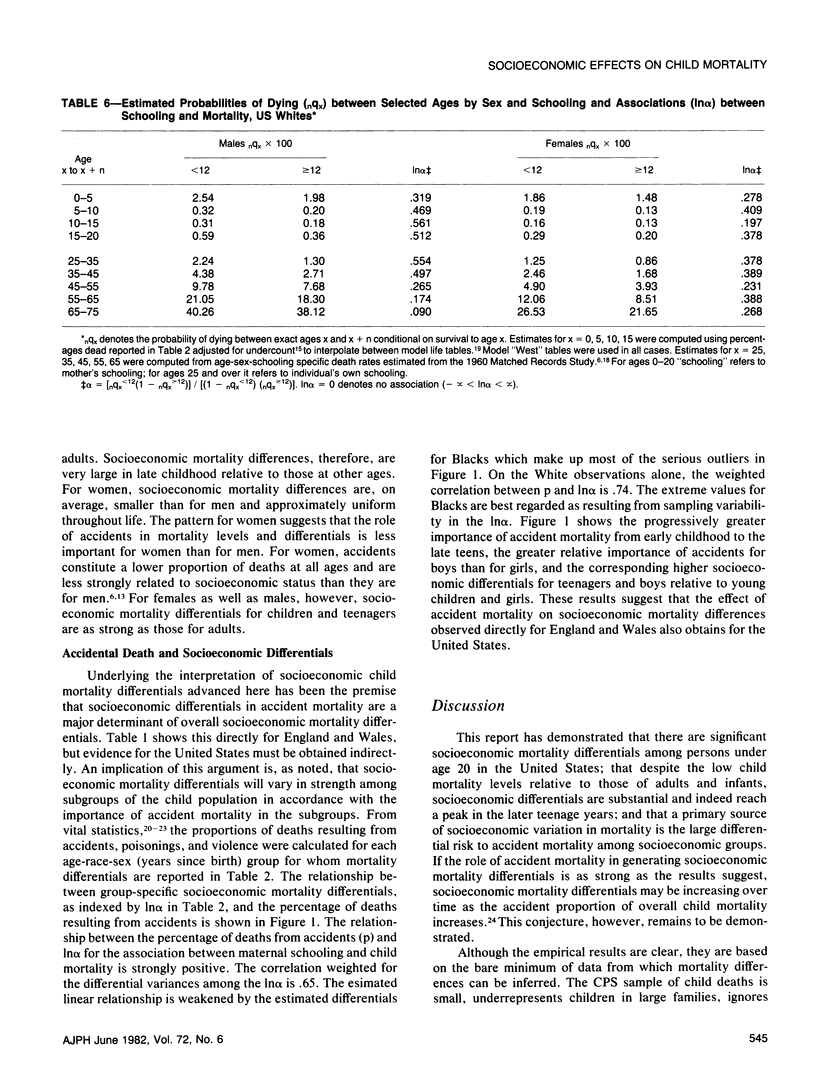
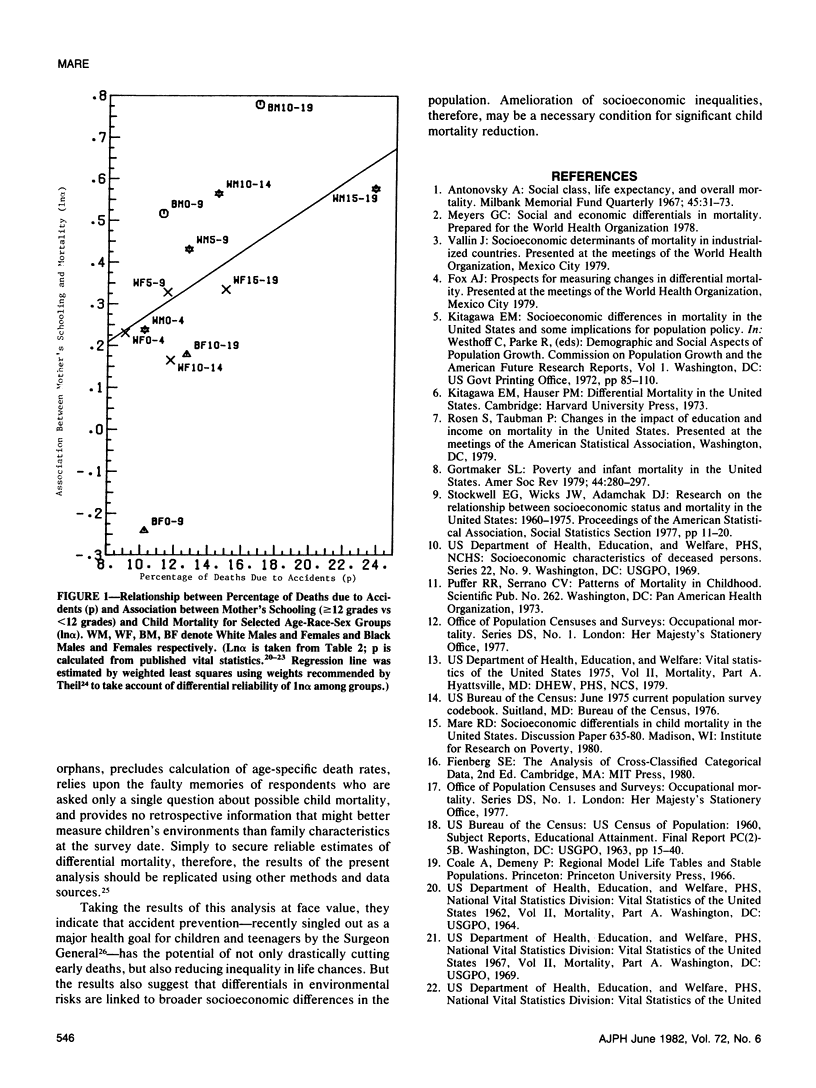
Despite considerable reason for scholarly and policy interest in socioeconomic mortality differentials, socioeconomic effects on child and teenage mortality in the United States have been a neglected research topic because of several data limitations. Exploiting data obtained for other purposes, this paper reports socioeconomic effects on the mortality of children and teenagers. Socioeconomic mortality differentials among children are large--at least as large as those among adults. The major source of socioeconomic mortality differences among children is apparently differential risk to accidental death. Within the child population, the strength of socioeconomic effects varies directly with the relative importance of accidents as a component of overall mortality.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonovsky A. Social class, life expectancy and overall mortality. Milbank Mem Fund Q. 1967 Apr;45(2):31–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gortmaker S. L. Poverty and infant mortality in the United States. Am Sociol Rev. 1979 Apr;44(2):280–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


