Abstract
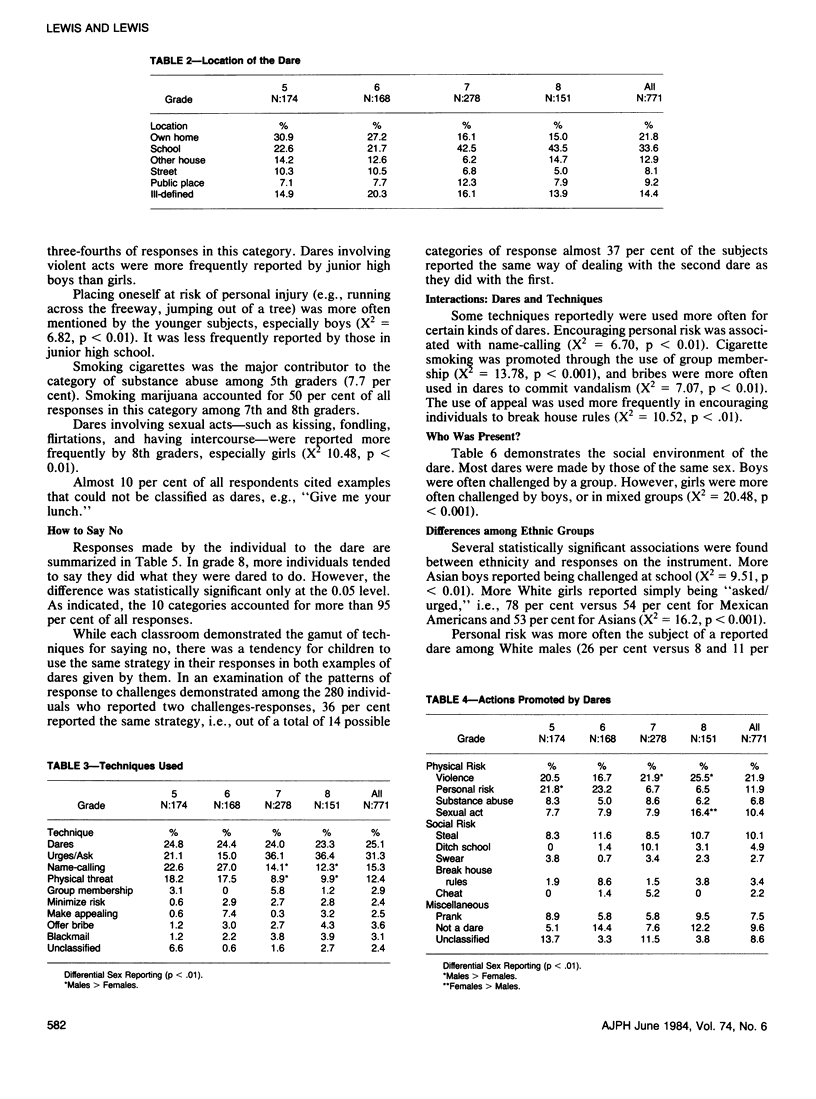
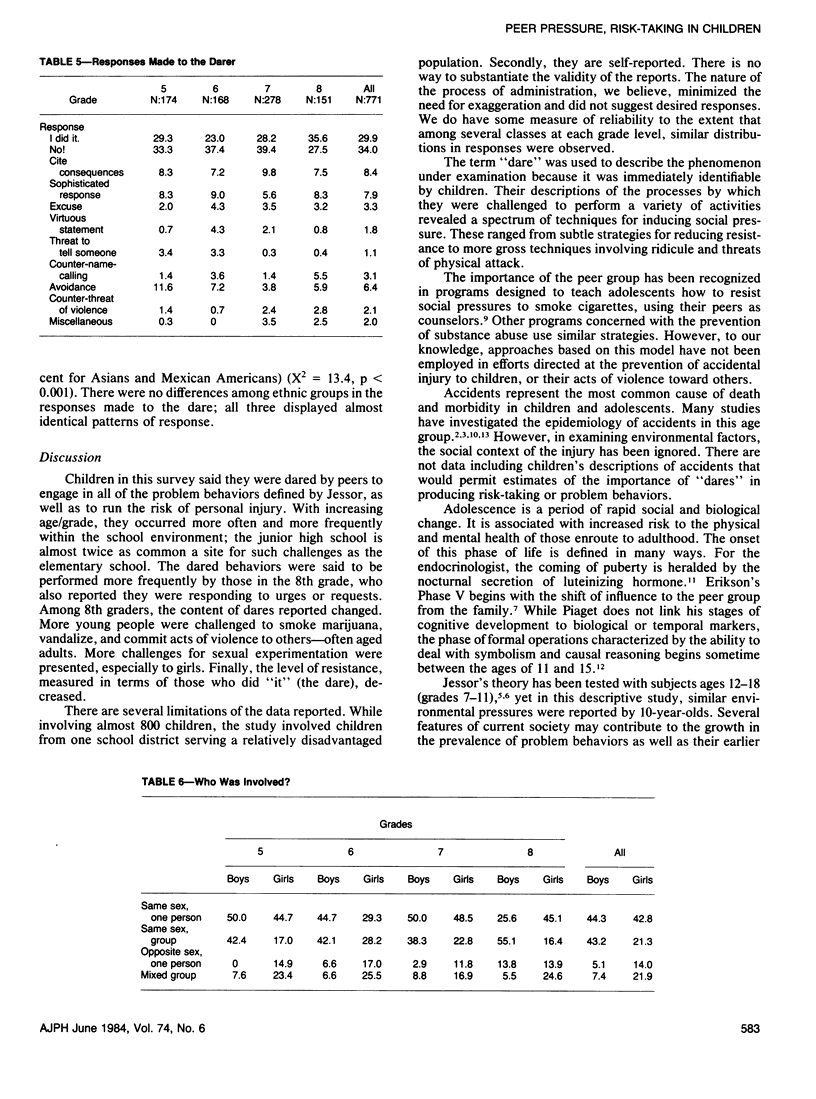
We asked 771 children in grades 5-8 about the dares or challenges they received from other children. A pilot study established categories for classification of the actions proposed ("What did they try to get you to do?"); the techniques utilized ("How did they try to get you to do that?"); and children's responses ("What did you say or do?"). Peer pressure was reported most frequently by 8th grade students. About 50 per cent of the dares encouraged problem behaviors that placed the children (or others) at risk for personal injury, or the potential development of habits hazardous to their health. With increasing age, more occurred in the school environment and fewer involved risk of personal injury. Among 7th and 8th graders, more boys were dared to perform acts of violence, and more girls were challenged to be sexually active.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyar R. M., Rosenfeld R. S., Kapen S., Finkelstein J. W., Roffwarg H. P., Weitzman E. D., Hellman L. Human puberty. Simultaneous augmented secretion of luteinizing hormone and testosterone during sleep. J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):609–618. doi: 10.1172/JCI107798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddon W., Jr Advances in the epidemiology of injuries as a basis for public policy. Public Health Rep. 1980 Sep-Oct;95(5):411–421. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessor R., Chase J. A., Donovan J. E. Psychosocial correlates of marijuana use and problem drinking in a national sample of adolescents. Am J Public Health. 1980 Jun;70(6):604–613. doi: 10.2105/ajph.70.6.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. E., Siegel J. M., Lewis M. A. Feeling bad: exploring sources of distress among pre-adolescent children. Am J Public Health. 1984 Feb;74(2):117–122. doi: 10.2105/ajph.74.2.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pless I. B., Stulginskas J. Accidents and violence as a cause of morbidity and mortality in childhood. Adv Pediatr. 1982;29:471–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


