Abstract
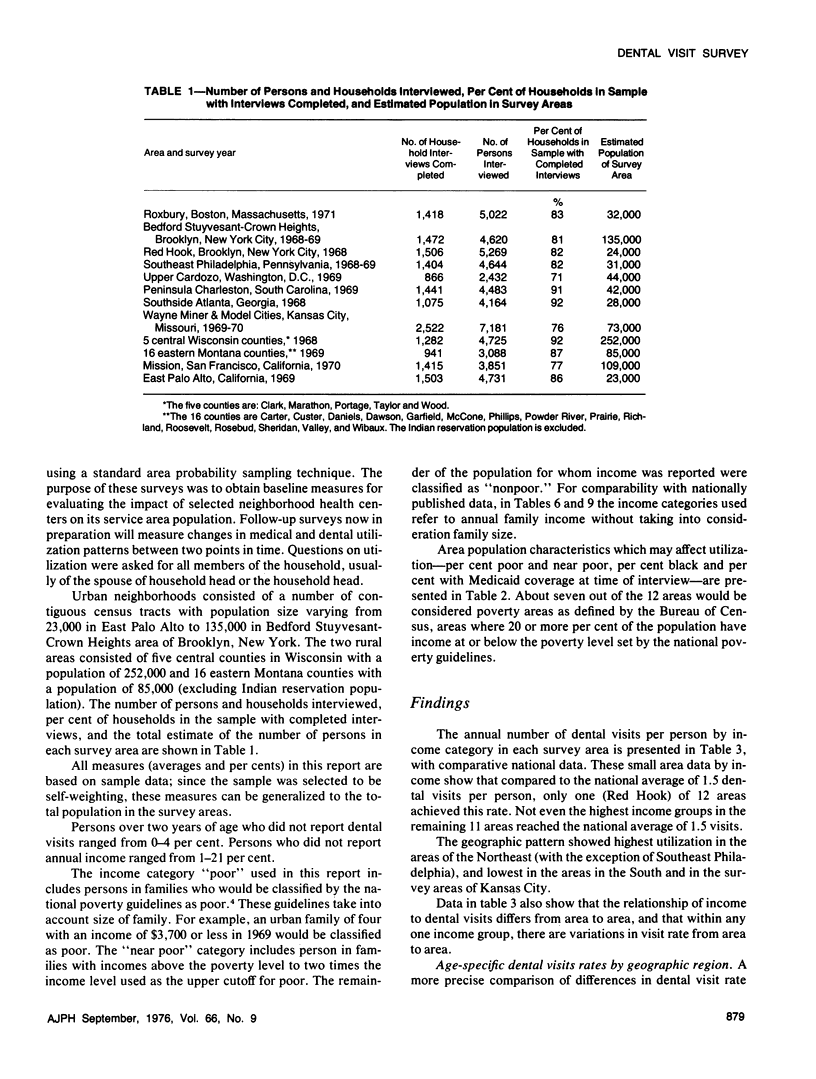
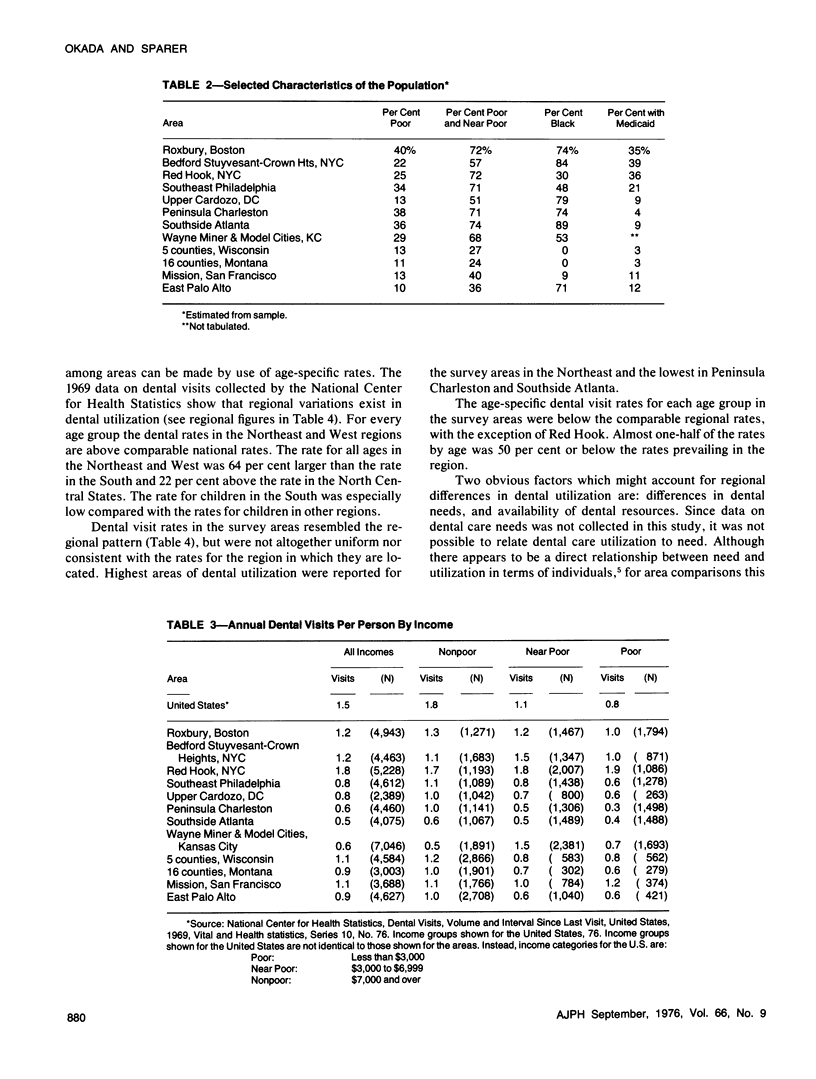
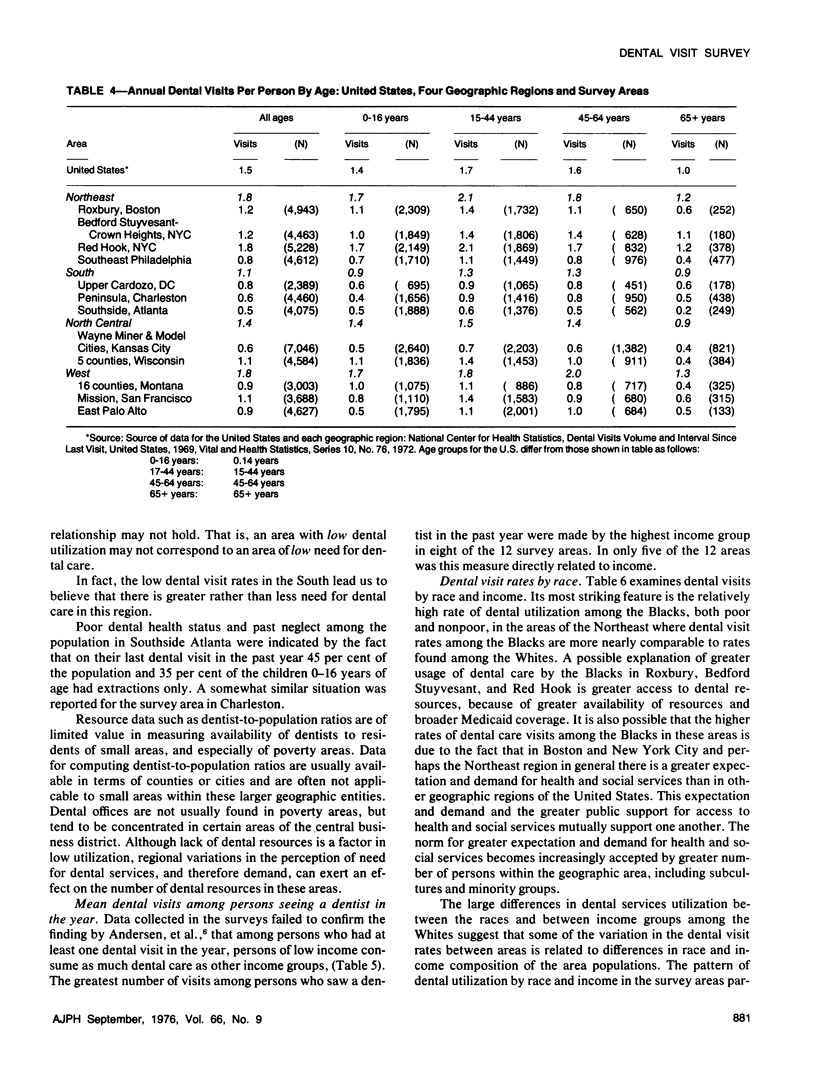
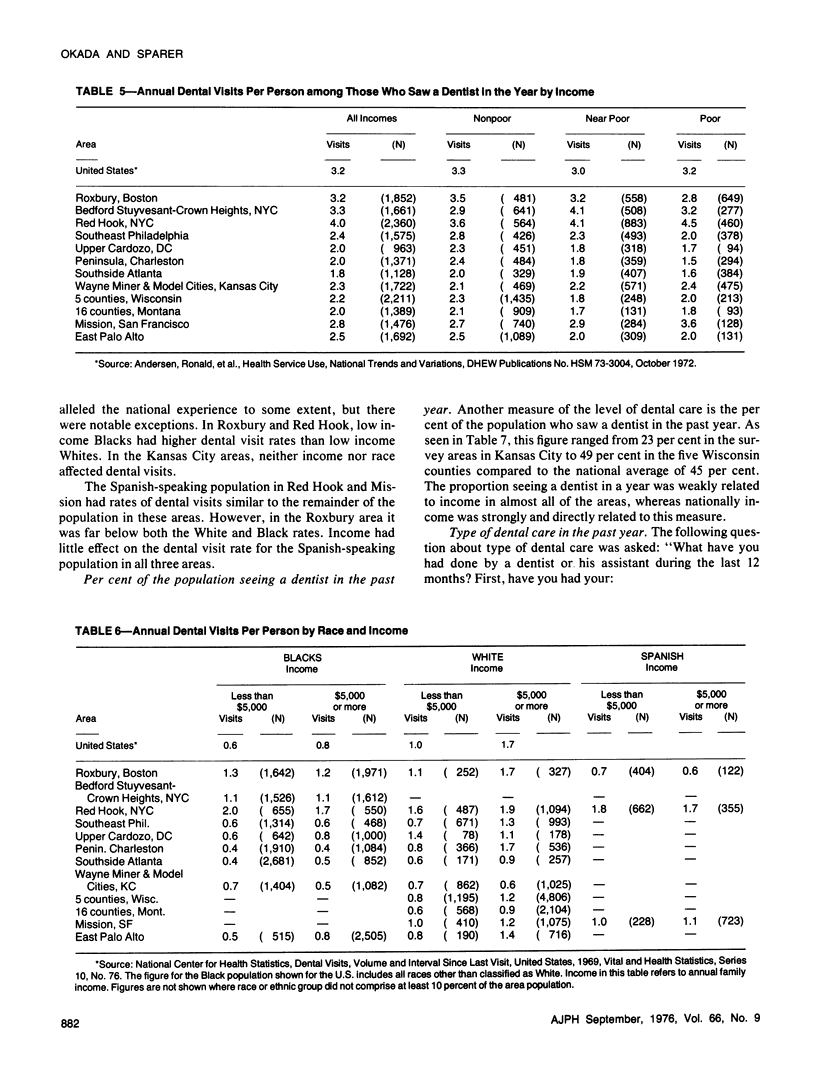
Household surveys in 12 low income areas found large differences in dental visit rates after control for income and race. The dental visit rate for Red Hook (NYC) exceeded the national rate whereas in seven of the areas the rate was below national averages by 40 per cent or more. The ranges in dental visit rate for low income Blacks was from two-thirds the national rate (in two areas of the South) to two to three times greater than the comparable national rate (in three areas of the Northeast). Lesser but nevertheless large variations among area dental visit rates existed for other race and income groups.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bice T. W., Eichhorn R. L., Fox P. D. Socioeconomic status and use of physician services: a reconsideration. Med Care. 1972 May-Jun;10(3):261–271. doi: 10.1097/00005650-197205000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikias M. K., Fink R., Shapiro S. Comparisons of poverty and nonpoverty groups on dental status, needs, and practices. J Public Health Dent. 1975 Fall;35(4):237–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-7325.1975.tb01017.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


