Abstract
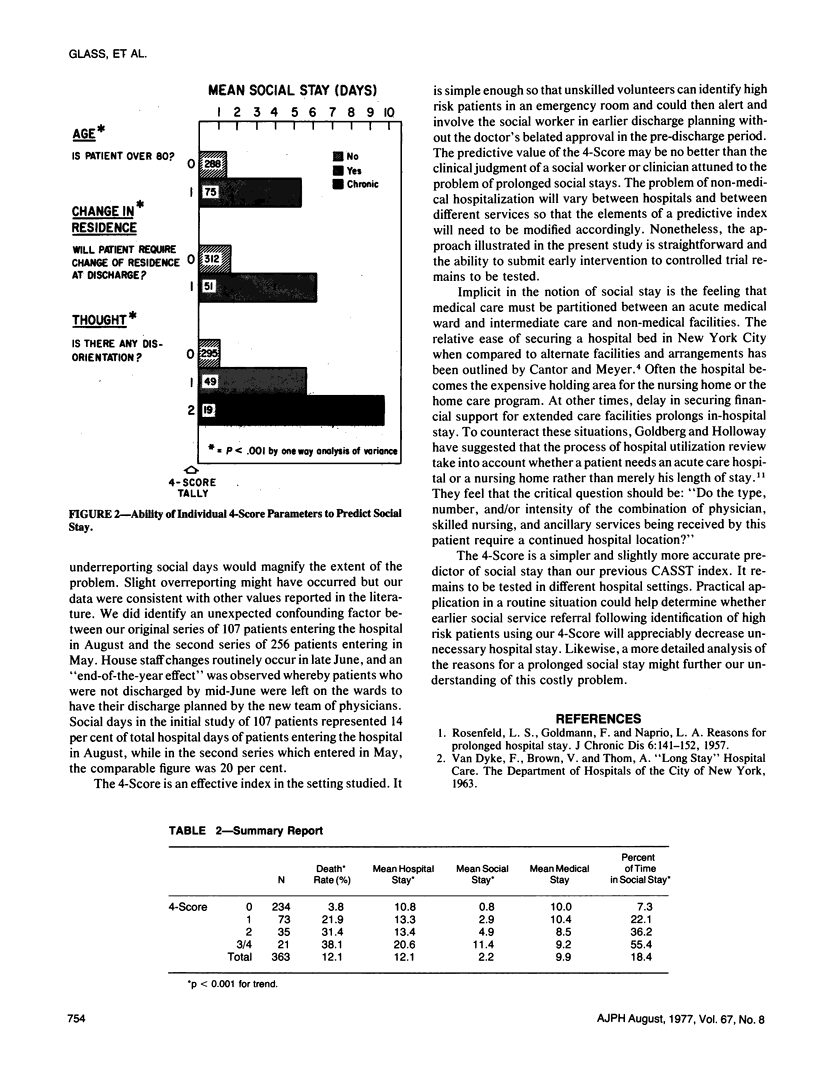
Three hundred sixty-three patients representing two groups of consecutive medical admissions to a large city hospital were evaluated on admission to determine what factors might predict "non-medical" or social stay. Periodic follow-up determined when patients were ready for discharge and when their social stay began. A composite index, the 4-Score, was derived as a simple indicator of risk for subsequent social stay; it is defined as the number of positive answers to the questions: 1) Is the patient 80 years old or more? 2) Will the patient have to live somewhere new at discharge? 3) Is there any disorientation? AND 4) If so, is the disorientation chronic? Eighteen per cent of the total inpatient hospital days of this group of patients could be attributed to social stay. The 56 patients with a 4-Score of two or more on admission had on average a week each of social stay while the 307 patients with a score of less than two averaged only one social day each.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkman B., Rehr H. The search for early indicators of social service need among elderly hospital patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1974 Sep;22(9):416–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1974.tb05411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass R. I., Weiner M. S. Seeking a social disposition for the medical patient: CAAST, a simple and objective clinical index. Med Care. 1976 Jul;14(7):637–641. doi: 10.1097/00005650-197607000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. A., Holloway D. C. Emphasizing "level of care" over "length of stay" in hospital utilization review. Med Care. 1975 Jun;13(6):474–485. doi: 10.1097/00005650-197506000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner J. R., Lin H. W. Effects of age on length of hospital stay in a low-income population. Med Care. 1975 Oct;13(10):855–875. doi: 10.1097/00005650-197510000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENFELD L. S., GOLDMANN F., KAPRIO L. A. Reasons for prolonged hospital stay; a study of need for hospital care. J Chronic Dis. 1957 Aug;6(2):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(57)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer J. G. Length of stay and hospital bed misutilization. Med Care. 1974 May;12(5):453–462. doi: 10.1097/00005650-197405000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



