Abstract
A study was conducted of family records and claim forms of a company-sponsored dental plan to determine the effects of several demographic variables on utilization of the plan and on patterns of expenditure. The plan was non-contributory on the part of the employees. Individual utilization of the plan (at least once during the study year) closely approximated the average for the entire U.S. population. Salaried employees, and families, were more likely to use the plan than hourly-paid employees and families. High income families were more likely than lower income families to use the plan. Most of the independent variables (income, age, hourly versus salaried) correlated with utilization patterns in a predictable manner. A notable exception was when one looked from one division of the corporation to another, with 25 per cent of families in one division using the plan in the study year, compared to 90 per cent at another division. The reasons for these dramatic differences may be related, at least in part, to institutional factors rather than to patient behavior, and further study is indicated.
Full text
PDF

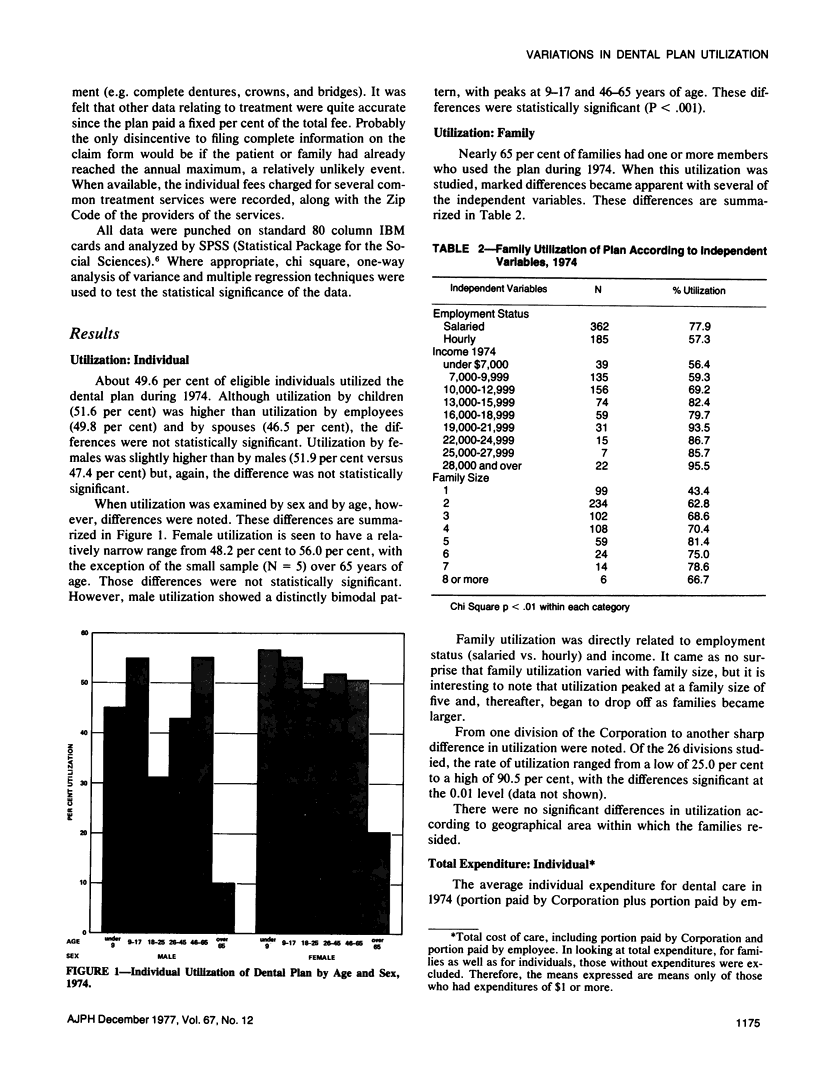


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Mulvihill J. E., Bear W. S., Dunning J. M., Giddon D. B. Utilization of a prepaid plan of commercial dental insurance. J Public Health Dent. 1972 Summer;32(3):187–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-7325.1972.tb03970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUCHMAN E. A., ROTHMAN A. A. THE UTILIZATION OF DENTAL SERVICES. N Y State Dent J. 1965 Apr;31:151–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]