Abstract
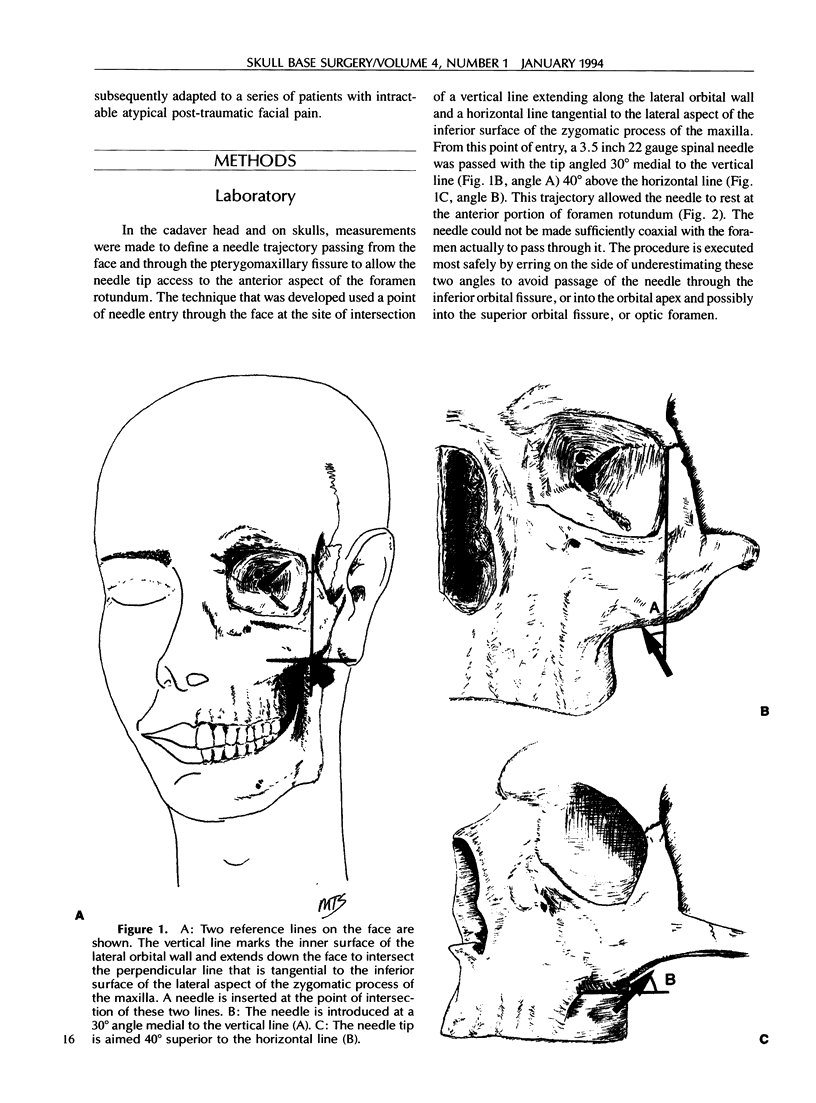
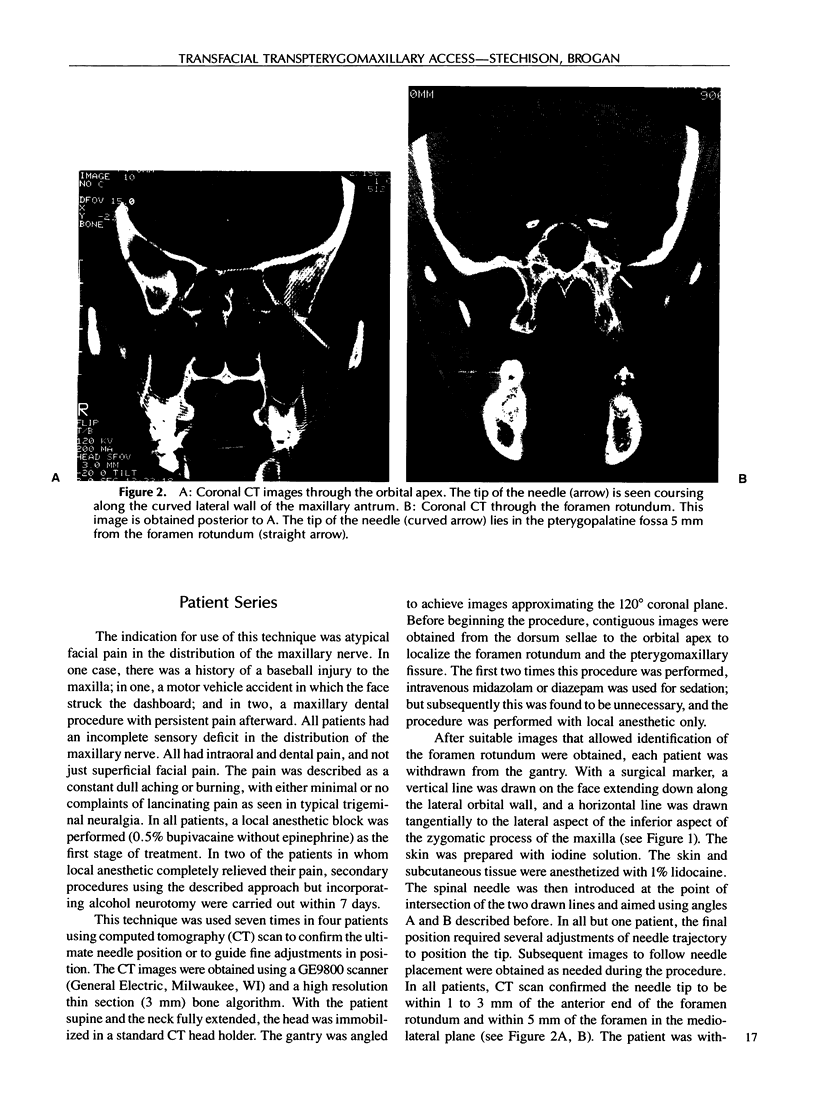
Post-traumatic atypical facial pain syndromes are refractory to medical therapy and thus challenging to treat. Some of these patients have a facial causalgia syndrome that may include autonomic as well as trigeminal fibers as the anatomic mediators. A procedure that may be of both diagnostic and therapeutic benefit is a nerve block in the region of the foramen rotundum. This allows access to both the maxillary nerve and the sphenopalatine ganglion. A simple technique developed to perform this procedure is described, and the results in a series of six patients are presented.
Full text
PDF

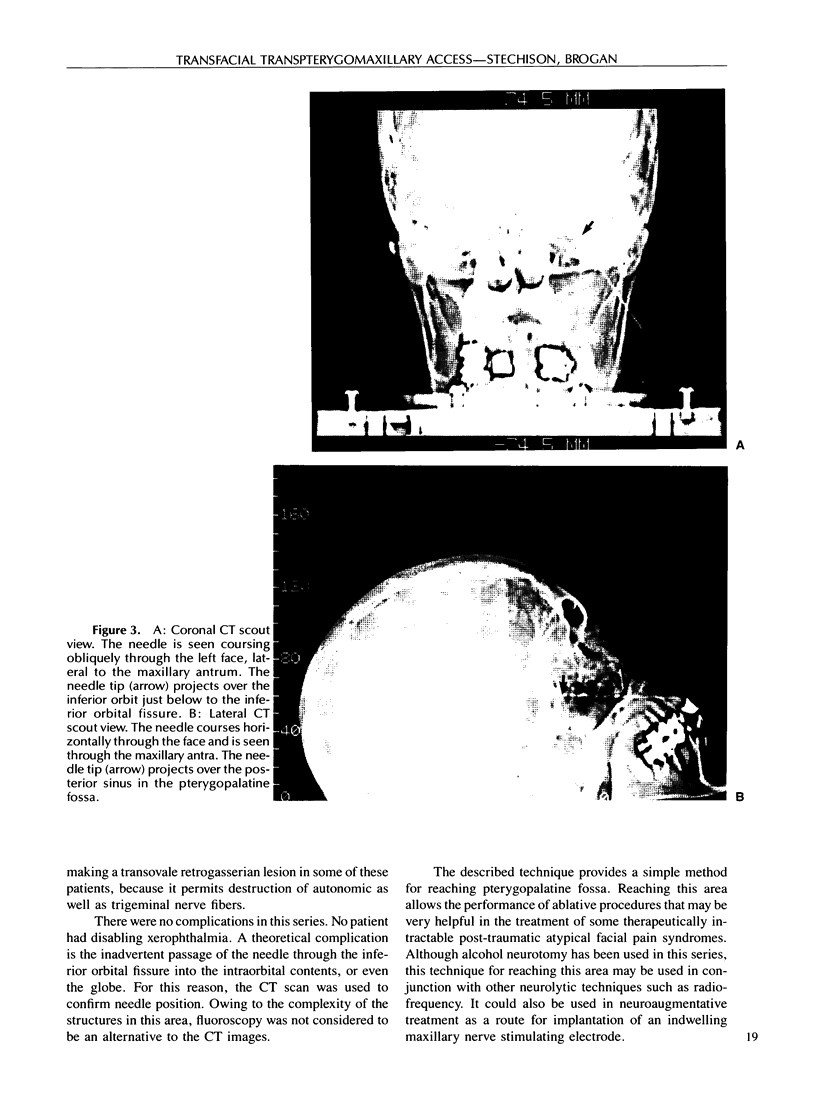

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Solomon S. Cluster headache and the nervus intermedius. Headache. 1986 Jan;26(1):3–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1986.hed2601003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]