Abstract
The introduction of computer-assisted navigation systems has played a significant role in assuring the integration and consistent intraoperative use of radiological information. We used a frameless stereotactic navigation system to treat 62 patients with a variety of skull base pathologies. The optoelectric appliance uses digital imaging information to locate surgical instruments in the operative area. The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical accuracy, practicality, and impact of this navigation system on otolaryngological procedures. In conjunction with rigid head fixation and bone-anchored registration markers, the precision of registration was 0.8 mm and the accuracy of clinical measurements was less than 2 mm. With conventional fiducials and flexible head positioning, deviations were as large as 4.5 mm. The additional use of surface registration increased the precision of registration. Preoperative preparations took 15 to 35 minutes, depending on the complexity of the planning. Intraoperative computer support is an important aid to a surgeon's orientation, especially when a patient's anatomy is atypical. Navigation systems will likely improve the quality of surgery and facilitate training.
Keywords: Navigation, computer-assisted surgery, image-guided surgery, skull base surgery, frameless stereotaxy
Full text
PDF

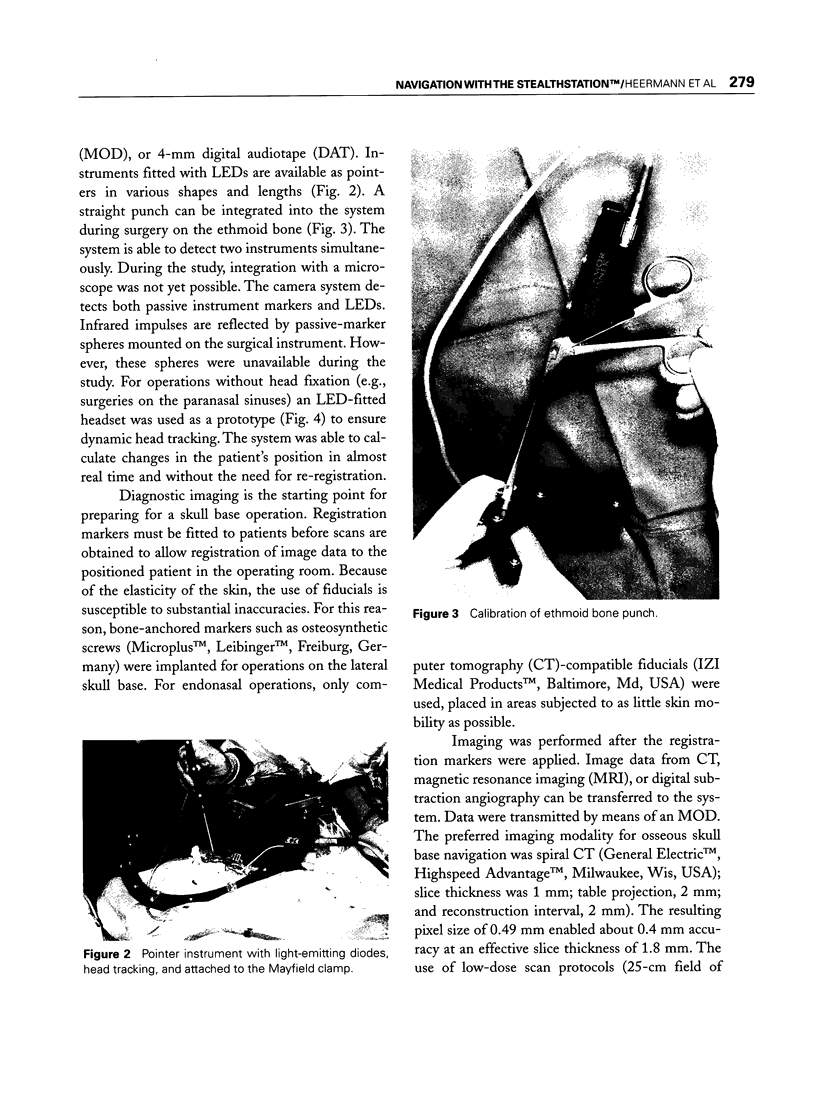






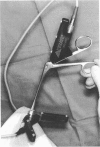
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anon J. B. Computer-aided endoscopic sinus surgery. Laryngoscope. 1998 Jul;108(7):949–961. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199807000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anon J. B., Klimek L., Mosges R., Zinreich S. J. Computer-assisted endoscopic sinus surgery. An international review. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1997 Jun;30(3):389–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale R. J., Vogele M., Freysinger W., Gunkel A. R., Martin A., Bumm K., Thumfart W. F. Minimally invasive head holder to improve the performance of frameless stereotactic surgery. Laryngoscope. 1997 Mar;107(3):373–377. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199703000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casiano R. R., Numa W. A., Jr Efficacy of computed tomographic image--guided endoscopic sinus surgery in residency training programs. Laryngoscope. 2000 Aug;110(8):1277–1282. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200008000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. J., Hawkes D. J., Hill D. L., Jewell D., Spink R., Strong A., Gleeson M. Augmentation of reality using an operating microscope for otolaryngology and neurosurgical guidance. J Image Guid Surg. 1995;1(3):172–178. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1522-712X(1995)1:3<172::AID-IGS7>3.0.CO;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freysinger W., Gunkel A. R., Martin A., Bale R. J., Vogele M., Thumfart W. F. Advancing ear, nose, and throat computer-assisted surgery with the arm-based ISG viewing wand: the stereotactic suction tube. Laryngoscope. 1997 May;107(5):690–693. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199705000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M. P., Kleefield J., Gopal H., Reardon E., Ho B. T., Kuhn F. A. Image-guided endoscopic surgery: results of accuracy and performance in a multicenter clinical study using an electromagnetic tracking system. Laryngoscope. 1997 May;107(5):594–601. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199705000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M. P., Morrison P. R. Computer-augmented endoscopic sinus surgery. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1998 Apr;31(2):331–340. doi: 10.1016/s0030-6665(05)70052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germano I. M., Villalobos H., Silvers A., Post K. D. Clinical use of the optical digitizer for intracranial neuronavigation. Neurosurgery. 1999 Aug;45(2):261–270. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199908000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunkel A. R., Freysinger W., Thumfart W. F. Computer-assisted surgery in the frontal and maxillary sinus. Laryngoscope. 1997 May;107(5):631–633. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199705000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunkel A. R., Vogele M., Martin A., Bale R. J., Thumfart W. F., Freysinger W. Computer-aided surgery in the petrous bone. Laryngoscope. 1999 Nov;109(11):1793–1799. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199911000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassfeld S., Mühling J., Zöller J. Intraoperative navigation in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1995 Feb;24(1 Pt 2):111–119. doi: 10.1016/s0901-5027(05)80871-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser R., Westermann B., Probst R. Noninvasive tracking of patient's head movements during computer-assisted intranasal microscopic surgery. Laryngoscope. 1997 Apr;107(4):491–499. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199704000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husstedt H., Heermann R., Becker H. Contribution of low-dose CT-scan protocols to the total positioning error in computer-assisted surgery. Comput Aided Surg. 1999;4(5):275–280. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0150(1999)4:5<275::AID-IGS5>3.0.CO;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamimura M., Ebara S., Itoh H., Tateiwa Y., Kinoshita T., Takaoka K. Accurate pedicle screw insertion under the control of a computer-assisted image guiding system: laboratory test and clinical study. J Orthop Sci. 1999;4(3):197–206. doi: 10.1007/s007760050094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimek L., Wenzel M., Mösges R. Computer-assisted orbital surgery. Ophthalmic Surg. 1993 Jun;24(6):411–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenarz T., Heermann R. Image-guided and computer-aided surgery in otology and neurotology: is there already a need for it? Am J Otol. 1999 Mar;20(2):143–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann W., Klimek L. Indications for computer-assisted surgery in otorhinolaryngology. Comput Aided Surg. 1998;3(4):202–204. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0150(1998)3:4<202::AID-IGS11>3.0.CO;2-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metson R. B., Cosenza M. J., Cunningham M. J., Randolph G. W. Physician experience with an optical image guidance system for sinus surgery. Laryngoscope. 2000 Jun;110(6):972–976. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200006000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metson R., Cosenza M., Gliklich R. E., Montgomery W. W. The role of image-guidance systems for head and neck surgery. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999 Oct;125(10):1100–1104. doi: 10.1001/archotol.125.10.1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metson R., Gliklich R. E., Cosenza M. A comparison of image guidance systems for sinus surgery. Laryngoscope. 1998 Aug;108(8 Pt 1):1164–1170. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199808000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosges R., Klimek L. Computer-assisted surgery of the paranasal sinuses. J Otolaryngol. 1993 Apr;22(2):69–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann A. M., Jr, Pasquale-Niebles K., Bhuta T., Sillers M. J. Image-guided transnasal endoscopic surgery of the paranasal sinuses and anterior skull base. Am J Rhinol. 1999 Nov-Dec;13(6):449–454. doi: 10.2500/105065899781329746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson G., Citardi M. J. Image-guided functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000 Sep;123(3):188–194. doi: 10.1067/mhn.2000.107453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhardt H., Meyer H., Amrein E. A computer-assisted device for the intraoperative CT-correlated localization of brain tumors. Eur Surg Res. 1988;20(1):51–58. doi: 10.1159/000128741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent E. W., Bucholz R. D. Middle cranial fossa surgery with image-guided instrumentation. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997 Jul;117(1):131–134. doi: 10.1016/S0194-59989770222-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. R., Frank K. J., Bucholz R. D. The NeuroStation--a highly accurate, minimally invasive solution to frameless stereotactic neurosurgery. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 1994 Jul-Aug;18(4):247–256. doi: 10.1016/0895-6111(94)90049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorbeck F., Cartellieri M., Ehrenberger K., Imhof H. Experiences in intraoperative computer-aided navigation in ENT sinus surgery with the Aesculap navigation system. Comput Aided Surg. 1998;3(6):306–311. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0150(1998)3:6<306::AID-IGS4>3.0.CO;2-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz C. R., Knauth M., Hassfeld S., Tronnier V. M., Albert F. K., Bonsanto M. M., Kunze S. Neuronavigation--first experiences with three different commercially available systems. Zentralbl Neurochir. 1998;59(1):14–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]