Abstract
1. DL-1-(2-acetyl-4-n-butyramidophenoxy)-2-hydroxy-3-isopropylaminopropane hydrochloride (M & B 17803A) was given to four healthy volunteers in single oral doses of up to 300 mg. There were no subjective effects and no significant alterations in the heart rate, systolic and diastolic blood pressure in the seated position or in the forced expiratory volume or in the electrocardiogram within 6 h of the dose. There were no abnormalities in haematological tests and estimations of the serum glutamyloxaloacetic transaminase.
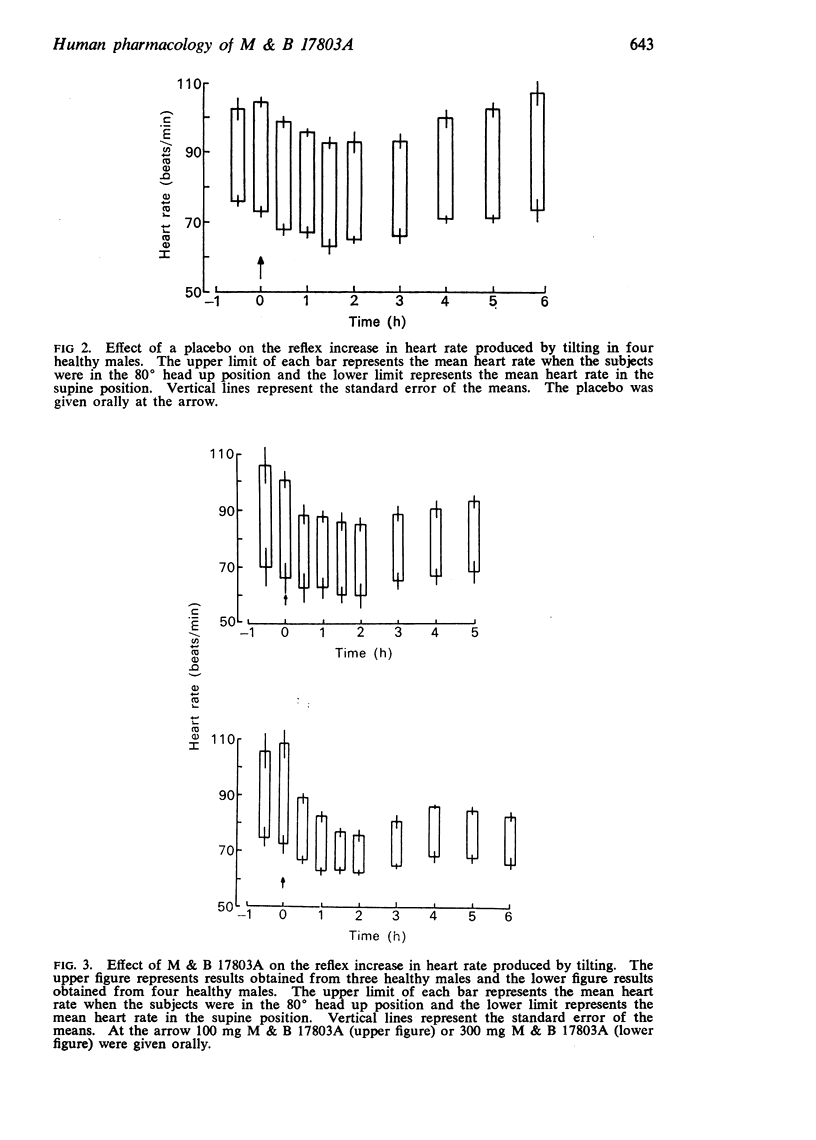
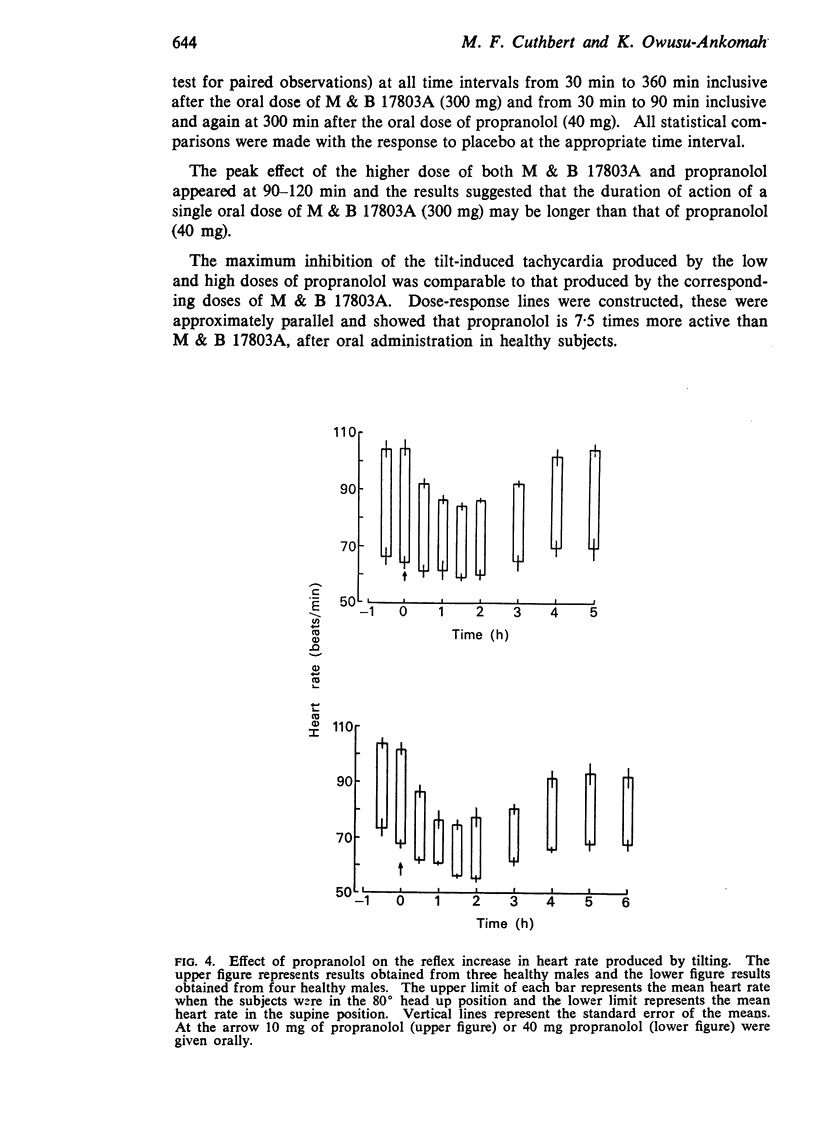
2. Oral doses of both M & B 17803A and propranolol inhibited the increase in heart rate which occurs on tilting from the supine to the 80° head up position. The results suggest that the degree of β-adrenoceptor blockade produced by M & B 17803A (100 and 300 mg) is comparable to that of propranolol (10 and 40 mg) respectively. Propranolol is 7·5-10·0 times as potent as M & B 17803A when compared by this method. There were no significant changes in the systolic or diastolic blood pressure after any of the treatments, in either of the positions studied.
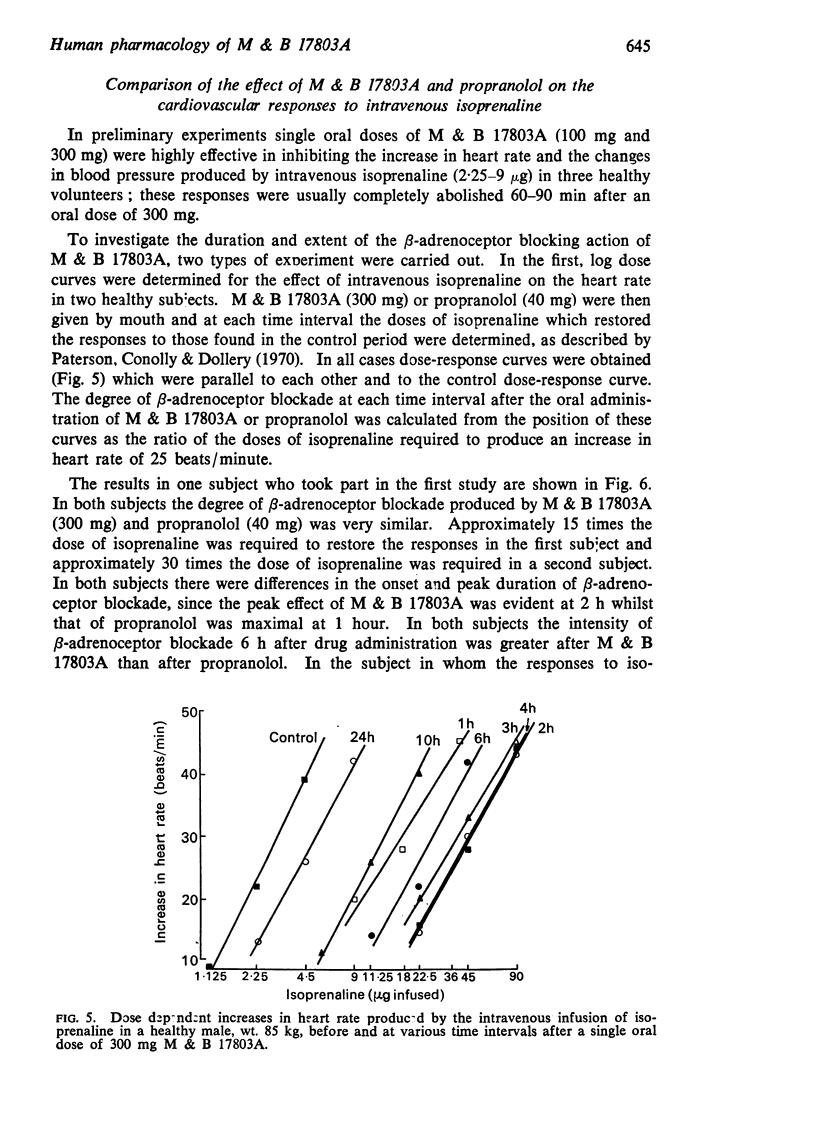
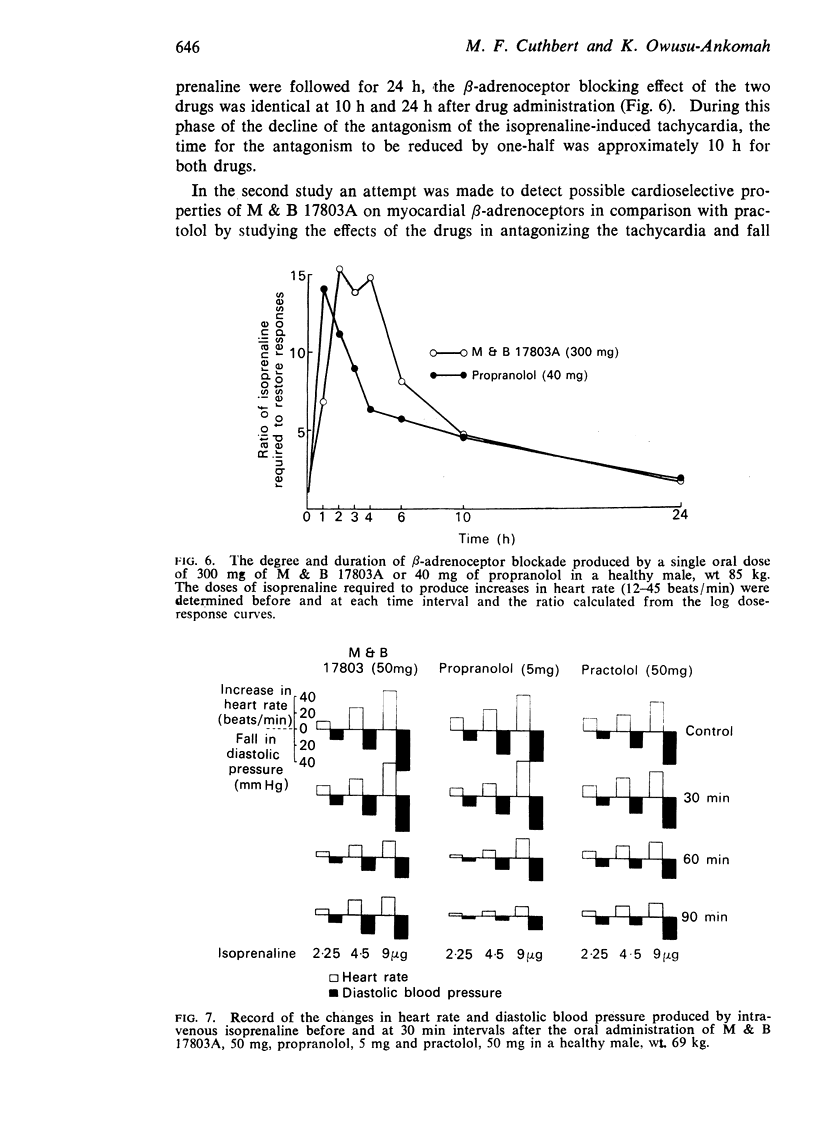
3. M & B 17803A was also effective in inhibiting the increase in heart rate produced by the intravenous infusion of isoprenaline and in two subjects the degree of β-adrenoceptor blockade produced by M & B 17803A (300 mg) was comparable to that of propranolol (40 mg). M & B 17803A is a competitive β-adrenoceptor blocking agent and the duration of the pharmacological activity of both M & B 17803A and propranolol appeared to be very similar as assessed by this method.
4. In separate experiments with small oral doses of M & B 17803A no evidence of a selective action on myocardial β-adrenoceptors was obtained from the study of changes in heart rate and diastolic blood pressure (sphygmomanometric recording).
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett A. M., Crowther A. F., Dunlop D., Shanks R. G., Smith L. H. Cardio-selective beta-blockade. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1968;259(2):152–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00537746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brick I., Hutchison K. J., McDevitt D. G., Roddie I. C., Shanks R. G. Comparison of the effects of I.C.I. 50172 and propranolol on the cardiovascular responses to adrenaline, isoprenaline and exercise. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Sep;34(1):127–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb07956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop D., Shanks R. G. Selective blockade of adrenoceptive beta receptors in the heart. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jan;32(1):201–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne J. F. Variation of blood-pressure in untreated hypertensive outpatients. Lancet. 1969 Feb 22;1(7591):391–392. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARROW J. S. ZERO-MUDDLER FOR UNPREJUDICED SPHYGMOMANOMETRY. Lancet. 1963 Dec 7;2(7319):1205–1205. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92929-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J., Turner P. Comparison of propranolol and I.C.I. 50,172 on isoprenaline-induced increase in skin temperature in man. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 May;36(1):177P–178P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer K. N., Hamilton W. F., Lge J. S., Diament M. L. Effect of a selectivebeta-adrenergic blocker in preventing falls in arterial oxygen tension following isoprenaline in asthmatic subjects. Lancet. 1969 Nov 22;2(7630):1092–1094. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90701-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powles R., Shinebourne E., Hamer J. Selective cardiac sympathetic blockade as an adjunct to bronchodilator therapy. Thorax. 1969 Sep;24(5):616–618. doi: 10.1136/thx.24.5.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson B. F., Epstein S. E., Beiser G. D., Braunwald E. Control of heart rate by the autonomic nervous system. Studies in man on the interrelation between baroreceptor mechanisms and exercise. Circ Res. 1966 Aug;19(2):400–411. doi: 10.1161/01.res.19.2.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


