Abstract
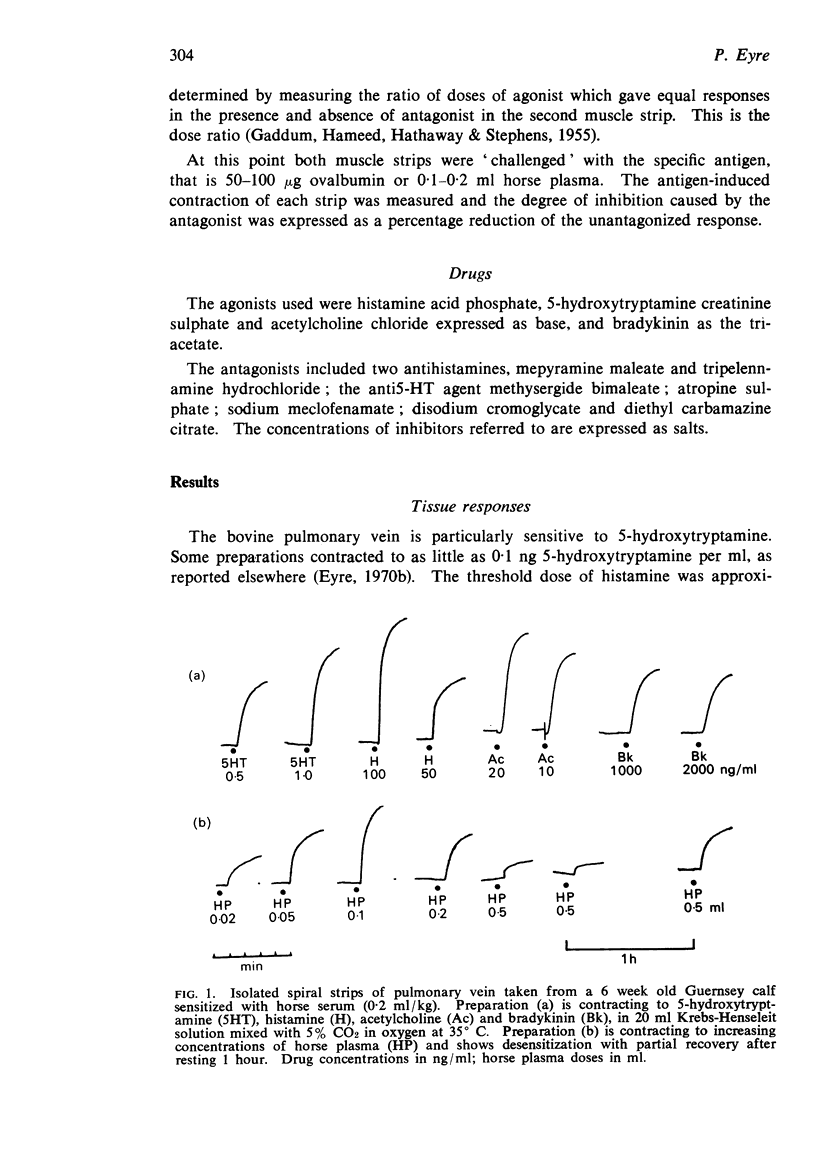
1. The bovine pulmonary vein contracts in response to acetylcholine, histamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine and bradykinin. The tissue is particularly sensitive to 5-hydroxytryptamine (>0·1 ng/ml). Specific Schultz-Dale reactions were elicited in the pulmonary vein in response to horse plasma.
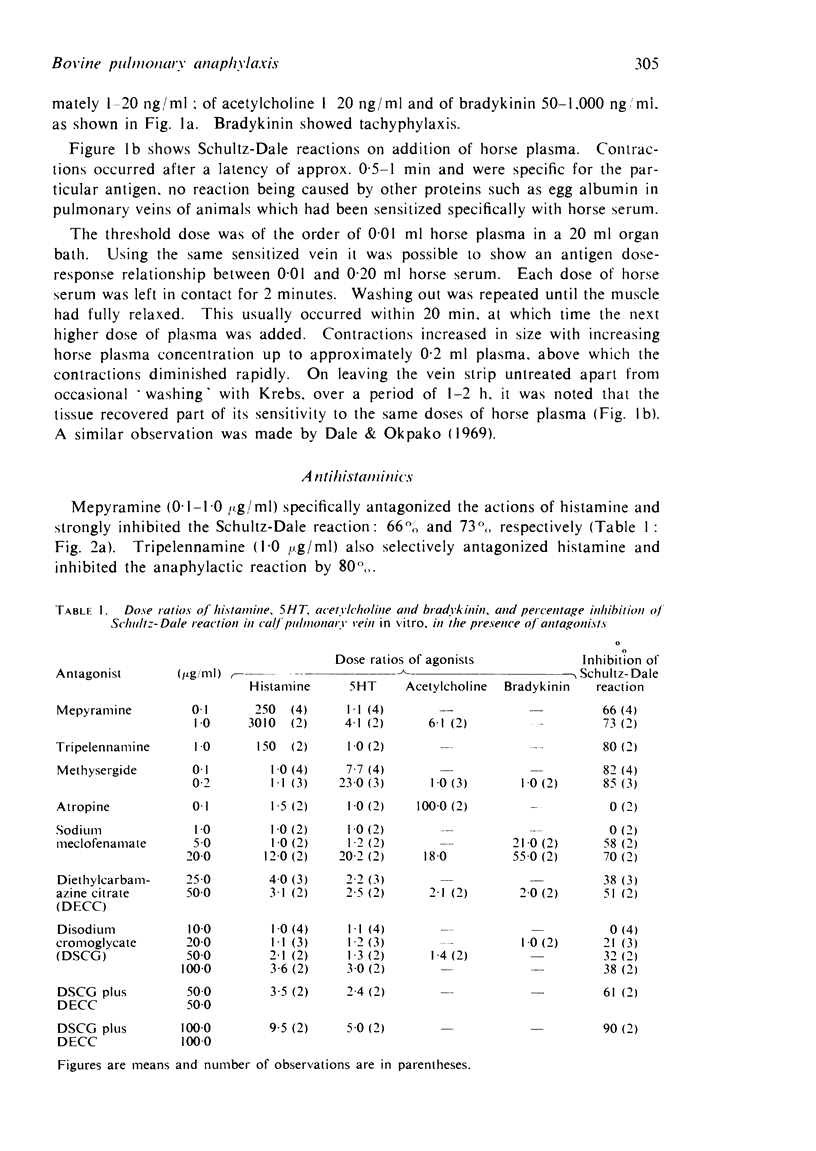
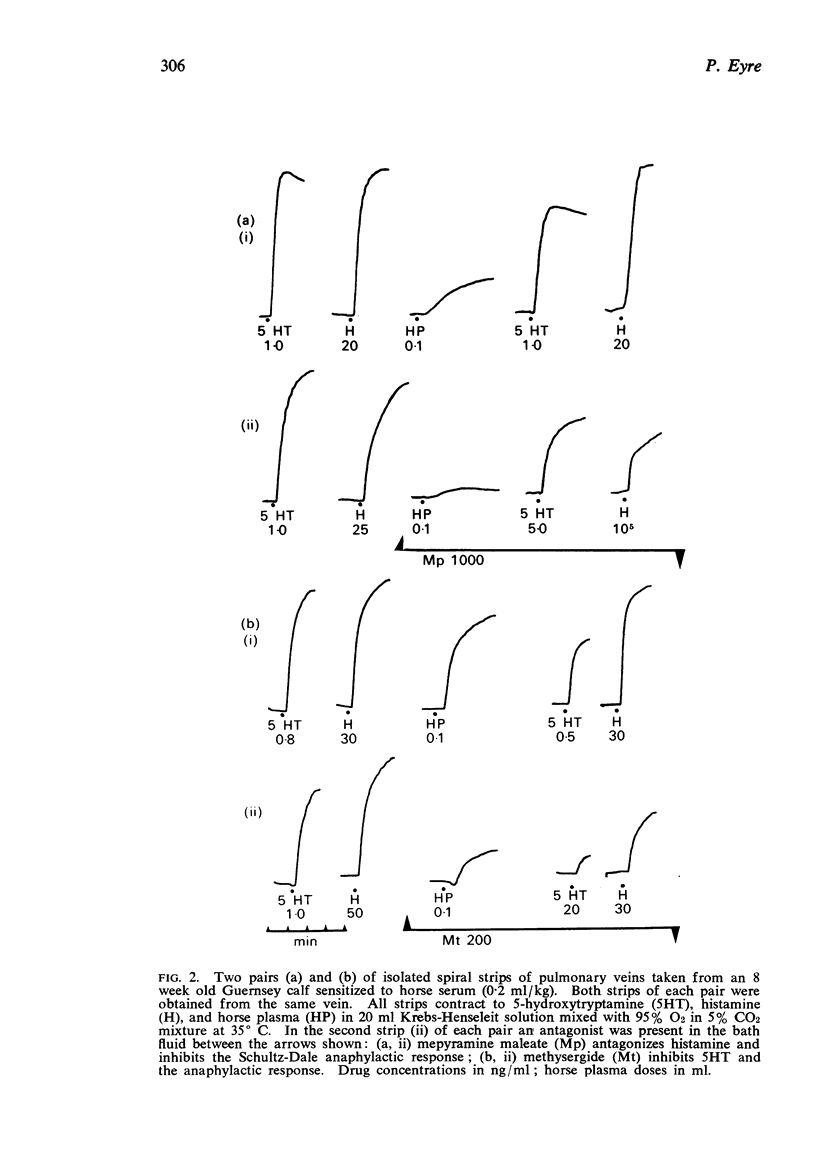
2. The Schultz-Dale reaction is inhibited both by antihistaminics and by the anti-5-hydroxytryptamine agent methysergide, but not by atropine.
3. Sodium meclofenamate inhibited anaphylactic contraction but showed a strong tendency to antagonize many agonists indiscriminately.
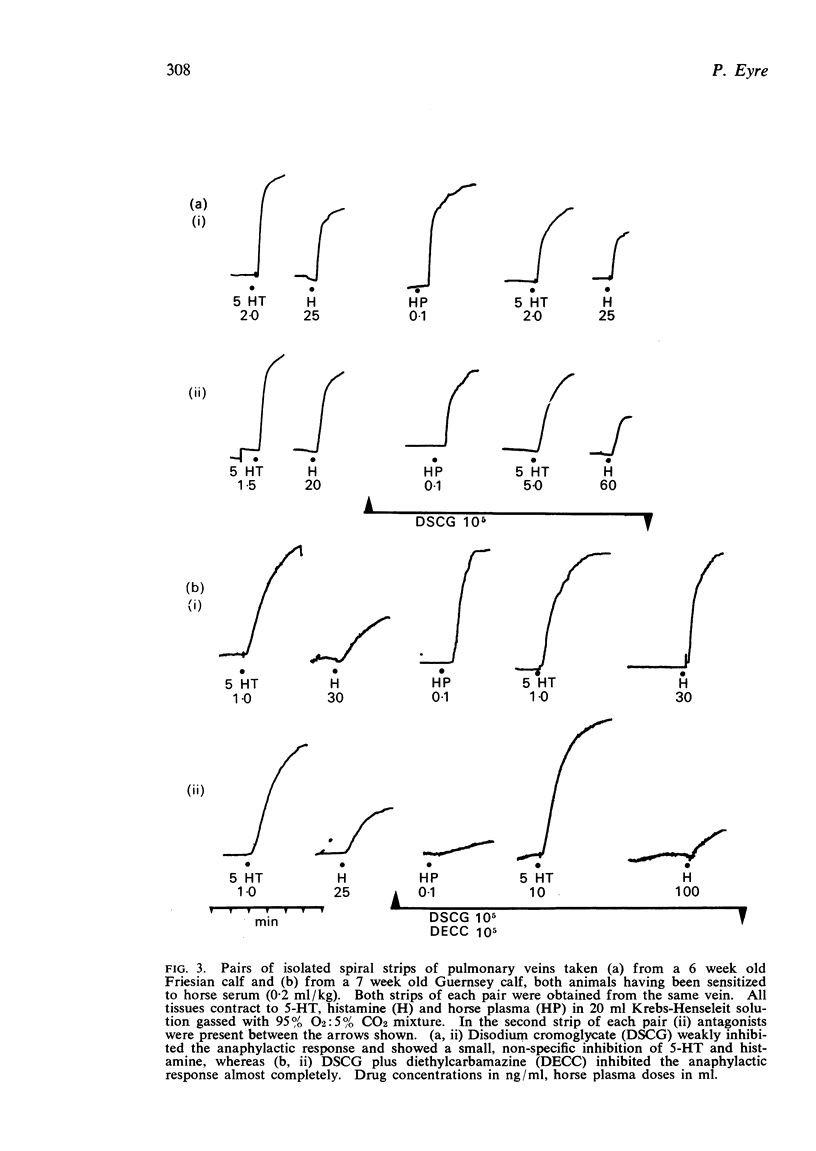
4. Disodium cromoglycate (DSCG: 100 μg/ml) which inhibits some immunological reactions of mast cells, and diethylcarbamazine citrate (DECC: 50 μg/ml) which inhibits slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) elaboration, each inhibited anaphylaxis incompletely (50% or less). However, a combination of DSCG and DECC virtually abolished the Schultz-Dale reaction in this preparation. It is tentatively suggested that the component of the anaphylactic contraction which is resistant to cromoglycate but sensitive to diethylcarbamazine could be due to SRS-A.
5. The bovine pulmonary Schultz-Dale reaction appears to be a complex interaction of histamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine, SRS-A and possible other agents including kinins.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken M. M., Sanford J. Experimental anaphylaxis in cattle. J Comp Pathol. 1969 Jan;79(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(69)90038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken M. M., Sanford J. Protection of cattle against experimentally induced anaphylaxis. Nature. 1969 Jul 19;223(5203):314–316. doi: 10.1038/223314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander F., Eyre P., Head K. W., Sanford J. Effects of anaphylaxis and chemical histamine liberators in sheep. J Comp Pathol. 1970 Jan;80(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(70)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERRY P. A., COLLIER H. O. BRONCHOCONSTRICTOR ACTION AND ANTAGONISM OF A SLOW-REACTING SUBSTANCE FROM ANAPHYLAXIS OF GUINEA-PIG ISOLATED LUNG. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Aug;23:201–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O., James G. W. Humoral factors affecting pulmonary inflation during acute anaphylaxis in the guinea-pig in vivo. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Jun;30(2):283–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb02135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O., James G. W., Piper P. J. Antagonism by fenamates and like-acting drugs of bronchoconstriction induced by bradykinin or antigen in the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Sep;34(1):76–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb07952.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. S. Disodium cromoglycate (FPL 670) ('Intal'): a specific inhibitor of reaginic antibody-antigen mechanisms. Nature. 1967 Dec 30;216(5122):1328–1329. doi: 10.1038/2161328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale M. M., Okpako D. T. Recovery of anaphylactic sensitivity in the guinea-pig ileum after desensitization. Immunology. 1969 Nov;17(5):653–663. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre P. Cutaneous vascular permeability factors (histamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine, bradykinin) and passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in sheep. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1970 Feb;22(2):104–109. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1970.tb08401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre P. The Schultz-Dale reaction in bovine pulmonary smooth muscles. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Sep;40(1):166P–167P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GADDUM J. H., HAMEED K. A., HATHWAY D. E., STEPHENS F. F. Quantitative studies of antagonists for 5-hydroxytryptamine. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1955 Jan;40(1):49–74. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1955.sp001097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALMAGYI D. F., COLEBATCH H. J. Serotonin-like cardiorespiratory effects of a serotonin antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 Oct;134:47–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALPERN B. N., NEVEU T., SPECTOR S. On the nature of the chemical mediators involved in anaphylactic reactions in mice. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Jun;20:389–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orange R. P., Valentine M. D., Austen K. F. Inhibition of the release of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis in the rat with diethylcarbamazine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jan;127(1):127–132. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr T. S., Gwilliam J., Cox J. S. Studies on passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in the rat with disodium cromoglycate. I. Cutaneous reactions induced by an anti-DNP 7S-gamma-2 antibody. Immunology. 1970 Sep;19(3):469–479. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARRATT J. R., WEST G. B. 5-Hydroxytryptamine and tissue mast cells. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):169–178. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARRATT J. R., WEST G. B. Release of 5-hydroxytryptamine and histamine from tissues of the rat. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):179–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTTER M. C. THE PHARMACOLOGY OF ISOLATED VEINS. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Jun;24:742–751. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb01630.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheard P., Blair A. M. Disodium cromoglycate. Activity in three in vitro models of the immediate hypersensitivity reaction in lung. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;38(2):217–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stechschulte D. J., Austen K. F., Bloch K. J. Antibodies involved in antigen-induced release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) in the guinea pig and rat. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):127–147. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells P. W., Eyre P. Homocytotropic antibodies demonstrated by passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in calves. Vet Rec. 1970 Aug 8;87(6):173–175. doi: 10.1136/vr.87.6.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


