Abstract
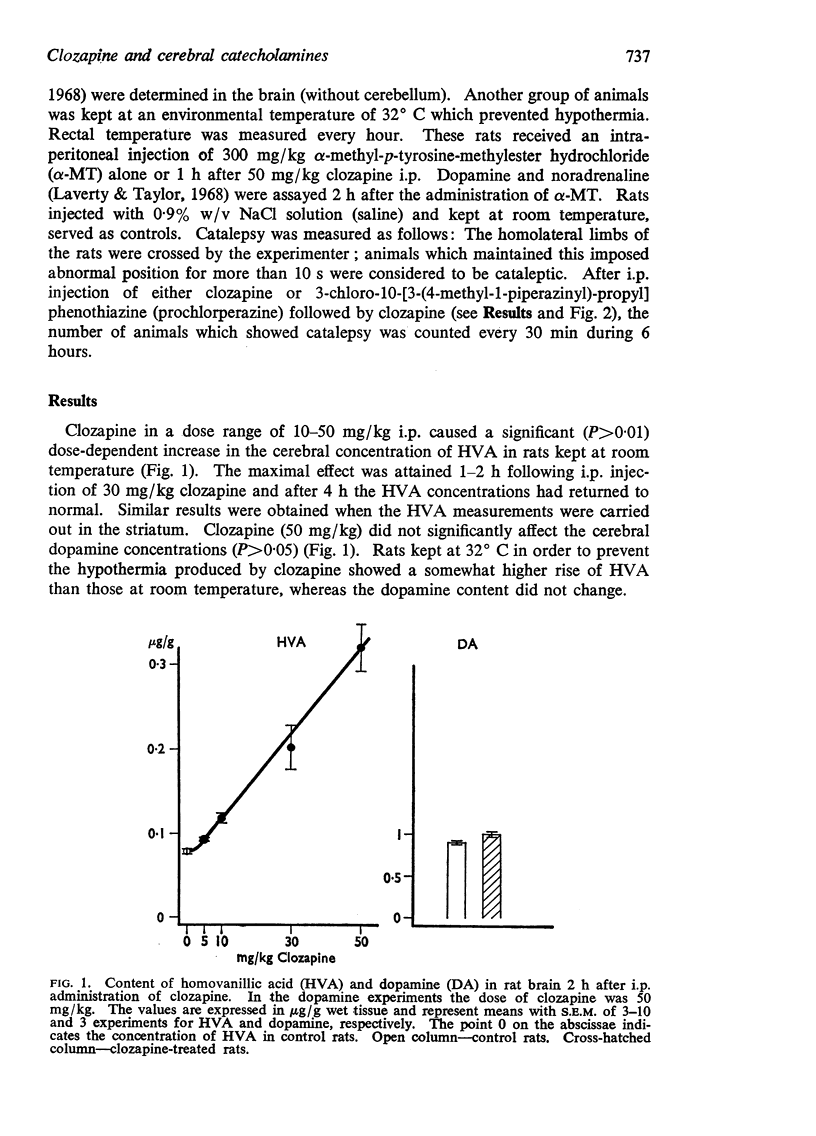
1. Clozapine, a dibenzodiazepine derivative claimed to possess antipsychotic properties in man without producing extrapyramidal disorders, greatly increased the turnover of cerebral dopamine in the rat.
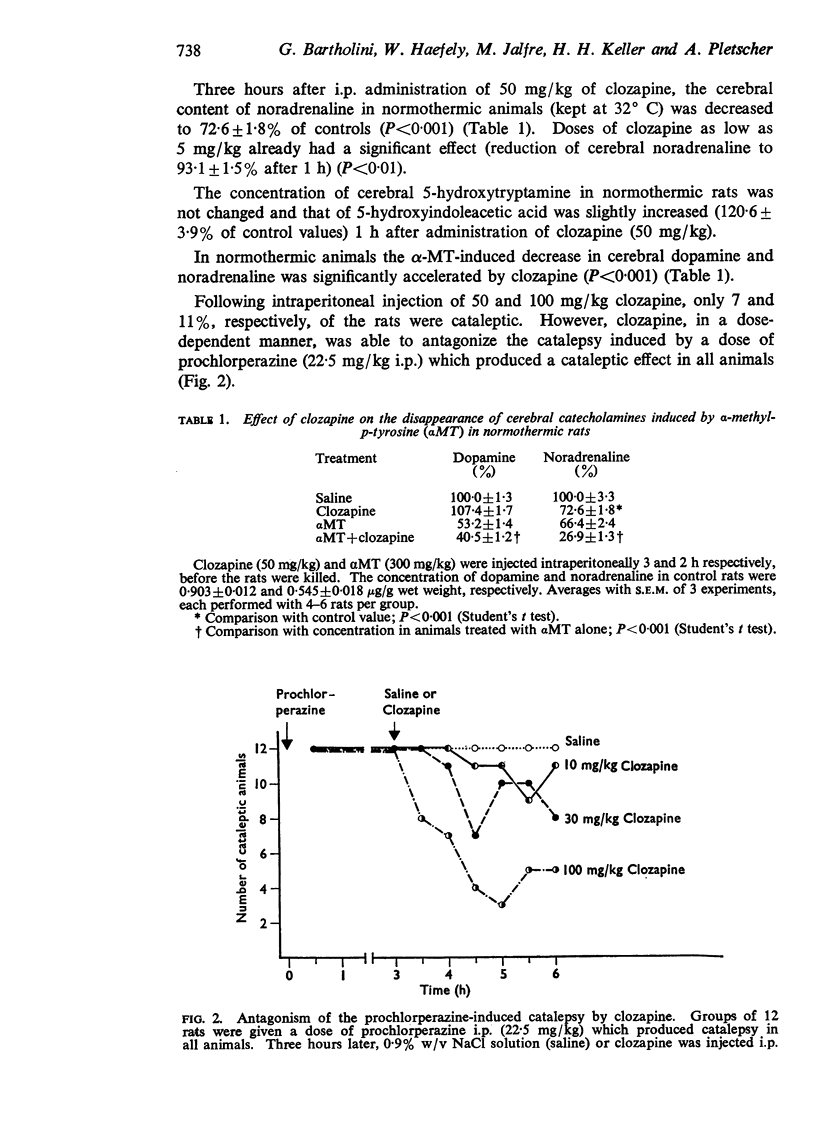
2. The drug itself was virtually devoid of cataleptigenic activity in rats; however, it antagonized prochlorperazine-induced catalepsy.
3. It is proposed that clozapine causes a blockade of striatal dopamine receptors which is of the surmountable type in contrast to that produced by cataleptigenic neuroleptics. In addition, clozapine may also increase the turnover of cerebral noradrenaline.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CARLSSON A., LINDQVIST M. EFFECT OF CHLORPROMAZINE OR HALOPERIDOL ON FORMATION OF 3METHOXYTYRAMINE AND NORMETANEPHRINE IN MOUSE BRAIN. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1963;20:140–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1963.tb01730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laverty R., Taylor K. M. The fluorometric assay of catecholamines and related compounds: improvements and extensions to the hydroxyindole technique. Anal Biochem. 1968 Feb;22(2):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90316-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. F., Robinson D., Sharman D. F. The effect of tropolone on the formation of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylacetic acid in the brain of the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 May;36(1):107–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb08308.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keeffe R., Sharman D. F., Vogt M. Effect of drugs used in psychoses on cerebral dopamine metabolism. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Feb;38(2):287–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb08517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stille G., Lauener H., Eichenberger E. The pharmacology of 8-chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-5H-dibenzo(b,e)(1,4)diazepine (clozapine). Farmaco Prat. 1971 Oct;26(10):603–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de JONGE M., FUNCKE A. B. Sinistrotorsion in guinea pigs as a method of screening central anticholinergic activity. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1962 Jun 1;137:375–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


