Abstract
1. The output of prostaglandins from the spleens of cats and dogs was studied. Comparison is made between the results found in the two species. 2. The release of prostaglandins was investigated in isolated saline-perfused spleens and in incubates of spleen slices. Release in response to nerve stimulation, and exposure to adrenaline or noradrenaline was compared with resting release. 3. A resting release of prostaglandins was found in the dog but not in the cat spleen. 4. Whereas stimulated dog spleens released microgram quantities of prostaglandins E2 and F2alpha, prostaglandin output from the cat spleen under similar conditions was undectectable or barely detectable. 5. The identity of the prostaglandins released from the dog spleen (prostaglandins E2 and F2alpha) was confirmed by mass spectrometry. 6. The species difference in prostaglandin output from the spleen is discussed in relation to the hypothesis that endogenous prostaglandins modify the responses of this organ to nervous stimuli.
Full text
PDF

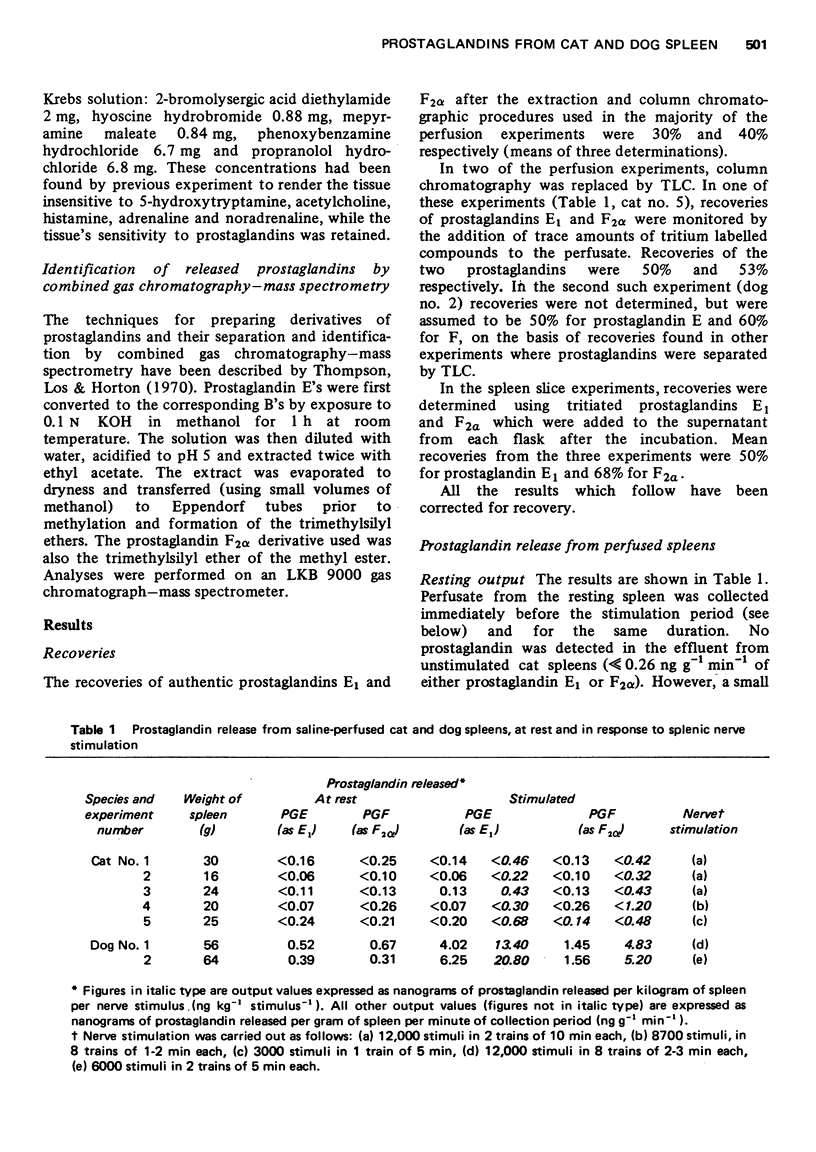
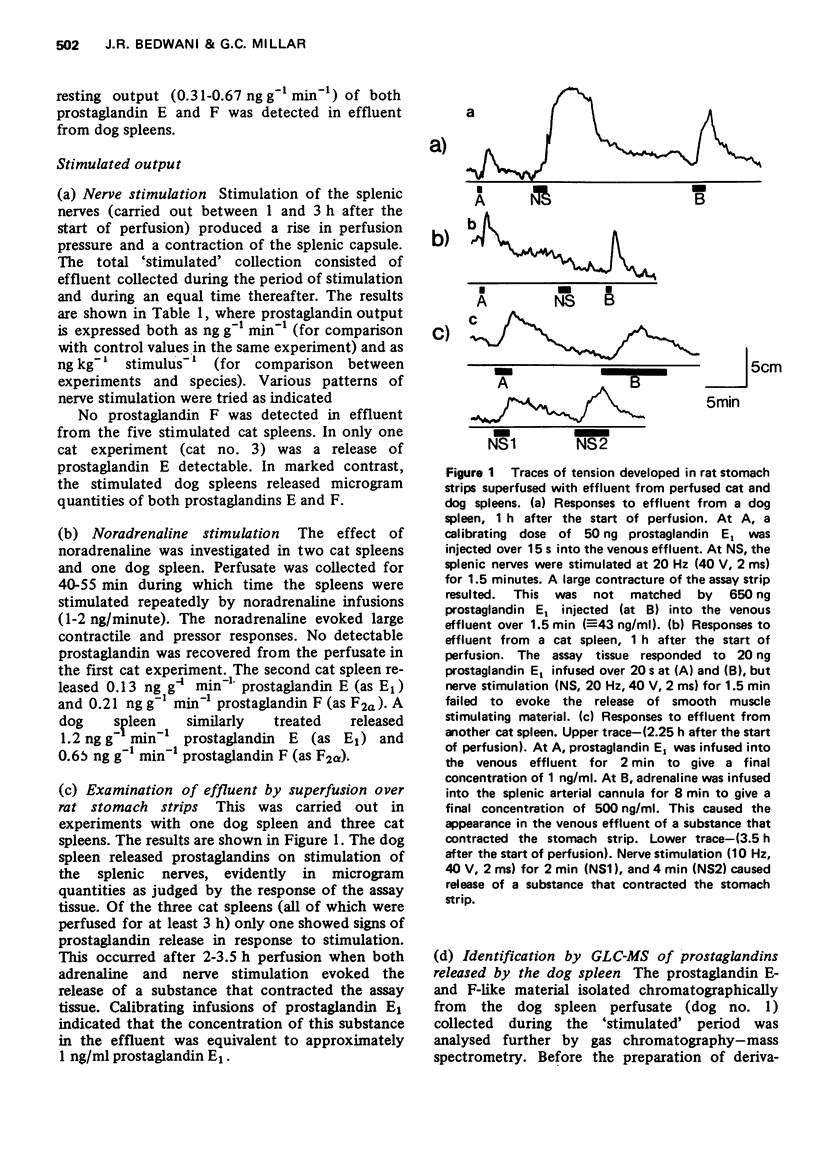



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett A., Friedmann C. A., Vane J. R. Release of prostaglandin E-1 from the rat stomach. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):873–876. doi: 10.1038/216873a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody M. J., Kadowitz P. J. Prostaglandins as modulators of the autonomic nervous system. Fed Proc. 1974 Jan;33(1):48–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coceani F., Pace-Asciak C., Volta F., Wolfe L. S. Effect of nerve stimulation on prostaglandin formation and release from the rat stomach. Am J Physiol. 1967 Oct;213(4):1056–1064. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.4.1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies B. N., Horton E. W., Withrington P. G. The occurrence of prostaglandin E2 in splenic venous blood of the dog following splenic nerve stimulation. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(2):38P–39P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies B. N., Horton E. W., Withrington P. G. The occurrence of prostaglandin E2 in splenic venous blood of the dog following splenic nerve stimulation. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jan;32(1):127–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00436.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies B. N., Withrington P. G. Actions of prostaglandin F2-alpha on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Jan;41(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb09929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies B. N., Withrington P. G. The effects of prostaglandins E1 and E2 on the smooth muscle of the dog spleen and on its responses to catecholamines, angiotensin and nerve stimulation. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jan;32(1):136–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis H. A., Horton E. W. Output of prostaglandins from the rabbit kidney, its increase on renal nerve stimulation and its inhibition by indomethacin. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Dec;46(4):658–675. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb06891.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham E. W., Zimmerman B. G. Release of prostaglandin-like material from dog kidney during nerve stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1970 Nov;219(5):1279–1285. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.5.1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Indomethacin and aspirin abolish prostaglandin release from the spleen. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):237–239. doi: 10.1038/newbio231237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Some effects of inhibiting endogenous prostaglandin formation on the responses of the cat spleen. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Jan;47(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins: their disappearance from and release into the circulation. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):868–873. doi: 10.1038/216868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore N., Vane J. R., Wyllie J. H. Prostaglandins released by the spleen. Nature. 1968 Jun 22;218(5147):1135–1140. doi: 10.1038/2181135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P. Antagonism by calcium of the inhibitory action of prostaglandin E2 on sympathetic neurotransmission in the cat spleen. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Oct;80(2):269–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04790.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P., Brundin J. Inhibition by prostaglandin E1 of noradrenaline release and of effector response to nerve stimulation in the cat spleen. Life Sci. 1969 Apr 1;8(7):389–395. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90232-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P. Control by prostaglandin E2 of sympathetic neurotrans-mission in the spleen. Life Sci. 1970 Mar 1;9(5):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P. Modulating effect of prostaglandin E2 on noradrenaline release from the isolated cat spleen. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Mar;75(3):511–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P., Stjärne L., Wennmalm A. Facilitation of sympathetic neurotransmission in the cat spleen after inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Nov;83(3):430–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb05099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P., von Euler U. S. Prostaglandin controls neuromuscular transmission in guinea-pig vas deferens. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 29;236(65):113–115. doi: 10.1038/newbio236113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoszowska A., Panczenko B. Effects of inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis on noradrenaline release from isolated perfused spleen of the cat. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm. 1974 Jan-Apr;26(1):137–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Crowshaw K., Terragno N. A., Malik K. U., Lonigro A. J. Differential effect of noradrenaline and renal nerve stimulation on vascular resistance in the dog kidney and the release of a prostaglandin E-like substance. Clin Sci. 1972 Feb;42(2):223–233. doi: 10.1042/cs0420223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar G. C. Letter to the editor: A solvent system for thin layer chromatographic separation of prostaglandins and blood pigment. Prostaglandins. 1974 Aug 10;7(3):207–208. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(74)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peskar B., Hertting G. Release of prostaglandins from isolated cat spleen by angiotensin and vasopressin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1973;279(3):227–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00500602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B., Wennmalm A. Increased nerve stimulation induced release of noradrenaline from the rabbit heart after inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Oct;83(2):163–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb05065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. E., Ramwell P. W. Release of prostaglandin from rat epididymal fat pad on nervous and hormonal stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1498–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. J., Los M., Horton E. W. The separation, identification and estimation of prostaglandins in nanogram quantities by combined gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Life Sci I. 1970 Sep 1;9(17):983–988. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennmalm A., Stjärne L. Inhibition of the release of adrenergic transmitter by a fatty acid in the perfusate from sympathetically stimulated rabbit heart. Life Sci I. 1971 Apr 15;10(8):471–479. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(71)90113-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


