Abstract
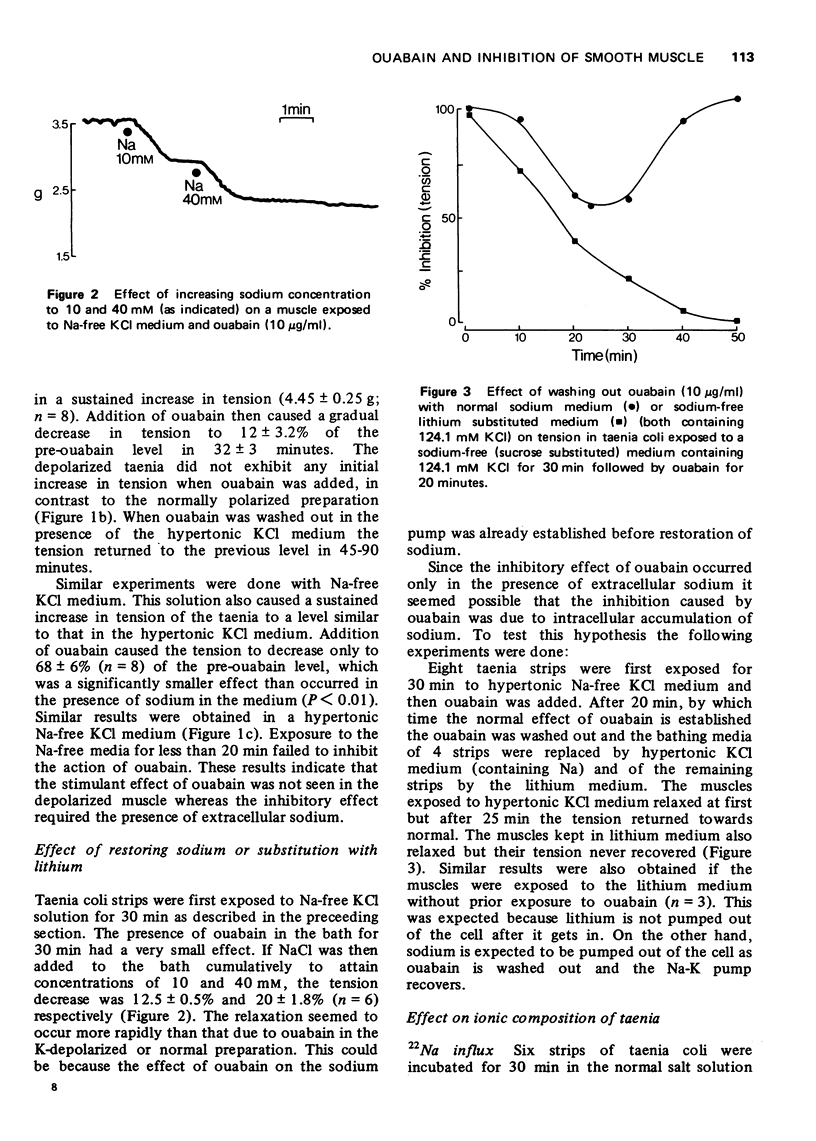
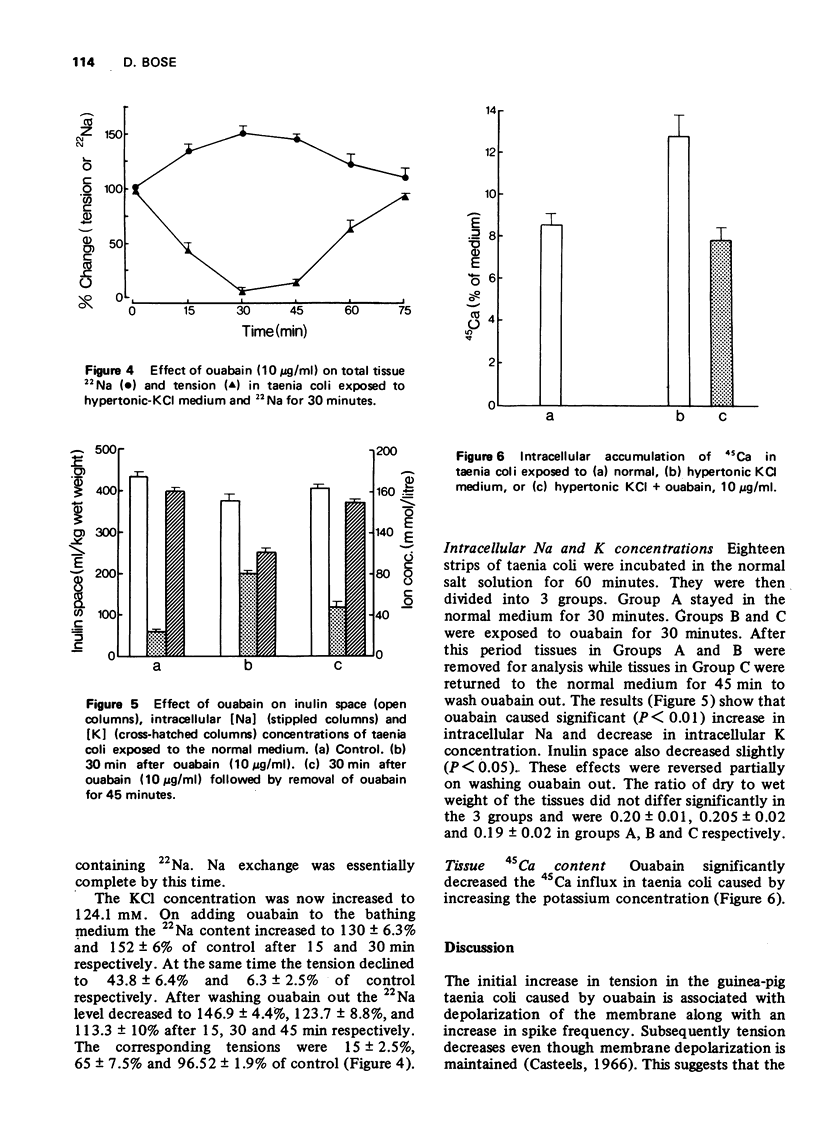
1 Ouabain (10 mug/ml) caused an initial increase followed by a decrease in tension in guinea-pig taenia coli bathed in normal sodium and potassium containing medium. 2 The excitatory effect of ouabain was prevented by the elevation of extracellular potassium while the inhibitory effect was abolished in the absence of sodium in the bathing medium. 3 In the presence of sodium, the inhibitory effect of ouabain disappeared when the drug was washed out, but in the presence of lithium (which is not extruded by the Na-K pump) the inhibition was not abolished. 4 The inhibitory effect of ouabain was accompanied by an increase in tissue Na and a decrease in tissue K concentration. The increase in intracellular [45Ca] which occurred when extracellular [k] was varied, was also reduced by ouabain. 5 It is concluded that a high intracellular level of sodium inhibits contractions in visceral smooth muscle probably by a mechanism involving decreased Ca influx.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bose D. Mechanism of inhibition of smooth muscle tension in guinea-pig taenia coli by ouabain. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1974 Aug;52(4):898–901. doi: 10.1139/y74-116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle P. J., Conway E. J., Kane F., O'reilly H. L. Volume of interfibre spaces in frog muscle and the calculation of concentrations in the fibre water. J Physiol. 1941 Jun 30;99(4):401–414. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1941.sp003911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekaert A., Godfraind T. The actions of ouabain on isolated arteries. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1973 Jun;203(2):393–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels R. The action of ouabain on the smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig's taenia coli. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(1):131–142. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. D., Szaro R. P., Weltman J. K. Ouabain antagonism of smooth muscle contraction. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Sep;182(3):378–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai S., Takeda K. Actions of calcium and certain multivalent cations on potassium contracture of guinea-pig's taenia coli. J Physiol. 1967 May;190(1):155–169. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katase T., Tomita T. Influences of sodium and calcium on the recovery process from potassium contracture in the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):489–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEONARD E. Alteration of contractile response of artery strips by a potassium-free solution, cardiac glycosides and changes in stimulation frequency. Am J Physiol. 1957 Apr;189(1):185–190. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.189.1.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Sutter M. C. Ouabain-induced changes in the contractile and electrical activity, potassium content, and response to drugs, of smooth muscle cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1967 May;45(3):509–520. doi: 10.1139/y67-060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Blaustein M. P., Haeusler G. Na-Ca exchange and tension development in arterial smooth muscle. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Mar 15;265(867):87–94. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1973.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHATZMANN H. J., ACKERMANN H. [The action of strophanthin on intestinal muscle and its relation to the cation content of the medium]. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1961;19:196–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOU J. C. ENZYMATIC BASIS FOR ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF NA+ AND K+ ACROSS CELL MEMBRANE. Physiol Rev. 1965 Jul;45:596–617. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.3.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Breemen C., Farinas B. R., Gerba P., McNaughton E. D. Excitation-contraction coupling in rabbit aorta studied by the lanthanum method for measuring cellular calcium influx. Circ Res. 1972 Jan;30(1):44–54. doi: 10.1161/01.res.30.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


