Abstract
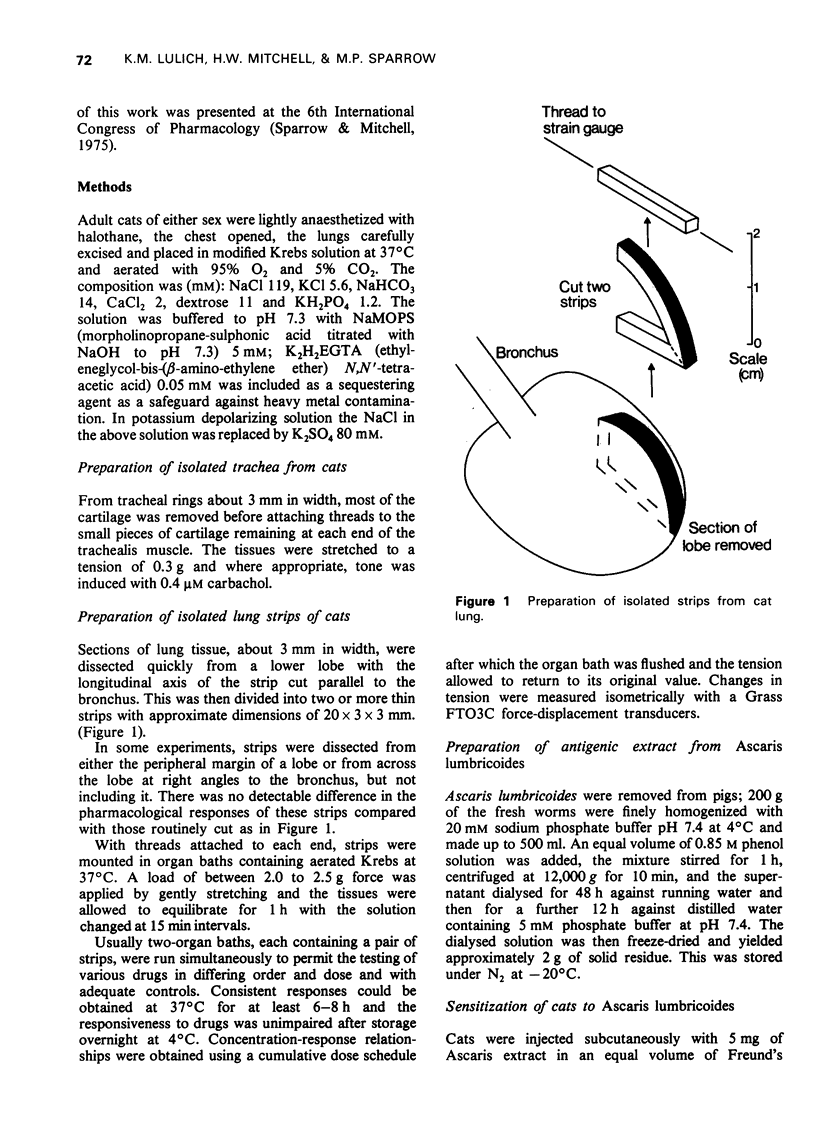
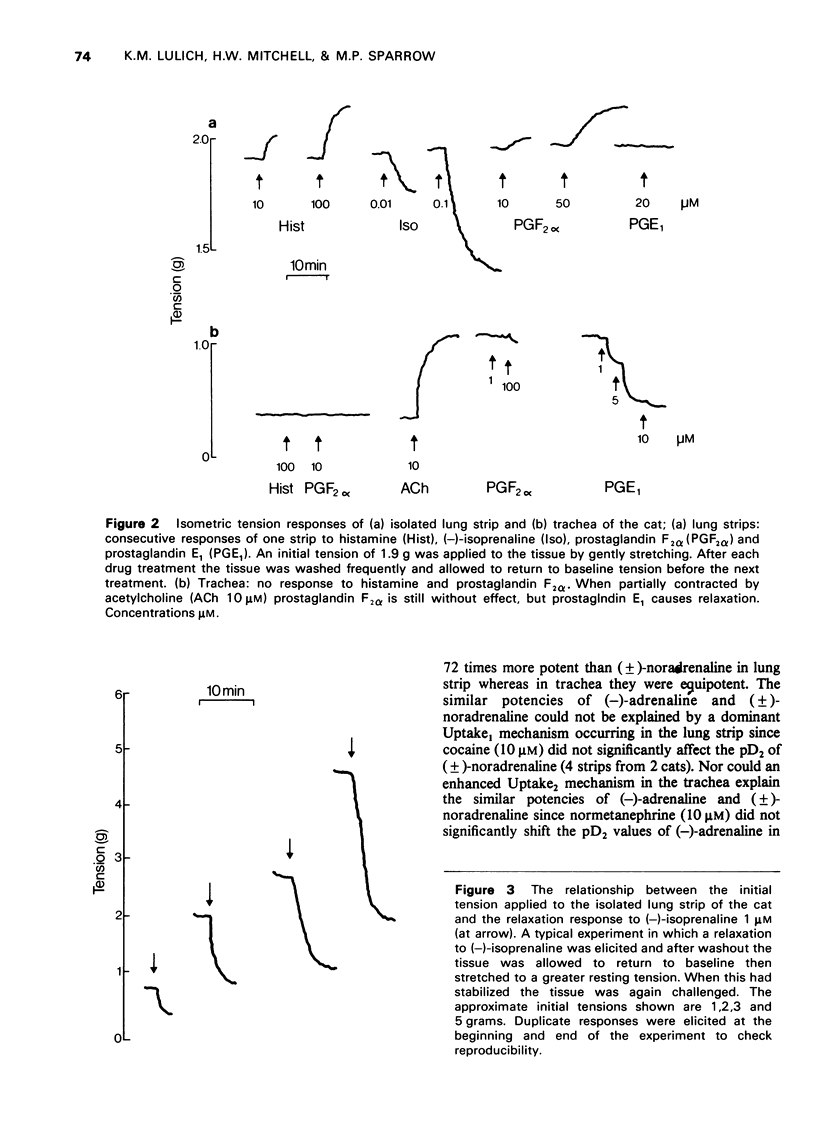
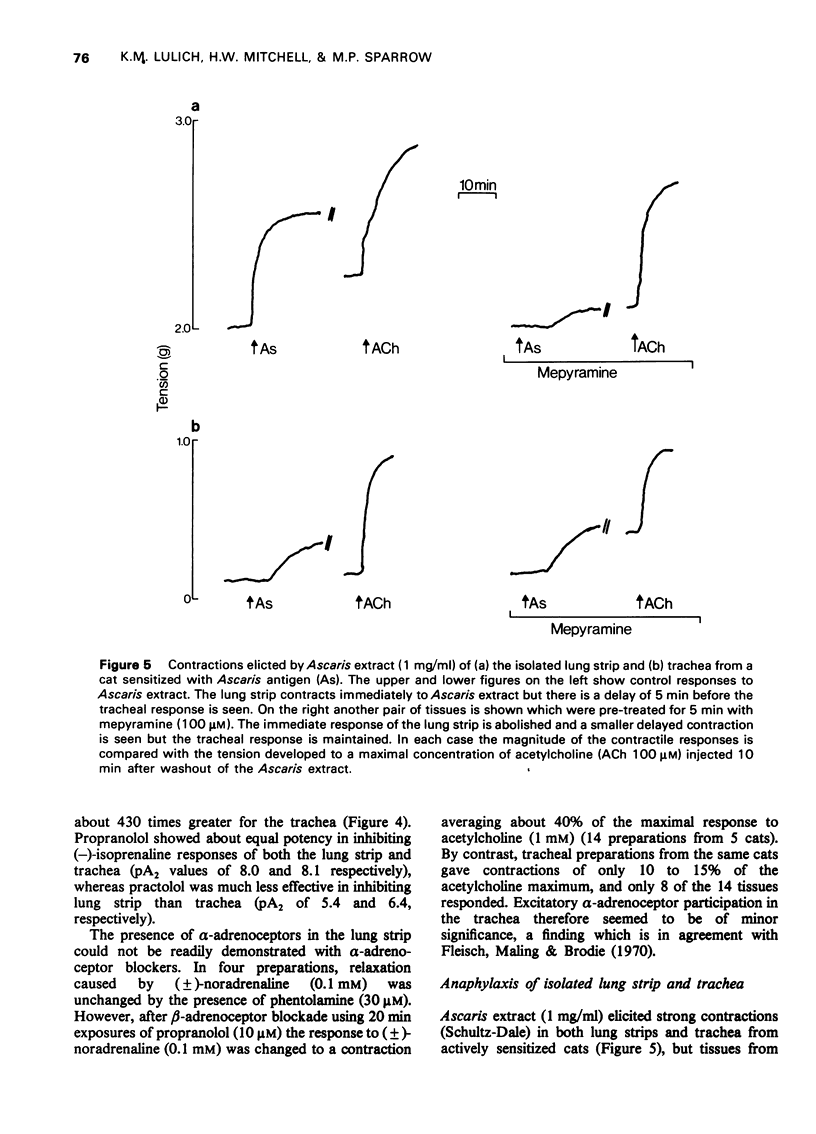
1 A new in vitro preparation, the isolated lung strip of the cat, is described for investigating the direct effect of drugs on the smooth muscle of the peripheral airways of the lung. The preparation comprises a thin strip of lung parenchyma which can be mounted in a conventional organ bath for isometric tension recording. Its pharmacological responses have been characterized and compared with the isolated tracheal preparation of the cat. 2 The lung strip exhibited an intrinsic tone which was relaxed by catecholamines, aminophylline and flufenamate. It was contracted strongly by histamine, prostaglandin F2alpha, acetylcholine, compound 48/80, potassium depolarizing solution and alternating current field stimulation. In contrast, the cat trachea was unresponsive to histamine and prostaglandin F2alpha and did not exhibit an intrinsic tone. 3 (-)-Isoprenaline and (-)-adrenaline were much more potent in relaxing the lung strip than the trachea. The potency order of relaxation responses to isoprenaline, adrenaline and (+/-)-noradrenaline in the lung strip was isoprenaline greater than adrenaline greater than noradrenaline but in the trachea was isoprenaline greater than noradrenaline greater than or equal to adrenaline. 4 beta2-Adrenoceptor selective agonists salbutamol and terbutaline were more potent in the lung strip than the trachea, suggesting beta2-adrenoceptors predominated in the lung strip. Propranolol was equipotent in inhibiting isoprenaline relexations of the lung strip and trachea, whereas practolol was much less effective in inhibiting lung strip than trachea, further supporting a predominance of beta2-adrenoceptors in lung strip and beta1-adrenoceptors in trachea. 5 Strong Schultz-Dale type contractions were elicited in both lung strips and trachea by Ascaris lumbricoides antigen in actively sensitized cats. The initial phase of the contractile response of the lung strip following challenge was shown to be due to histamine release and was absent in the trachea. The delayed phase of the contraction which took several minutes to develop in both the mepyramine-treated lung strip and trachea was not due to prostaglandins E1, F2alpha or bradykinin, the probable mediator being slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A). 6 It is concluded that the isolated lung strip of the cat is useful as an in vitro model for investigating the effect of drugs on the smooth muscle of the peripheral airways of the lungs.
Full text
PDF

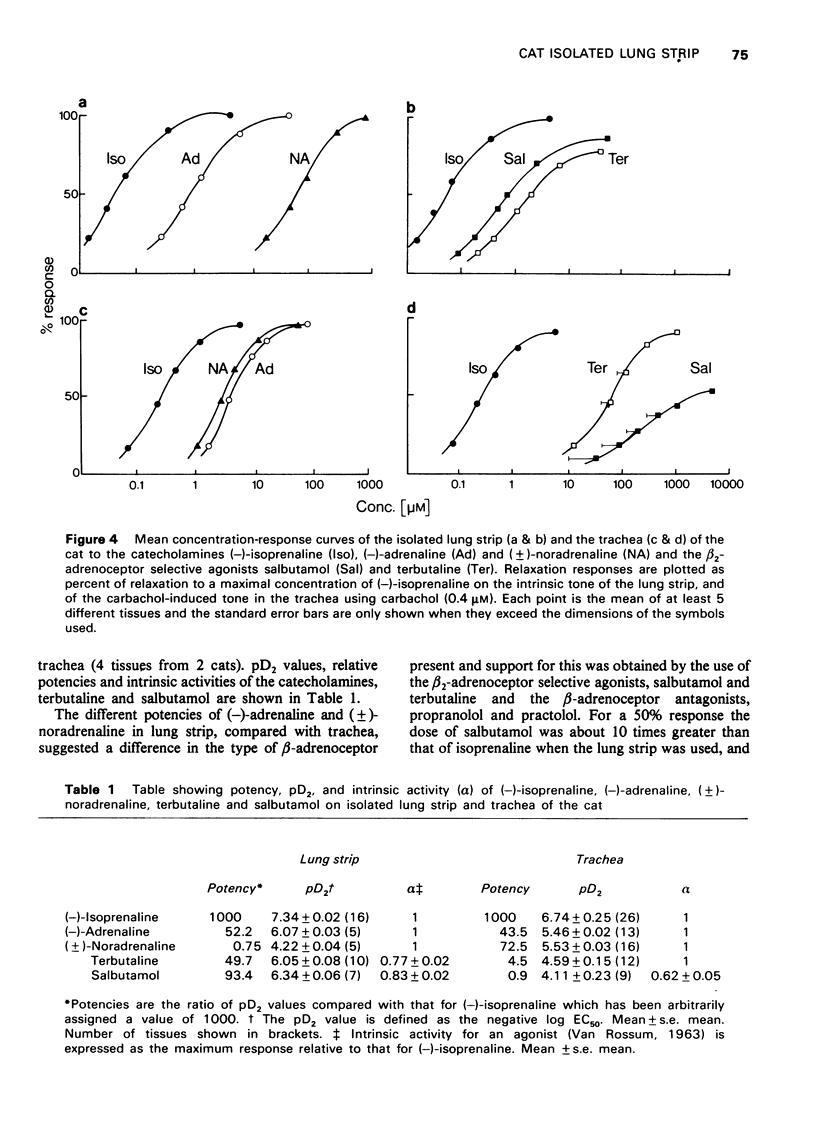



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AKCASU A. The physiologic and pharmacologic characteristics of the tracheal muscle. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1959 Oct 1;122:201–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. W., Duncan W. A., Durant C. J., Ganellin C. R., Parsons E. M. Definition and antagonism of histamine H 2 -receptors. Nature. 1972 Apr 21;236(5347):385–390. doi: 10.1038/236385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chahl L. A., O'Donnell S. R. The interaction of cocaine and propranolol with catecholamines on guinea pig trachea. Eur J Pharmacol. 1967 Nov;2(2):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(67)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazen J. M., Austen K. F. Effects of intravenous administration of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis, histamine, bradykinin, and prostaglandin F2alpha on pulmonary mechanics in the guinea pig. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1679–1685. doi: 10.1172/JCI107719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop D., Shanks R. G. Selective blockade of adrenoceptive beta receptors in the heart. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jan;32(1):201–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. B., Coleman R. A. A new preparation of the isolated intact trachea of the guinea-pig. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;22(1):46–50. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1970.tb08383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. B., Farrar D. G., Wilson J. Antagonism of tone and prostaglandin-mediated responses in a tracheal preparation by indomethacin and SC-19220. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Dec;52(4):559–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09724.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleisch J. H., Maling H. M., Brodie B. B. Evidence for existence of alpha-adrenergic receptors in the mammalian trachea. Am J Physiol. 1970 Feb;218(2):596–599. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.2.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F. The pharmacological differentiation of adrenergic receptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Feb 10;139(3):553–570. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb41229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands A. M., Arnold A., McAuliff J. P., Luduena F. P., Brown T. G., Jr Differentiation of receptor systems activated by sympathomimetic amines. Nature. 1967 May 6;214(5088):597–598. doi: 10.1038/214597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell S. R. An examination of some -adrenoreceptor stimulants for selectivity using the isolated trachea and atria of the guinea pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1972 Sep;19(3):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(72)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell S. R., Wanstall J. C. Potency and selectivity in vitro of compounds related to isoprenaline and orciprenaline on beta-adrenoceptors in the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Nov;52(3):407–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb08610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN ROSSUM J. M. Cumulative dose-response curves. II. Technique for the making of dose-response curves in isolated organs and the evaluation of drug parameters. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963;143:299–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDDICOMBE J. G. Regulation of tracheobronchial smooth muscle. Physiol Rev. 1963 Jan;43:1–37. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1963.43.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


