Abstract
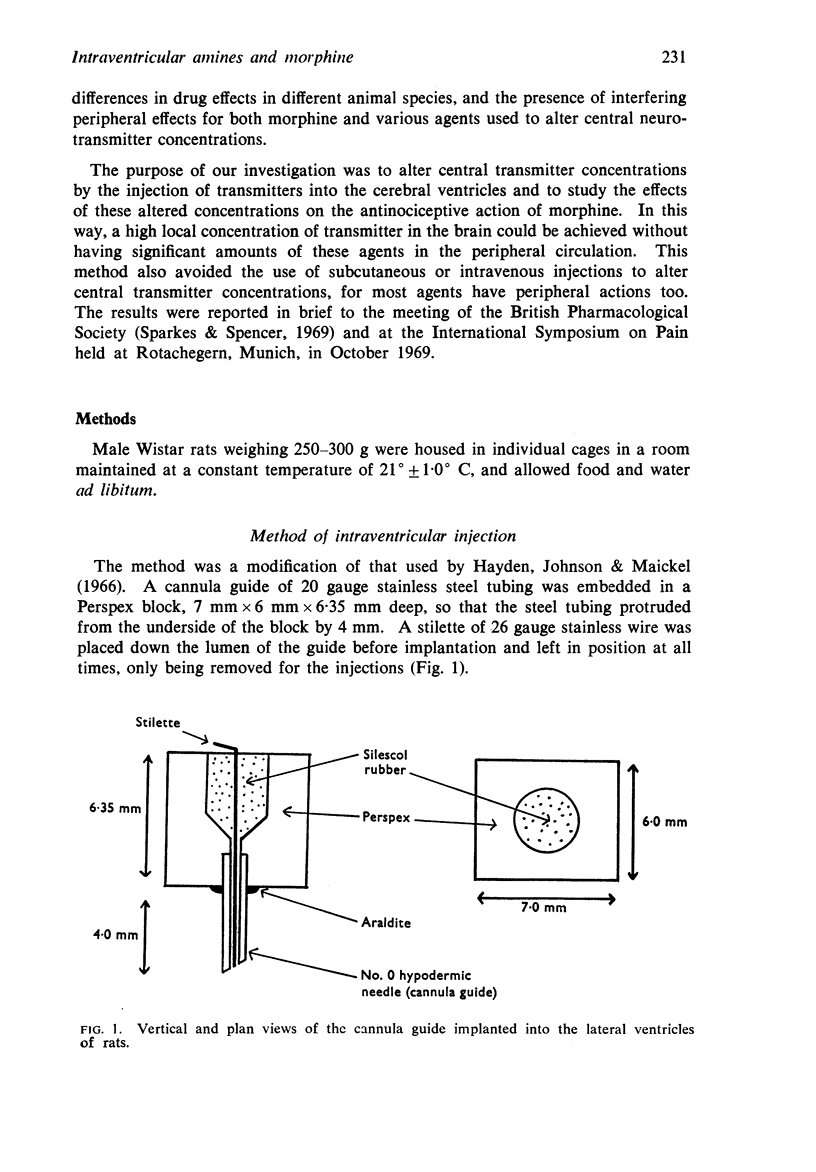
1. A simple cannula and a cannula guide for making injections into the cerebral ventricles of conscious rats are described.
2. Intraventricular injections of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) or of noradrenaline (NA) were without effect on the nociceptive threshold of rats.
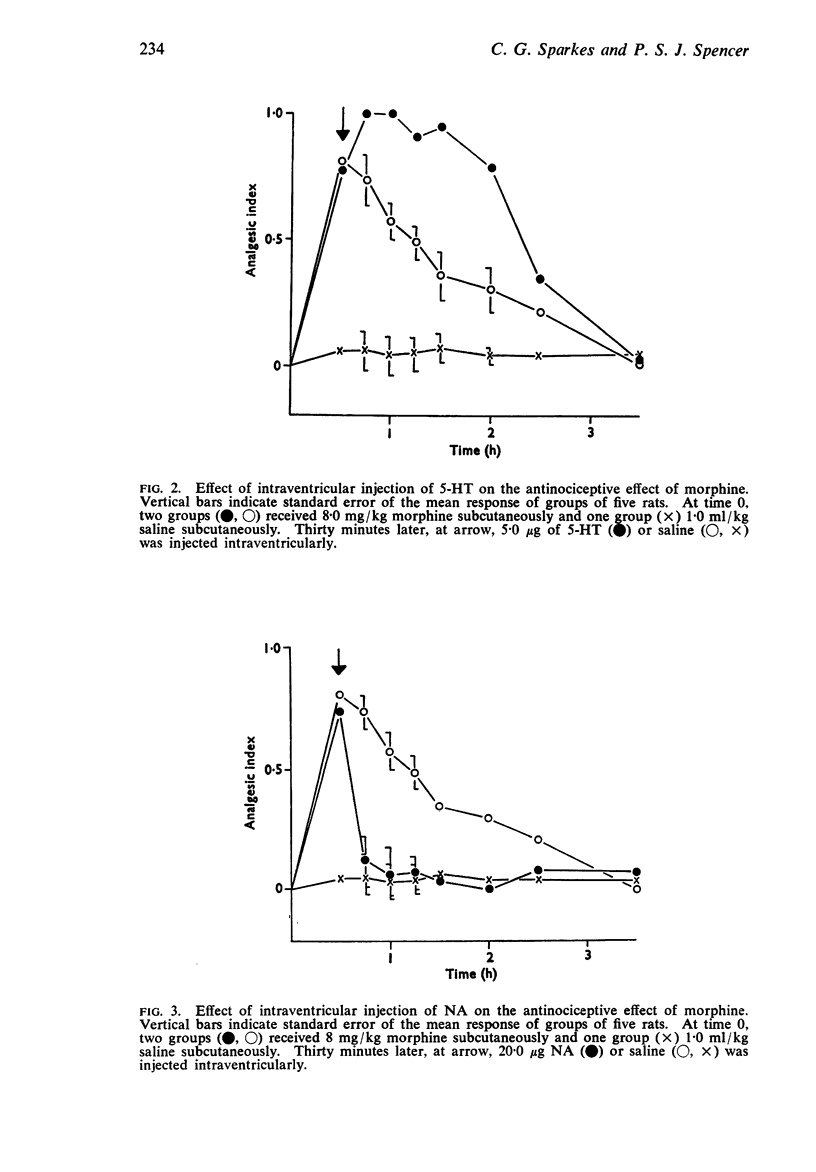
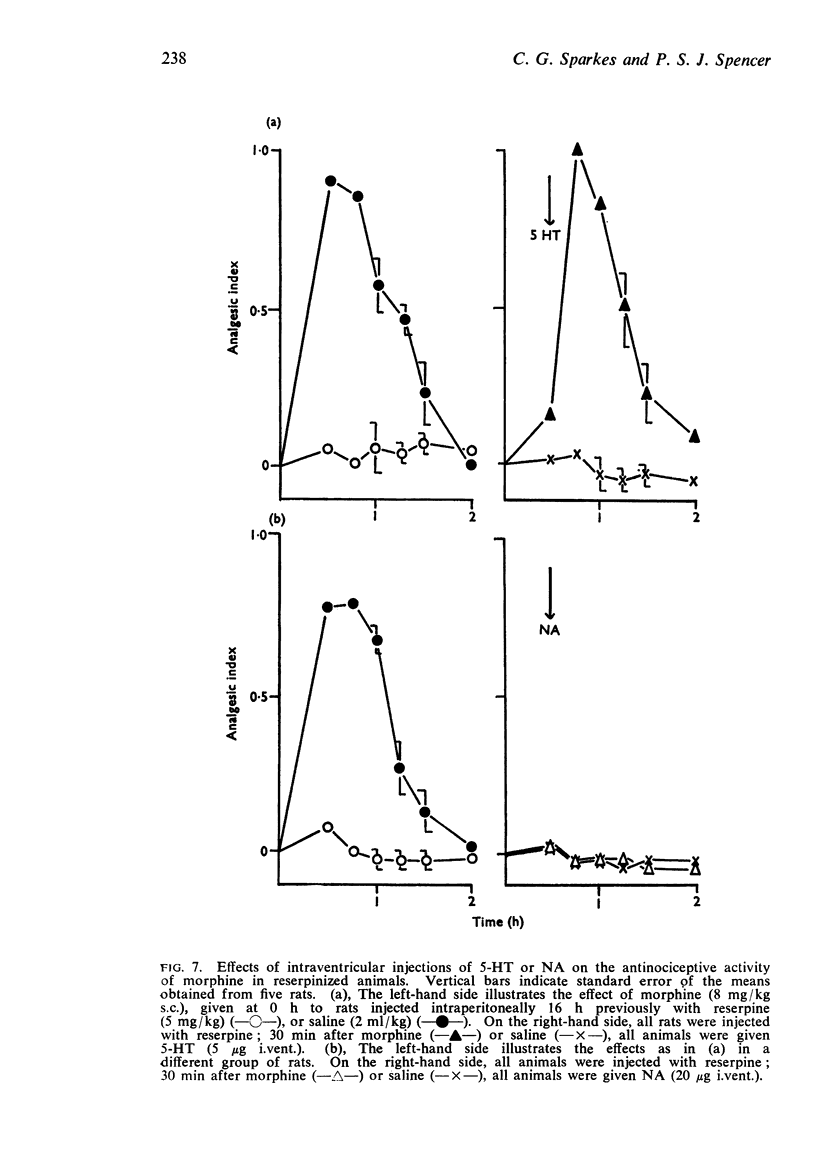
3. Intraventricular injection of 5-HT potentiated the antinociceptive effect of morphine. Reserpine pretreatment antagonized the antinociceptive effect of morphine; this effect was reversed by intraventricular injection of 5-HT.
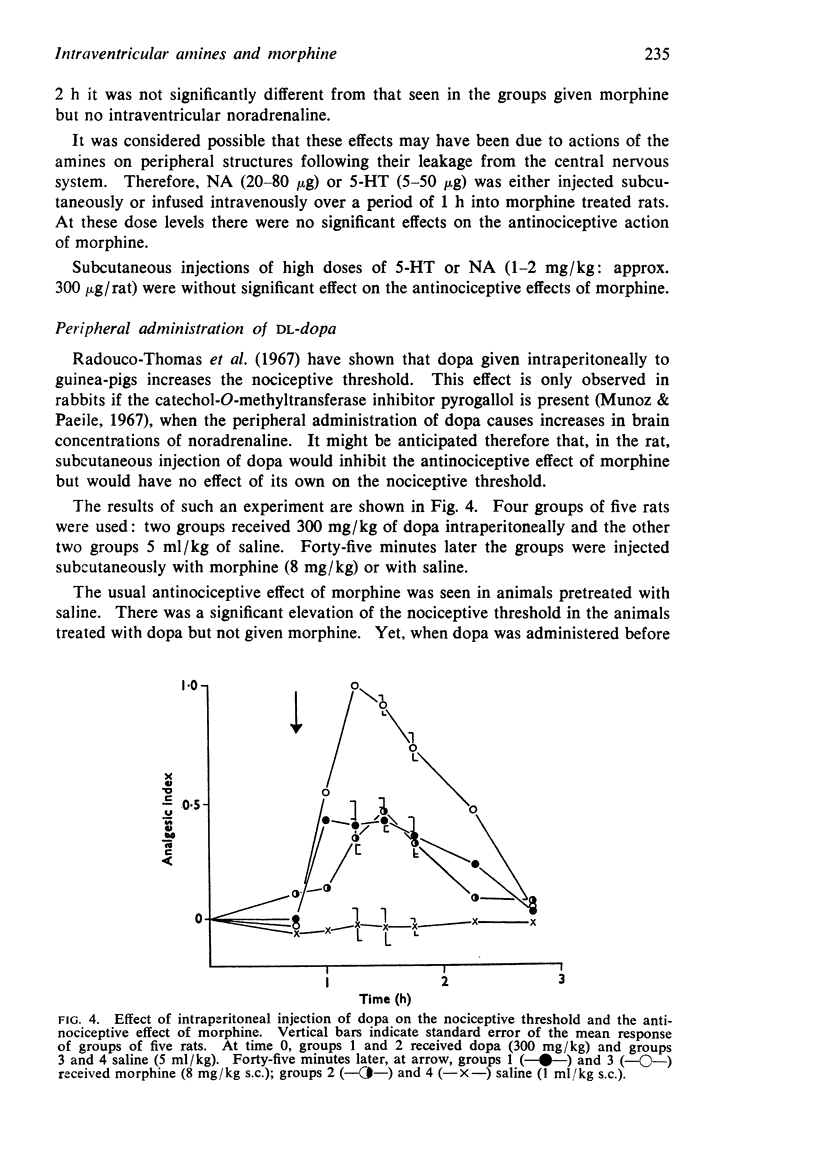
4. Intraventricular injection of NA attenuated the antinociceptive action of morphine but was without effect on the inhibition by reserpine of the antinociceptive effect of morphine.
5. Subcutaneous injection or slow intravenous infusion of either 5-HT or NA (up to 300 μg/rat) were without significant effect on the antinociceptive effects of morphine.
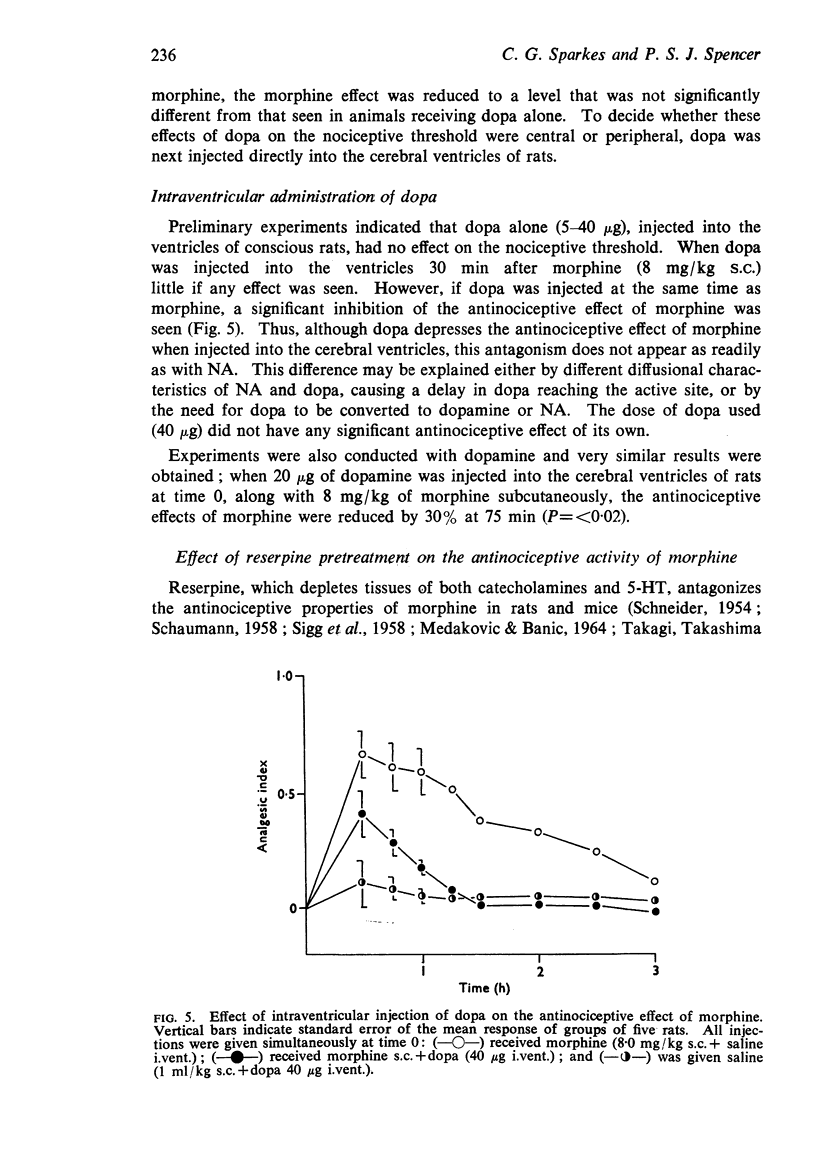
6. Intraperitoneal administration of dopa increased the nociceptive threshold above normal, but reduced the antinociceptive effect of morphine. Intraventricular injection of either dopa or dopamine had no antinociceptive effect but inhibited that of morphine.
7. It is suggested that the antinociceptive effect of morphine may depend on the balance between the concentrations of 5-HT and NA in the brain.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andén N. E. Effect of reserpine and other drugs on the monoamine metabolism with special reference to the CNS. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1968;46(3):361–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLVILLE K. I., CHAPLIN E. SYMPATHOMIMETICS AS ANALGESICS: EFFECTS OF METHOXAMINE, METHAMPHETAMINE, METARAMINOL AND NOREPINEPHRINE. Life Sci. 1964 Apr;3:315–322. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(64)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras E., Tamayo L. Effects of drugs acting in relation to sympathetic functions on the analgesic action of morphine. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1966 Apr;160(2):312–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. M., Ginsburg M., Osman O. H. Acute tolerance to narcotic analgesic drugs in rats. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jun;33(2):245–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris L. S., Dewey W. L., Howes J. F., Kennedy J. S., Pars H. Narcotic-antagonist analgesics: interactions with cholinergic systems. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Sep;169(1):17–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden J. F., Johnson L. R., Maickel R. P. Construction and implantation of a permanent cannula for making injections into the lateral ventricle of the rat brain. Life Sci. 1966 Aug;5(16):1509–1515. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(66)90227-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
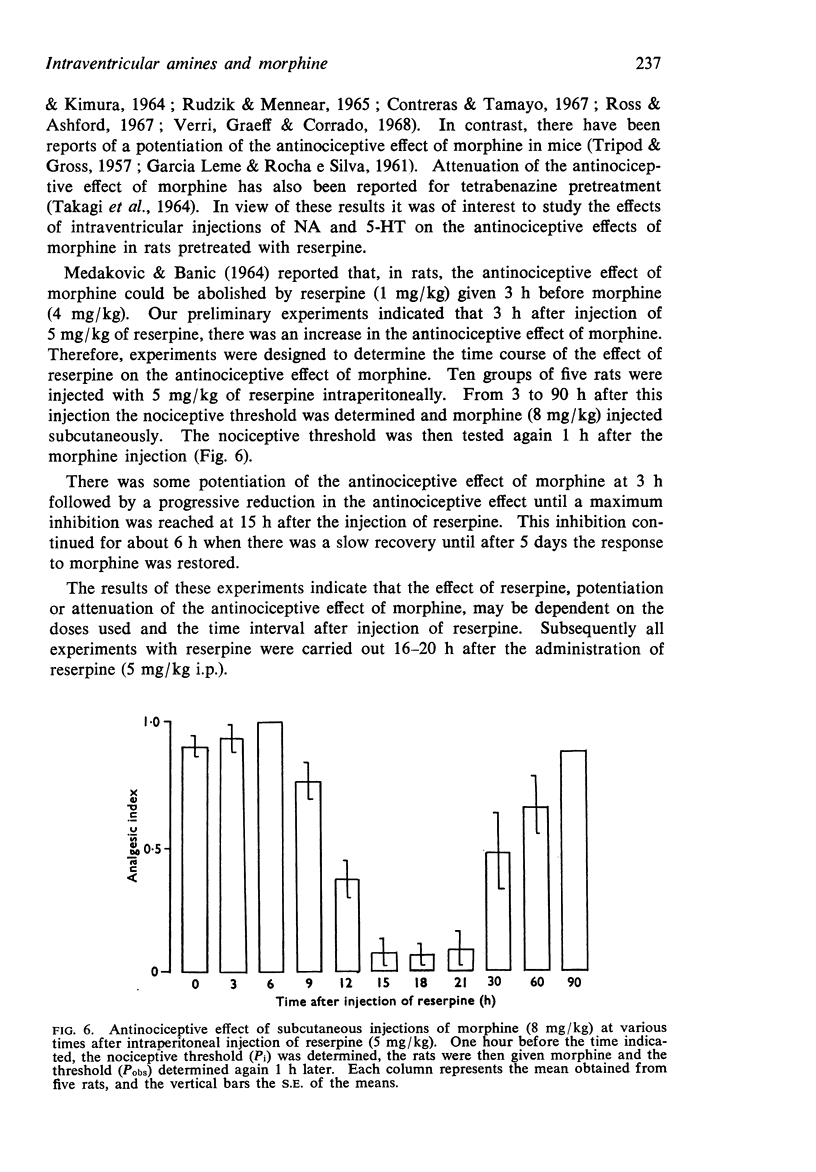
- MEDAKOVIC M., BANIC B. THE ACTION OF RESERPINE AND ALPHA-METHYL-M-TYROSINE ON THE ANALGESIC EFFECT OF MORPHINE IN RATS AND MICE. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1964 Mar;16:198–206. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1964.tb07443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILOSEVIC M. P. Effect of adrenaline on the analgesic response of mice to morphine and related drugs. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1955 Nov 1;104(1):50–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicák A. The influence of serotonine and amphetamine on analgesic effect of morphine after reserpine premedication in rats and mice. Med Pharmacol Exp Int J Exp Med. 1965;13(1):43–48. doi: 10.1159/000135591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nott M. W. Potentiation of morphine analgesia by cocaine in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1968 Dec;5(1):93–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(68)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RADOUCO-THOMAS S., RADOUCO-THOMAS C., LE BRETON E. Action de la noradrénaline et de la réserpine sur l'analgésie expérimentale. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1957;232(1):279–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDALL L. O., SELITTO J. J. A method for measurement of analgesic activity on inflamed tissue. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1957 Sep 1;111(4):409–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHBALLER A. B. The effects of catecholamines on the central nervous system. Pharmacol Rev. 1959 Jun;11(2 Pt 2):494–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. W., Ashford A. The effect of reserpine and alpha-methyldopa on the analgesic action of morphine in the mouse. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1967 Nov;19(11):709–713. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1967.tb08021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudzik A. D., Mennear J. H. Antagonism of analgesics by amine-depleting agents. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1965 May;17(5):326–327. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1965.tb07677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAUMANN W. Beeinflussung der analgetischen Wirkung des Morphins durch Reserpin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1958;235(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER J. A. Reserpine antagonism of morphine analgesia in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Dec;87(3):614–615. doi: 10.3181/00379727-87-21461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIGG E. B., CAPRIO G., SCHNEIDER J. A. Synergism of amines and antagonism of reserpine to morphine analgesia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Jan;97(1):97–100. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLAUGHTER D. Neostigmine and opiate analgesia. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1950 Jun 1;83(1):143–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saarnivaara L. Analgesic activity of some sympathetic drugs and their effect on morphine analgesia in rabbits. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1969;47(3):180–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saarnivaara L. Effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine on morphine analgesia in rabbits. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1969;47(2):113–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAGI H., TAKASHIMA T., KIMURA K. ANTAGONISM OF THE ANALGETIC EFFECT OF MORPHINE IN MICE BY TETRABENAZINE AND RESERPINE. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1964 Jun 1;149:484–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRIPOD J., GROSS F. Unterschiedliche Beeinflussung der analgetischen und der erregenden Wirkung von Morphin durch zentral dämpfende Pharmaka. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1957;15(1):105–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSOU K., JANG C. S. STUDIES ON THE SITE OF ANALGESIC ACTION OF MORPHINE BY INTRACEREBRAL MICRO-INJECTION. Sci Sin. 1964 Jul;13:1099–1109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen S. S. Antagonism of the analgesic effect of morphine and other drugs by p-chlorophenylalanine, a serotonin depletor. Psychopharmacologia. 1968;12(4):278–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00401407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M. The concentration of sympathin in different parts of the central nervous system under normal conditions and after the administration of drugs. J Physiol. 1954 Mar 29;123(3):451–481. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verri R. A., Graeff F. G., Corrado A. P. Effect of reserpine and alpha-methyl-tyrosine on morphine analgesia. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1968 May;7(3):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(68)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


