Abstract
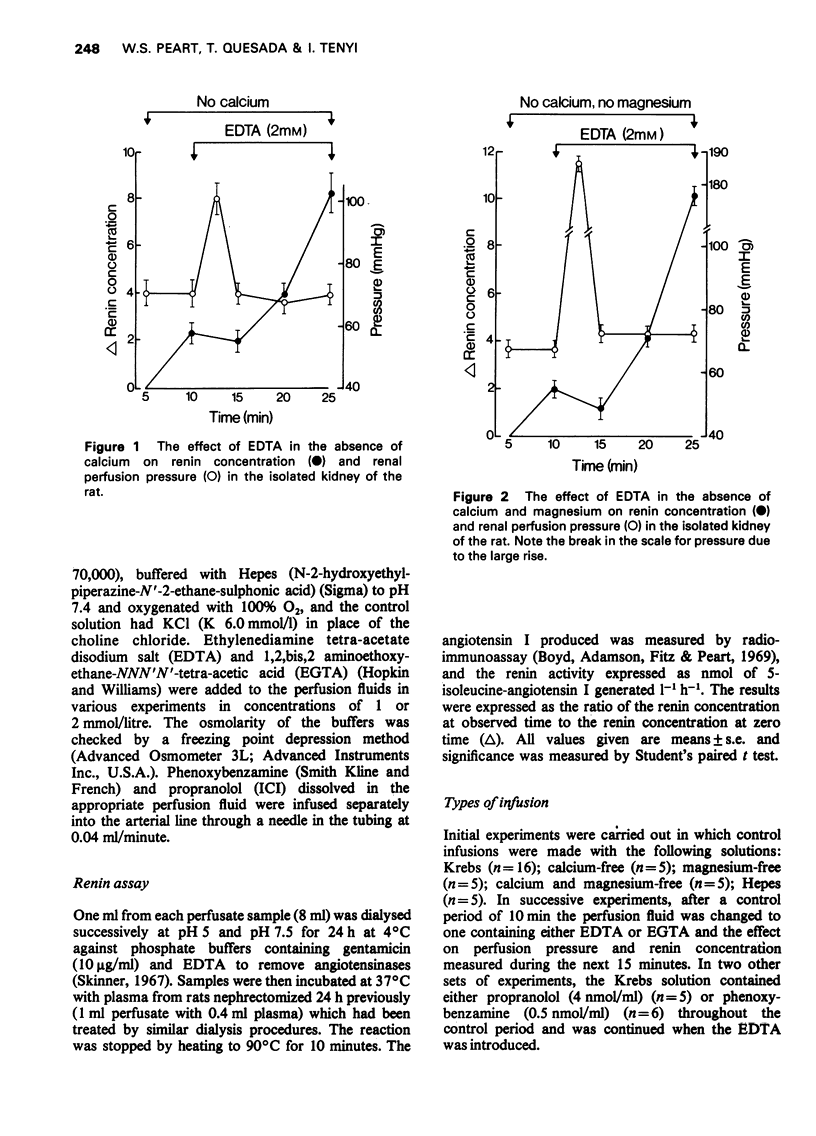
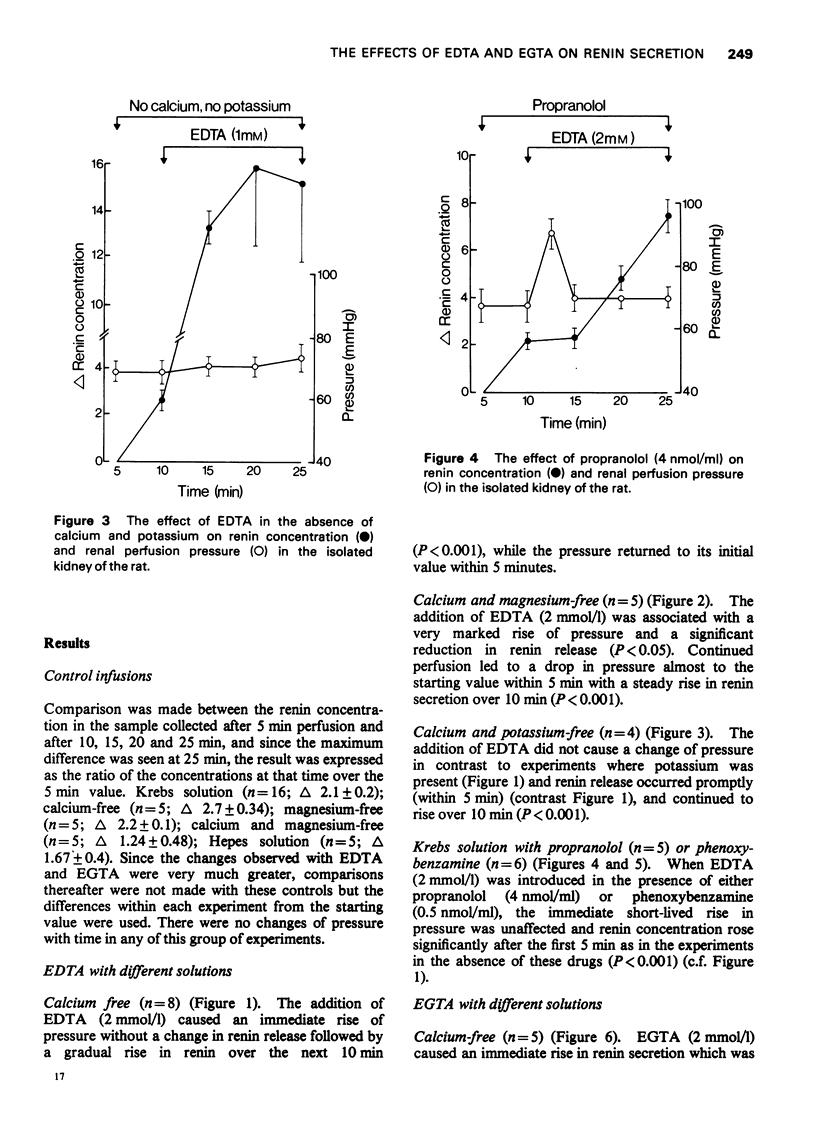
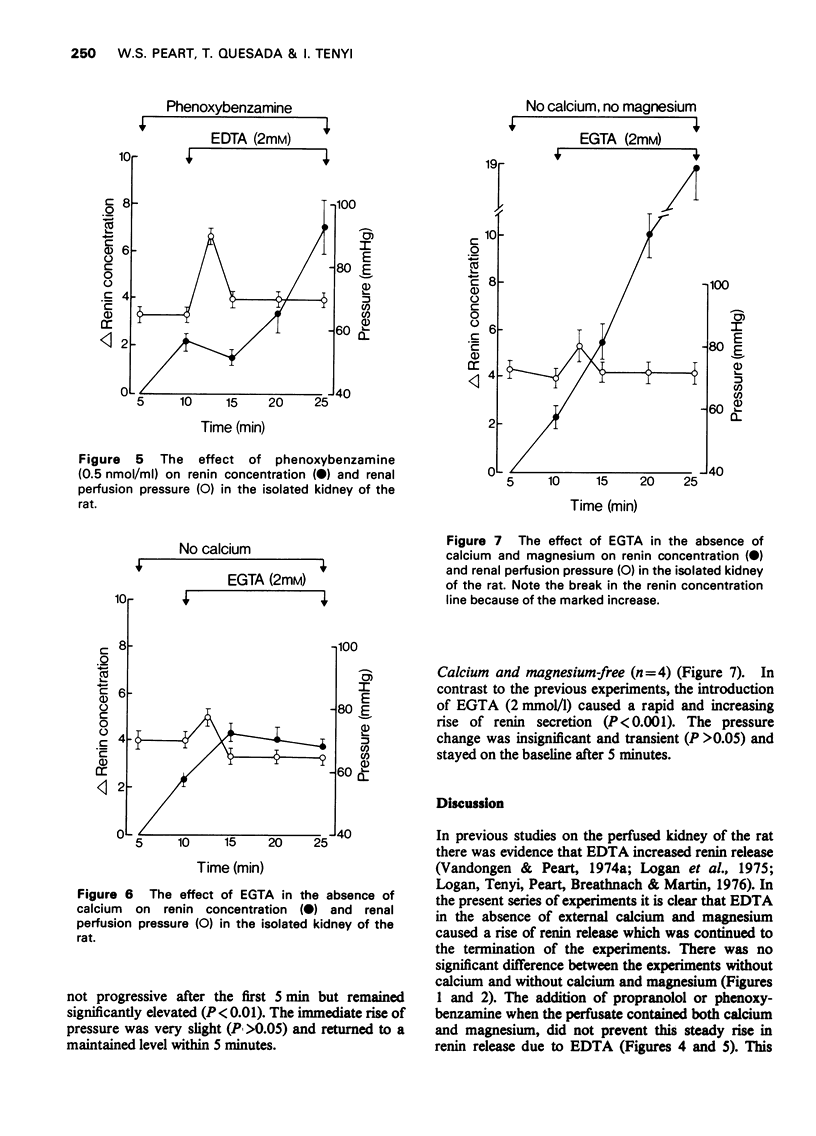
1 The effects of the disodium salt of ethylenediamine tetra-acetate (EDTA) and 1, 2, bis, 2 aminoethoxyethane-NNN'N'-tetra-acetic acid (EGTA) on renin secretion and vascular resistance were studied in the isolated perfused kidney of the rat. 2 Both substances produced a significant increase of renin release 3 In the absence of calcium and magnesium, EDTA still increased rein release and there was now a considerable increase of perfusion pressure. 4 The rise of pressure but not the rise of renin was inhibited by the removal of potassium from the perfusate when EDTA was administered in the absence of calcium. 5 Propranolol and phenoxybenzamine had no effect on the vasoconstrictor action of EDTA. 6 EGTA was less effective as a renin releaser than EDTA until magnesium was removed from the perfusate. Furter, it had only a small effect on perfusion pressure in contrast to EDTA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altura B. M., Altura B. T. Influence of magnesium on drug-induced contractions and ion content in rabbit aorta. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):938–944. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd G. W., Fitz A. E., Adamson A. R., Peart W. S. Radioimmunoassay determination of plasma-renin activity. Lancet. 1969 Feb 1;1(7588):213–218. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Podolsky R. J. Regenerative calcium release within muscle cells. Science. 1970 Jan 2;167(3914):58–59. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3914.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keatinge W. R. Ca concentration and flux in Ca-deprived arteries. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(1):35–59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner S. L. Improved assay methods for renin "concentration" and "activity" in human plasma. Methods using selective denaturation of renin substrate. Circ Res. 1967 Apr;20(4):391–402. doi: 10.1161/01.res.20.4.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V. Vascular smooth muscle. I. Normal structure, pathology, biochemistry, and biophysics. Pharmacol Rev. 1968 Dec;20(4):197–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dongen R., Peart W. S. Calcium dependence of the inhibitory effect of angiotensin on renin secretion in the isolated perfused kidney of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;50(1):125–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09599.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandongen R., Peart W. S., Boyd G. W. Andrenergic stimulation of renin secretion in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Circ Res. 1973 Feb;32(2):290–296. doi: 10.1161/01.res.32.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandongen R., Peart W. S. The inhibition of renin secretion by alpha-adrenergic stimulation in the isolated rat kidney. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Nov;47(5):471–479. doi: 10.1042/cs0470471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A. Effects of Ca ++ and Mg ++ on secretion in vitro by mouse thyroid glands. Endocrinology. 1972 Jun;90(6):1459–1463. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-6-1459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Breemen C., Farinas B. R., Casteels R., Gerba P., Wuytack F., Deth R. Factors controlling cytoplasmic Ca 2+ concentration. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Mar 15;265(867):57–71. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1973.0009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


