Abstract
1 The action of three polypeptides, bradykinin, substance P and eledoisin known to inhibit vascular smooth muscle has been examined on the anococcygeus muscle of the rat, cat and rabbit.
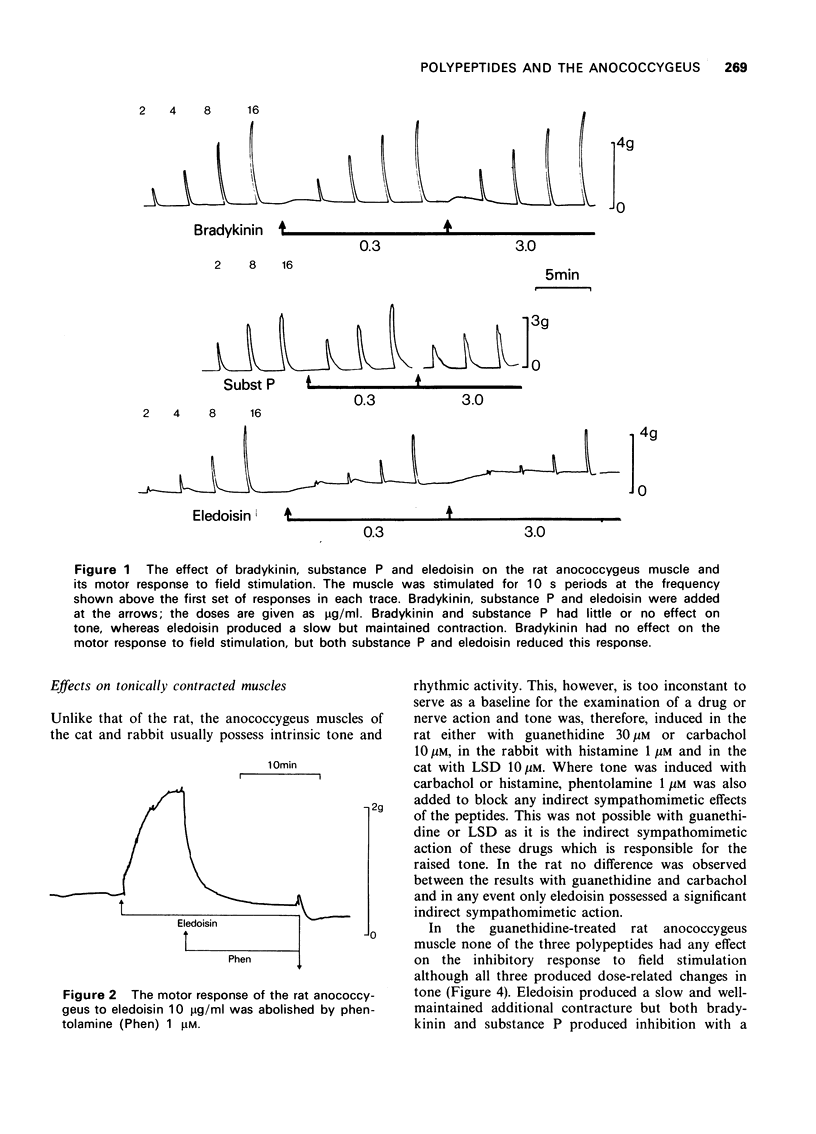
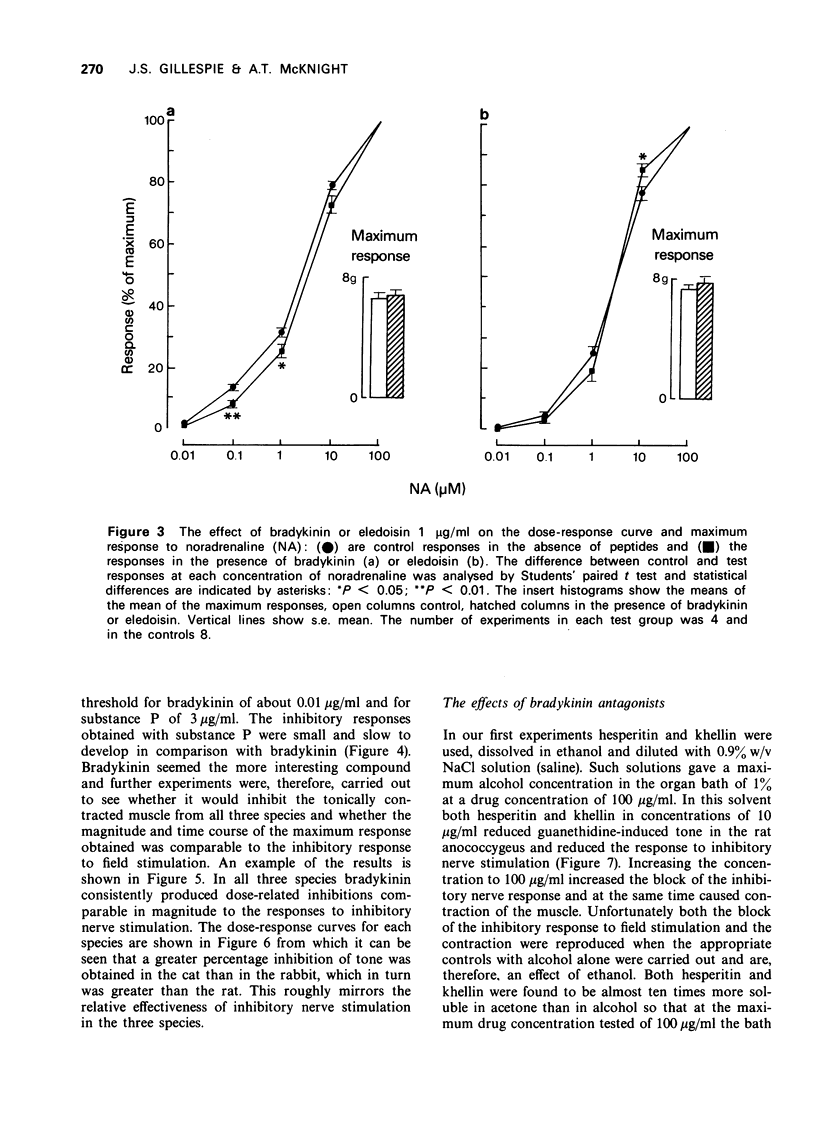
2 In the atonic rat muscle, bradykinin and substance P had little or no effect on tone but eledoisin produced a sustained dose-related contraction which could be abolished by phentolamine (1 μM) and is, therefore, probably an indirect sympathomimetic effect. On the motor response to field stimulation of adrenergic nerves, bradykinin had no effect whereas both substance P and eledoisin reduced this response. The mechanism of action was further analysed with eledoisin by examining its effect on the response to noradrenaline. Eledoisin did not alter the dose-response curve to noradrenaline and its inhibitory action is likely, therefore, to be presynaptic.
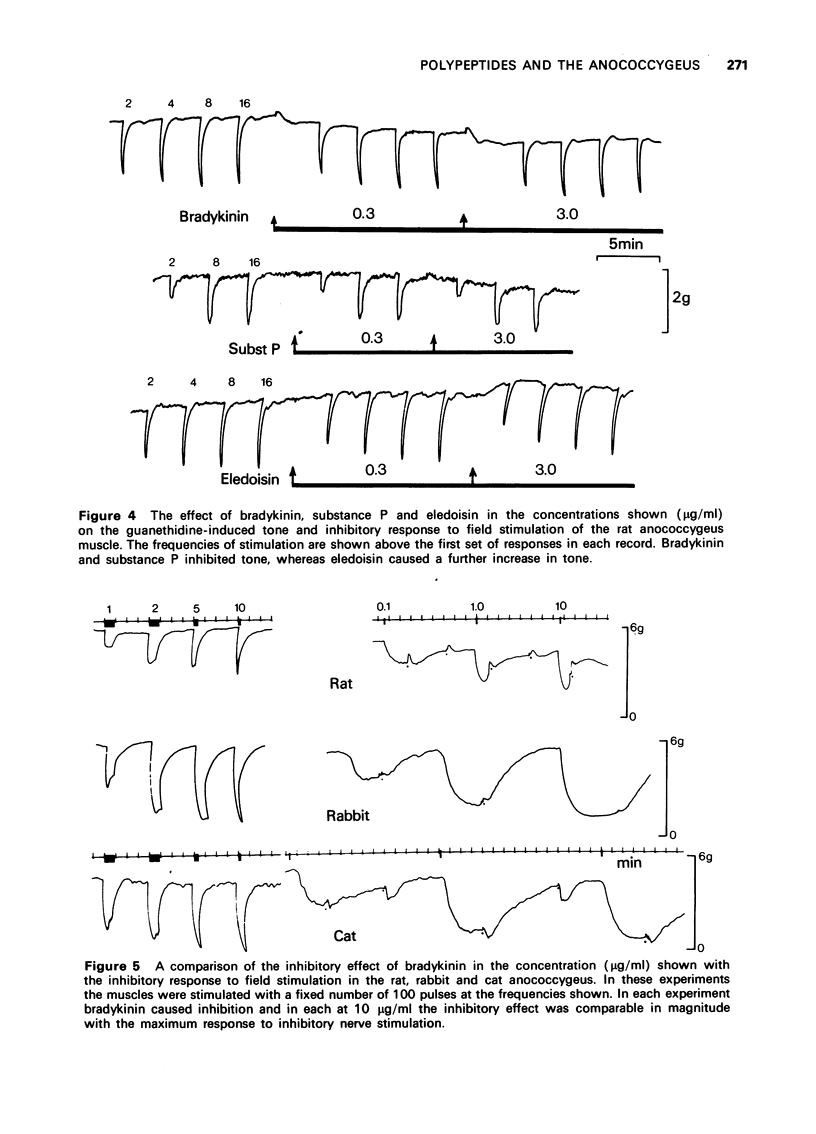
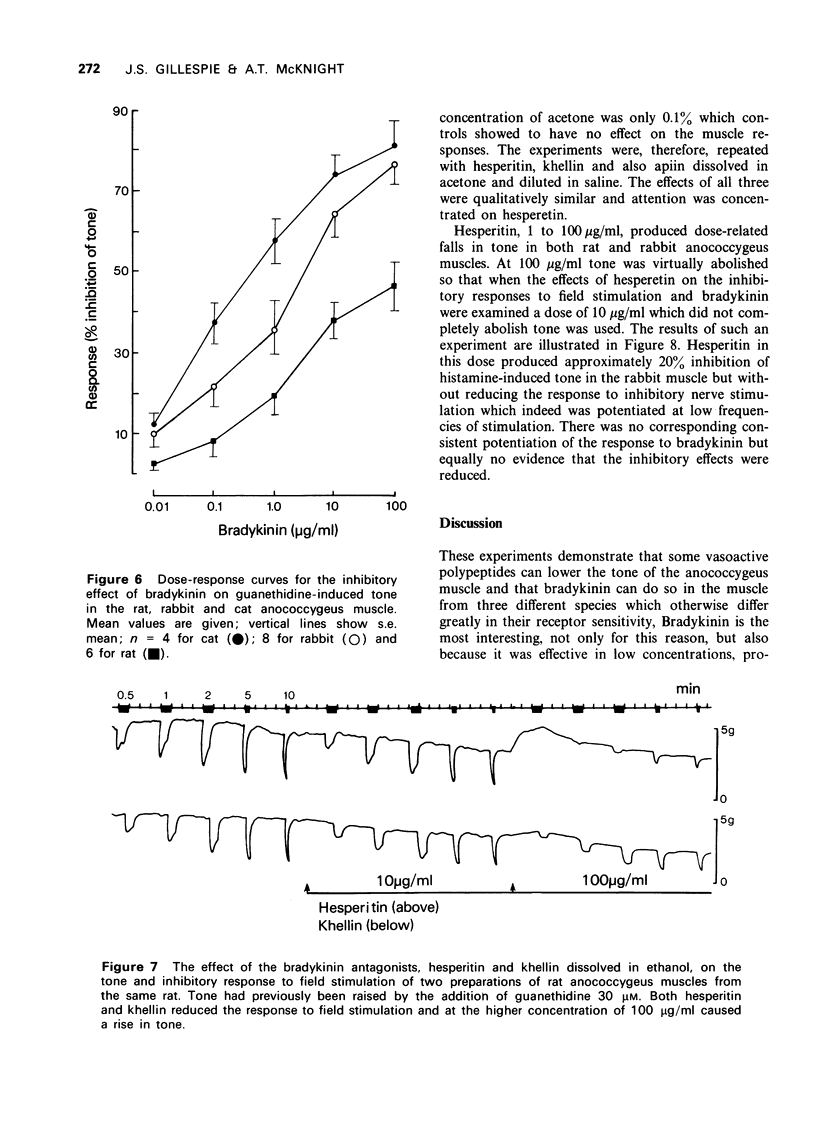
3 In the rat anococcygeus muscle in which the tone was raised by guanethidine or carbachol, bradykinin and substance P reduced this tone whereas eledoisin continued to exert a motor action. Compared with substance P the inhibitory effect of bradykinin appeared at lower concentrations (threshold 0.01 μg/ml), developed more rapidly and the size of the response was greater.
4 The effect of bradykinin on the tonically contracted cat and rabbit anococcygeus muscles was examined in addition to that of the rat. In all three species bradykinin caused inhibition and the magnitude of the response was equal to the maximum effect of inhibitory nerve stimulation. None of the peptides affected the inhibitory response to nerve stimulation itself.
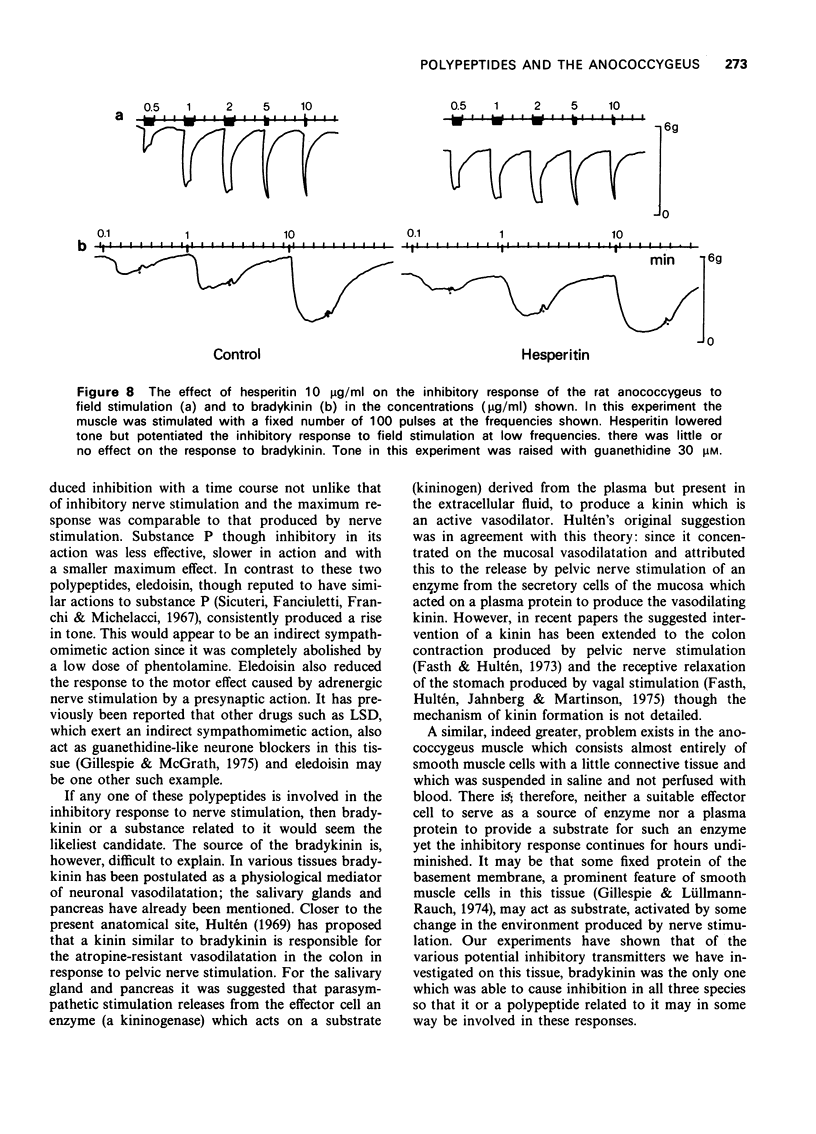
5 The effects of three substances, hesperitin, khellin and apiin, reported in other tissues to antagonize the action of bradykinin were examined both on the inhibitory response to bradykinin and to field stimulation. None of them was able to inhibit either response, although they reduced tone when given by themselves. During these experiments it was found that ethanol antagonized the inhibitory response to field stimulation.
6 The possibility that bradykinin or some related peptide might play a part in the inhibitory response to nerve stimulation in the anococcygeus is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BISSET G. W., LEWIS G. P. A spectrum of pharmacological activity in some biologically active peptides. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1962 Aug;19:168–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURN J. H., RAND M. J. Sympathetic postganglionic cholinergic fibres. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1960 Mar;15:56–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1960.tb01210.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERSPAMER V., ANASTASI A. Structure and pharmacological actions of eledoisin, the active endecapeptide of the posterior salivary glands of Eledone. Experientia. 1962 Feb 15;18:58–59. doi: 10.1007/BF02138250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasth S., Hultén L., Jahnberg T., Martinson J. Comparative studies on the effects of bradykinin and vagal stimulation on motility in the stomach and colon. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Jan;93(1):77–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb05792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasth S., Hultén L. The effect of bradykinin on intestinal motility and blood flow. Acta Chir Scand. 1973;139(8):699–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Lüllmann-Rauch R. On the ultrastructure of the rat anococcygeus muscle. Cell Tissue Res. 1974;149(1):91–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00209052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., McGrath J. C. The effects of lysergic acid diethylamide on the response to field stimulation of the rat vas deferens and the rat and cat anococcygeus muscles. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Aug;54(4):481–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., McGrath J. C. The response of the cat anococcygeus muscle to nerve or drug stimulation and a comparison with the rat anococcygeus. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;50(1):109–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., McGrath J. C. The spinal origin of the motor and inhibitory innervation of the rat anococcygeus muscles. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):659–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., McKnight A. T. The action of some vasoactive polypeptides and their antagonists on the anococcygeus muscle [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;260(2):19P–20P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S. The rat anococcygeus muscle and its response to nerve stimulation and to some drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Jul;45(3):404–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb08097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILTON S. M., LEWIS G. P. The relationship between glandular activity, bradykinin formation and functional vasodilatation in the submandibular salivary gland. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):471–483. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton S. M., Jones M. The role of plasma kinin in functional vasodilatation in the pancreas. J Physiol. 1968 Apr;195(3):521–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- V Euler U. S., Gaddum J. H. An unidentified depressor substance in certain tissue extracts. J Physiol. 1931 Jun 6;72(1):74–87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1931.sp002763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


