Abstract
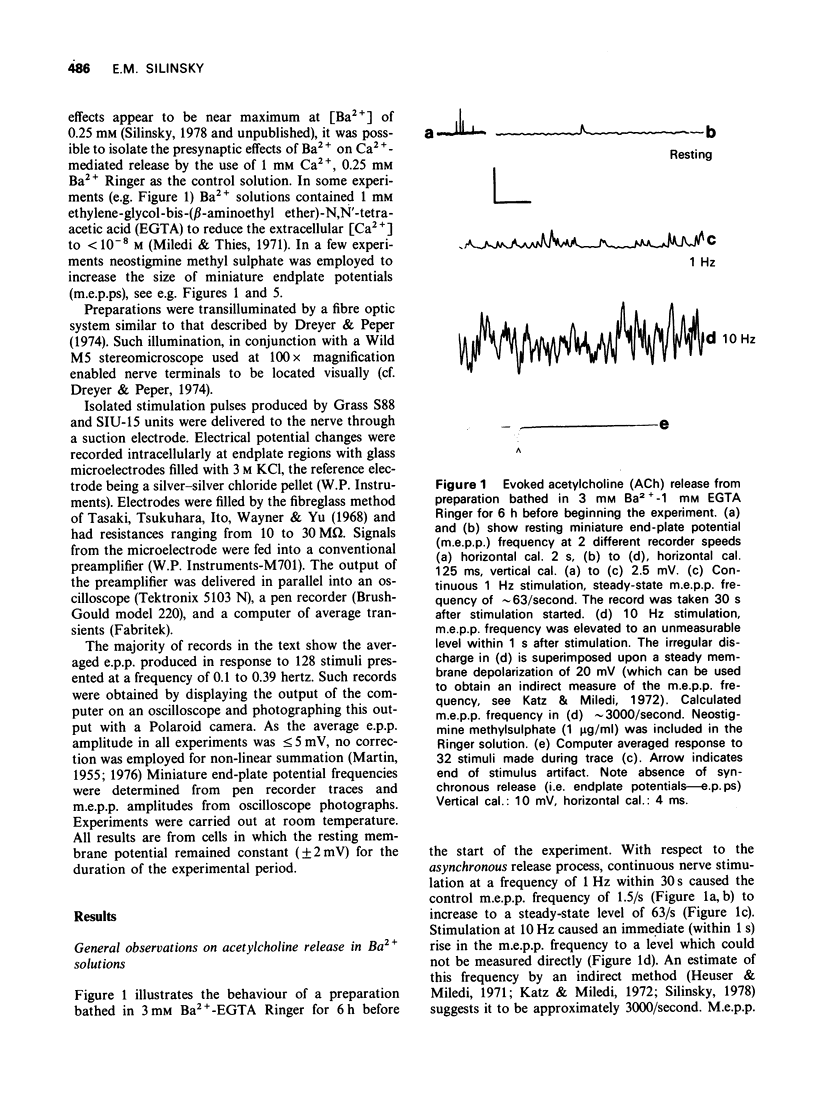
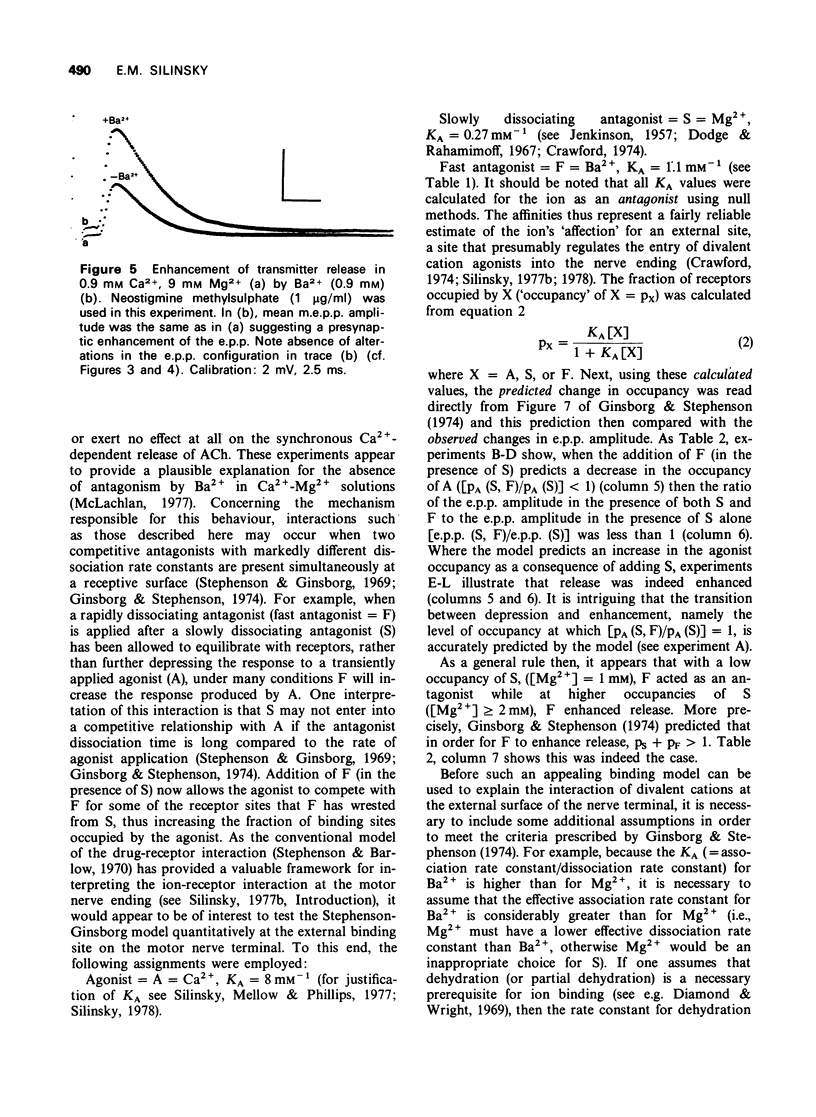
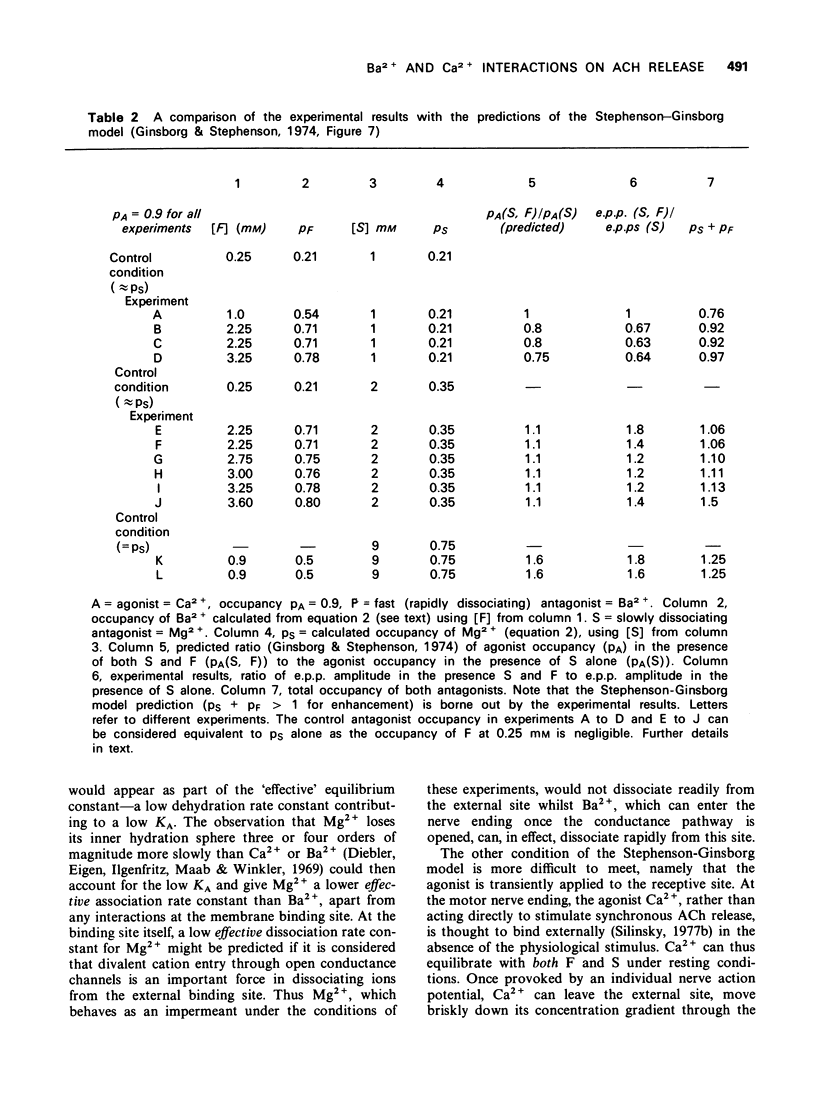
1 The effect of Ba2+ on the synchronous release of acetylcholine from frog motor nerve terminals was studied by conventional electrophysiological techniques. 2 When Ca2+ and Ba2+ were the only divalent cations in the bathing fluid, Ba2+ caused a presynaptic reduction in the amplitude of the endplate potential (e.p.p.). This effect was surmountable by increasing the Ca2+ concentration. 3 The affinity constant (KA) for Ba2+, calculated on the assumption that Ba2+ is a competitive inhibitor of the agonist, Ca2+, was 1.1 +/- 0.4 mM-1 (mean +/- s.e. mean, n = 8). 4 When e.p.ps were depressed by the addition of 1 mM Mg2+, addition of Ba2+ (1 to 3 mM) caused either a further presynaptic depression of moderate magnitude or had no additional effect. 5 When e.p.p.s were depressed with [Mg2+] greater than or equal to 2 mM, addition of Ba2+ greater than or equal to 0.9 mM enhanced the e.p.p. amplitude by a presynaptic mechanism. 6 The interaction of the divalent cation antagonists Mg2+ and Ba2+ with the agonist, Ca2+ is discussed. It is demonstrated that a model which considers the nonequilibrium, kinetic properties of binding can be used to describe interactions between divalent cations at the external surface of the motor nerve ending.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F. Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1972;24:177–223. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(72)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford A. C. The dependence of evoked transmitter release on external calcium ions at very low mean quantal contents. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(2):255–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Wright E. M. Biological membranes: the physical basis of ion and nonelectrolyte selectivity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1969;31:581–646. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.31.030169.003053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Rahamimoff R. Co-operative action a calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):419–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer F., Peper K. A monolayer preparation of innervated skeletal muscle fibres of the m. cutaneus pectoris of the frog. Pflugers Arch. 1974 Apr 22;348(3):257–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00587416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingsborg B. L., Stephenson R. P. On the simultaneous action of two competitive antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Jun;51(2):287–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J., Miledi R. Effects of lanthanum ions on function and structure of frog neuromuscular junctions. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Dec 14;179(1056):247–260. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The nature of the antagonism between calcium and magnesium ions at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1957 Oct 30;138(3):434–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R. A further study of the statistical composition on the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):114–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A. R. The effect of membrane capacitance on non-linear summation of synaptic potentials. J Theor Biol. 1976 Jun;59(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(76)80031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan E. M. The effects of strontium and barium ions at synapses in sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):497–518. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Thies R. Tetanic and post-tetanic rise in frequency of miniature end-plate potentials in low-calcium solutions. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(1):245–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts F., Stephenson R. P. The kinetics of competitive antagonists on guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Sep;58(1):57–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07693.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silinsky E. M. An estimate of the equilibrium dissociation constant for calcium as an antagonist of evoked acetylcholine release: implications for excitation-secretion coupling. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;61(4):691–693. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07562.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silinsky E. M. Can barium support the release of acetylcholine by nerve impulses? Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Jan;59(1):215–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb06997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silinsky E. M., Mellow A. M., Phillips T. E. Conventional calcium channel mediates asynchronous acetylcholine release by motor nerve impulses. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):528–530. doi: 10.1038/270528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silinsky E. M. On the role of barium in supporting the asynchronous release of acetylcholine quanta by motor nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:157–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson R. P., Ginsborg B. L. Potentiation by an antagonist. Nature. 1969 May 24;222(5195):790–791. doi: 10.1038/222790a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thron C. D., Waud D. R. The rate of action of atropine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Mar;160(1):91–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERMAN R., GRUNDFEST H. Graded and all-or-none electrogenesis in arthropod muscle. II. The effects of alkali-earth and onium ions on lobster muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1961 May;44:997–1027. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.5.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


