Abstract
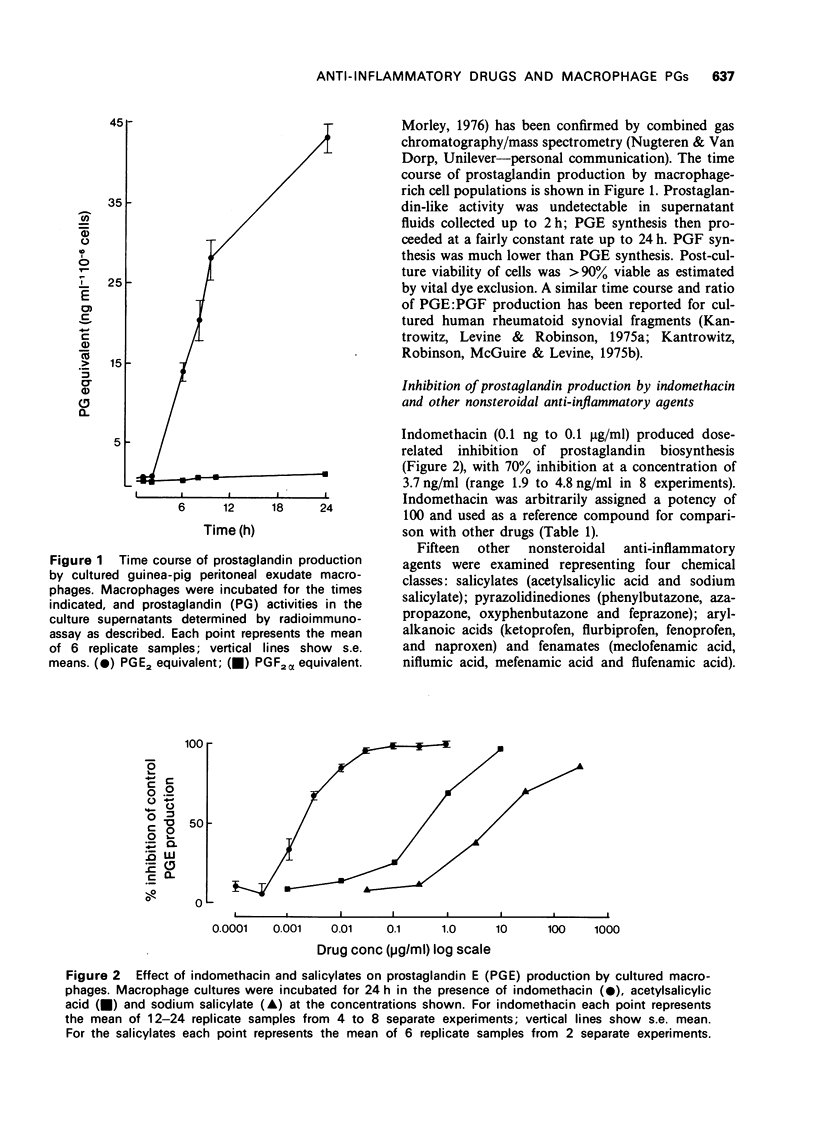
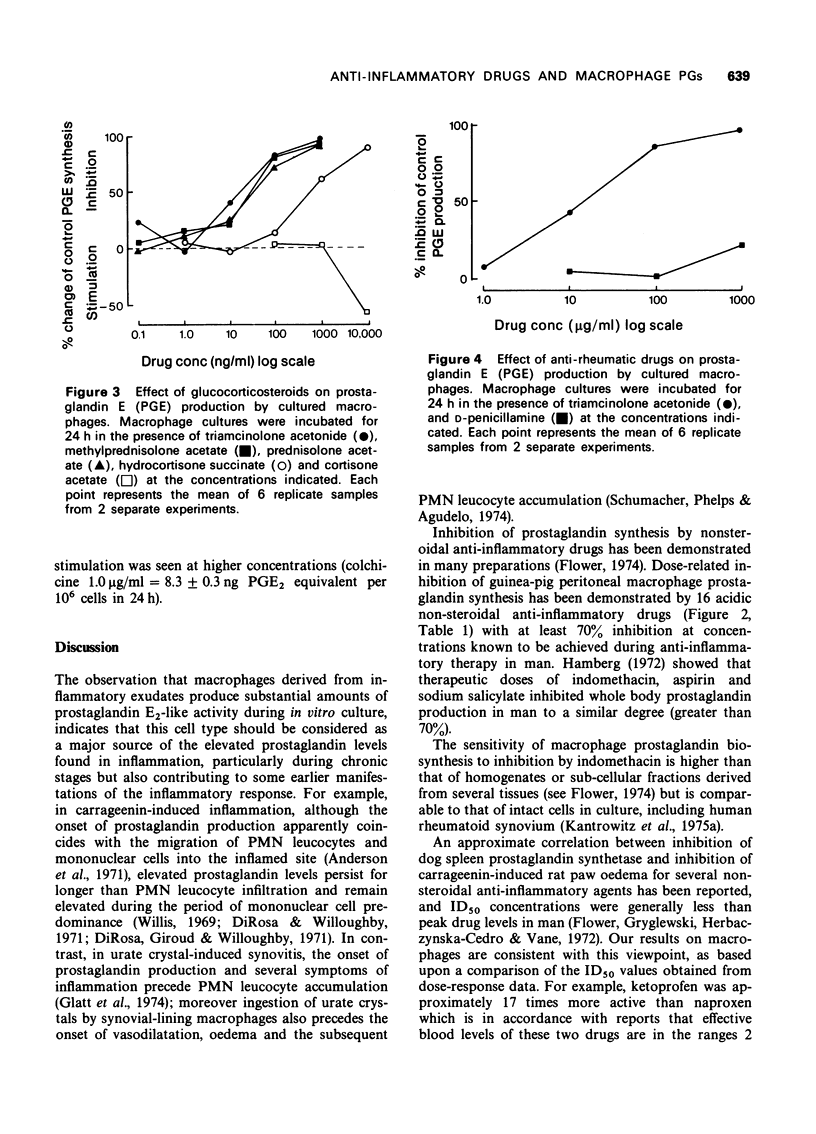
1 Macrophages derived from peritoneal cavity inflammatory exudates of guinea-pigs produced substantial amounts of prostaglandin E2-like activity during in vitro culture, so providing the basis for an experimental model of prostaglandin production during inflammatory reactions. 2 Dose-related inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis was demonstrated by 16 acidic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. 3 Seven anti-inflammatory glucocorticosteroid preparations inhibited prostaglandin production in a dose-related manner. The relative potencies of dexamethasone, prednisolone and hydrocortisone were consistent with clinical anti-inflammatory ranking. Cortisone, however, failed to inhibit macrophage prostaglandin production. 4 Three other agents used in the treatment of inflammatory joint diseases were examined. Sodium aurothiomalate inhibited prostaglandin production, although higher concentrations were toxic to macrophages. D-Penicillamine did not affect macrophage prostaglandin production. Colchicine, in contrast, enhanced prostaglandin production at some concentrations. 5 The probable significance of macrophages as a source of prostaglandins, during inflammatory responses, is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURNS J. J., ROSE R. K., CHENKIN T., GOLDMAN A., SCHULERT A., BRODIE B. B. The physiological disposition of phenylbutazone (butazolidin) in man and a method for its estimation in biological material. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1953 Nov;109(3):346–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackham A., Farmer J. B., Radziwonik H., Westwick J. The role of prostaglandins in rabbit monoarticular arthritis. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 May;51(1):35–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09629.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray M. A., Gordon D. Effects of anti-inflammatory drugs on macrophage prostaglandin biosynthesis [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;57(3):466P–467P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray M. A., Gordon D., Morley J. Proceedings: Role of prostaglandins in reactions of cellular immunity. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Nov;52(3):453P–453P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chériè Ligniêre G., Colombo B., Carrabba M., Ferrari P., Gallazzi A. DA 2370 serum and synovial fluids concentrations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Med Res Opin. 1974;2(1):51–56. doi: 10.1185/03007997409111741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Krane S. M., Russell R. G., Robinson D. R. Production of collagenase and prostaglandins by isolated adherent rheumatoid synovial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):945–949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Rosa M., Giroud J. P., Willoughby D. A. Studies on the mediators of the acute inflammatory response induced in rats in different sites by carrageenan and turpentine. J Pathol. 1971 May;104(1):15–29. doi: 10.1002/path.1711040103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Rosa M., Willoughby D. A. Screens for anti-inflammatory drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Apr;23(4):297–298. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb08661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori H. W., Champion G. D., Bluestone R., Paulus H. E. Simultaneous pharmacokinetics of indomethacin in serum and synovial fluid. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Sep;32(5):433–435. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.5.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Indomethacin and aspirin abolish prostaglandin release from the spleen. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):237–239. doi: 10.1038/newbio231237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J. Drugs which inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis. Pharmacol Rev. 1974 Mar;26(1):33–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R., Gryglewski R., Herbaczyńska-Cedro K., Vane J. R. Effects of anti-inflammatory drugs on prostaglandin biosynthesis. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):104–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio238104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franson R. C., Waite M. Lysosomal phospholipase A 1 and A 2 of normal and bacillus calmette guerin-induced alveolar macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1973 Mar;56(3):621–627. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatt M., Peskar B., Brune K. Leukocytes and prostaglandins in acute inflammation. Experientia. 1974 Nov 15;30(11):1257–1259. doi: 10.1007/BF01945171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D., Bray M. A., Morley J. Control of lymphokine secretion by prostaglandins. Nature. 1976 Jul 29;262(5567):401–402. doi: 10.1038/262401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosling R., Kerry R. J., Owen G. Creatine phosphokinase activity during lithium treatment. Br Med J. 1972 Aug 5;3(5822):327–329. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5822.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahame R., Billings R., Laurence M., Marks V., Wood P. J. Tissue gold levels after chrysotherapy. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 Nov;33(6):536–539. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.6.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. W., McDonald-Gibson W. Inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis by corticosteroids. Br Med J. 1972 Apr 8;2(5805):83–84. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5805.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis in man. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 1;49(3):720–726. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90470-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., McCall E., Youlten L. J. A chemotactic role for prostaglandins released from polymorphonuclear leucocytes during phagocytosis. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Apr;53(4):539–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humes J. L., Bonney R. J., Pelus L., Dahlgren M. E., Sadowski S. J., Kuehl F. A., Jr, Davies P. Macrophages synthesis and release prostaglandins in response to inflammatory stimuli. Nature. 1977 Sep 8;269(5624):149–151. doi: 10.1038/269149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe B. M., Smith J. W., Newton W. T., Parker C. W. Radioimmunoassay for prostaglandins. Science. 1971 Feb 5;171(3970):494–496. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3970.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantrowitz F., Robinson D. R., McGuire M. B., Levine L. Corticosteroids inhibit prostaglandin production by rheumatiod synovia. Nature. 1975 Dec 25;258(5537):737–739. doi: 10.1038/258737a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch-Weser J., Sellers E. M. Binding of drugs to serum albumin (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 5;294(6):311–316. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602052940605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L. Antibodies to pharmacologically active molecules: specificities and some applications of antiprostaglandins. Pharmacol Rev. 1973 Jun;25(2):293–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis G. P., Piper P. J. Inhibition of release of prostaglandins as an explanation of some of the actions of anti-inflammatory corticosteroids. Nature. 1975 Mar 27;254(5498):308–311. doi: 10.1038/254308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorber A., Atkins C. J., Chang C. C., Lee Y. B., Starrs J., Bovy R. A. Monitoring serum gold values to improve chrysotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Mar;32(2):133–139. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Stossel T. P., Vaughan M. Lipids of alveolar macrophages, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and their phagocytic vesicles. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2399–2407. doi: 10.1172/JCI107052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munder P. G., Ferber E., Modolell M., Fischer H. The influence of various adjuvants on the metabolism of phospholipids in macrophages. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1969;36(1):117–128. doi: 10.1159/000230731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENTHAL R. K., BAYLES T. B., FREMONT-SMITH K. SIMULTANEOUS SALICYLATE CONCENTRATIONS IN SYNOVIAL FLUID AND PLASMA IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. Arthritis Rheum. 1964 Apr;7:103–109. doi: 10.1002/art.1780070202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein H. M., Dietz A. A. Serum gold. II. Levels in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Mar;32(2):128–132. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runkel R., Forchielli E., Sevelius H., Chaplin M., Segre E. Nonlinear plasma level response to high doses of naproxen. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Mar;15(3):261–266. doi: 10.1002/cpt1974153261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R., Phelps P., Agudelo C. A. Urate crystal induced inflammation in dog joints: sequence of synovial changes. J Rheumatol. 1974 Mar;1(1):102–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sholkoff S. D., Eyring E. J., Rowland M., Riegelman S. Plasma and synovial fluid concentrations of acetylsalicylic acid in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Aug;10(4):348–351. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Willis A. L. Aspirin selectively inhibits prostaglandin production in human platelets. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):235–237. doi: 10.1038/newbio231235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Mason R. J., Smith A. L. Lipid peroxidation by human blood phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):638–645. doi: 10.1172/JCI107801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Voelkel E. F., McDonough J., Levine L. Hydrocortisone inhibits prostaglandin production by mouse fibrosarcoma cells. Nature. 1975 Dec 25;258(5537):739–741. doi: 10.1038/258739a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace S. L., Omokoku B., Ertel N. H. Colchicine plasma levels. Implications as to pharmacology and mechanism of action. Am J Med. 1970 Apr;48(4):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(70)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


